Soaps and Detergents
A soap is a sodium salt of long chain fatty acid. A soap molecule consists of along hydrocarbon chain. It composed of carbons and hydrogens, with a carboxylic acid group on one end which is ionic bonded to a metal ion, usually a sodium or potassium. The hydrocarbon end is nonpolar and is soluble in nonpolar substances, such as fats and oils; and the ionic end, the salt of a carboxylic acid is soluble in water. The structure of a soap molecule is represented below:
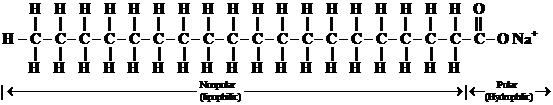
Non-polar hydrocarbon chain ionic end (soluble in nonpolar substances) (soluble in water)
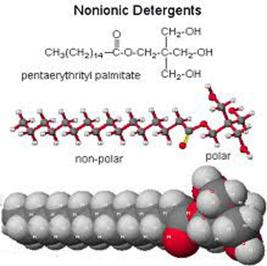
Detergents are structurally similar to soaps, but differ in the water-soluble portion. Three examples of detergents are shown below. When
more...