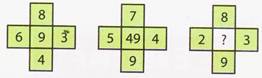
 (a) 64 (b) 100
(c) 81 more...
(a) 64 (b) 100
(c) 81 more...
 more...
more...
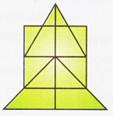 (a) 14 (b) 15
(c) 16 (d) 17
Explanation (c):
Let us label the given figure as shown in the adjoining figure.
(a) 14 (b) 15
(c) 16 (d) 17
Explanation (c):
Let us label the given figure as shown in the adjoining figure.
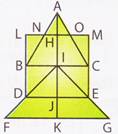 Triangles made up of one segment: ANH, AOH, LBN, MCO, BDI, CEI, IDJ, IEJ.
These are 8 triangles.
Triangles made up of two segments: ABI, ACI, IFK, IGK, ANO, IDE.
These are 6 triangles.
No triangles made up more...
Triangles made up of one segment: ANH, AOH, LBN, MCO, BDI, CEI, IDJ, IEJ.
These are 8 triangles.
Triangles made up of two segments: ABI, ACI, IFK, IGK, ANO, IDE.
These are 6 triangles.
No triangles made up more...
 more...
more...
 (a)
(a)  (b)
(b) 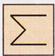 more...
more...
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
