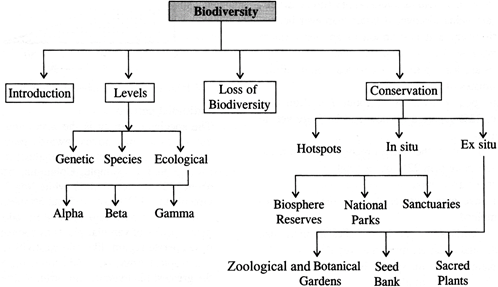
Biodiversity
Introduction
Biodiversity mean us diversity of heterogeneity at all levels of biological organisation, i.e from micro molecules of the cells to the biomass. The word biodiversity was postulated by the sociologist E.D. Wilson. Biodiversity is commonly used to replace the more clearly and long established terms, species diversity and species richness. Biologist define biodiversity in “totality of genes”, species and ecosystems of region.
This results in existence of a wide variety of plant and animal species in their natural environments, which is the conservationists. Who are mainly concerned about indiscriminate destruction of rainforests and other habitats?
Important Levels of Biodiversity
Genetic diversity
It is the diversity at genetic level, or at sub-species level below species level, in a single species. The
more...
 This results in existence of a wide variety of plant and animal species in their natural environments, which is the conservationists. Who are mainly concerned about indiscriminate destruction of rainforests and other habitats?
Important Levels of Biodiversity
This results in existence of a wide variety of plant and animal species in their natural environments, which is the conservationists. Who are mainly concerned about indiscriminate destruction of rainforests and other habitats?
Important Levels of Biodiversity
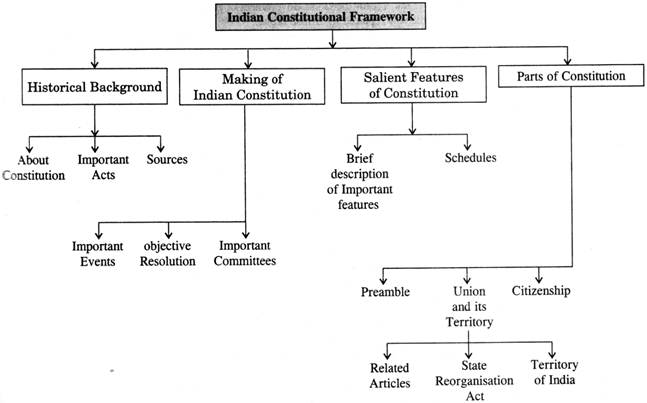 HISTORICAL BACKGROUND
HISTORICAL BACKGROUND