 Note: To keep you familiar with NCERT (which is the base book for CBSE), we have included portions of NCERT, at a few places, with some modifications.
We will basically be studying THREE categories of solids - PRISMS, PYRAMIDS and SPHERES. Lastly, we will touch little on POLYHEDRONS without going into much details.
What is a prism?
A prism is a solid in which two congruent and parallel polygons form more...
Note: To keep you familiar with NCERT (which is the base book for CBSE), we have included portions of NCERT, at a few places, with some modifications.
We will basically be studying THREE categories of solids - PRISMS, PYRAMIDS and SPHERES. Lastly, we will touch little on POLYHEDRONS without going into much details.
What is a prism?
A prism is a solid in which two congruent and parallel polygons form more...
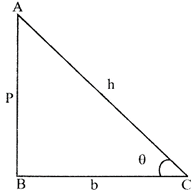 \[sin\theta =\frac{AB}{AC}=\frac{P}{h}\]
\[cos\theta =\frac{BC}{AC}=\frac{b}{h}\]
\[tan\theta =\frac{AB}{BC}=\frac{p}{b}\]
The ratio \[cosec\theta ,sec\theta \]and \[\cot \theta \]are respectively the reciprocals of the \[sin\theta ,cos\theta \] and \[tan\theta \].
i.e., \[\sin \theta =\frac{1}{\cos ec\theta }\text{ },cos\theta =\frac{1}{\cos ec\theta }\text{ }and\,tan\theta =\frac{1}{\cot \theta }\]
Trigonometric ratio of some specific angles
\[sin\theta =\frac{AB}{AC}=\frac{P}{h}\]
\[cos\theta =\frac{BC}{AC}=\frac{b}{h}\]
\[tan\theta =\frac{AB}{BC}=\frac{p}{b}\]
The ratio \[cosec\theta ,sec\theta \]and \[\cot \theta \]are respectively the reciprocals of the \[sin\theta ,cos\theta \] and \[tan\theta \].
i.e., \[\sin \theta =\frac{1}{\cos ec\theta }\text{ },cos\theta =\frac{1}{\cos ec\theta }\text{ }and\,tan\theta =\frac{1}{\cot \theta }\]
Trigonometric ratio of some specific angles
| \[\angle \theta \] | more...
TRIGONOMETRY
FUNDAMENTALS
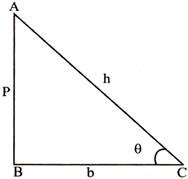 \[\sin \theta =\frac{AB}{AC}=\frac{P}{h}\]
\[Cos\theta =\frac{AB}{AC}=\frac{b}{h}\]
\[\tan \theta =\frac{AB}{AC}=\frac{p}{b}\]
The ratio \[\text{cosec}\theta ,\,\text{sec}\theta \] and \[\cot \theta \] are respectively the reciprocals of the \[sin\theta ,cos\theta \]and \[tan\theta .\]
i.e., \[\text{sin}\,\theta =\frac{1}{\text{cosec}\,\theta },\text{cos}\theta =\frac{1}{\sec \theta }\text{and}\,\,\text{tan}\,\theta =\frac{1}{\cot \theta }\]
Trigonometric ratio of some specific angles
\[\sin \theta =\frac{AB}{AC}=\frac{P}{h}\]
\[Cos\theta =\frac{AB}{AC}=\frac{b}{h}\]
\[\tan \theta =\frac{AB}{AC}=\frac{p}{b}\]
The ratio \[\text{cosec}\theta ,\,\text{sec}\theta \] and \[\cot \theta \] are respectively the reciprocals of the \[sin\theta ,cos\theta \]and \[tan\theta .\]
i.e., \[\text{sin}\,\theta =\frac{1}{\text{cosec}\,\theta },\text{cos}\theta =\frac{1}{\sec \theta }\text{and}\,\,\text{tan}\,\theta =\frac{1}{\cot \theta }\]
Trigonometric ratio of some specific angles
|