General Organic Chemistry
- Wohler prepared the first organic compound urea while preparing ammonium cyanate.
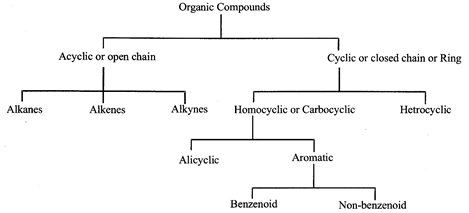
- Classification of organic compounds:
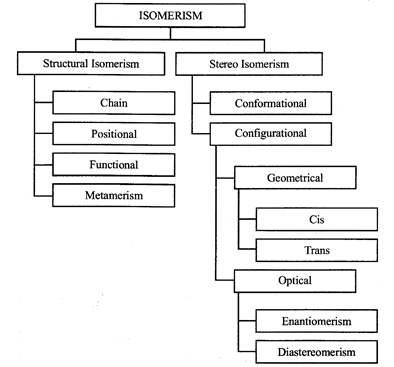
The existence of two or more chemical compounds with the same molecular formula but having different properties owing to different arrangement of atoms within the molecule is termed as isomerism
- Hydrocarbons: All those compounds which contain just carbon and hydrogen are called hydrocarbons.
- Functional group: The atom or group of atoms which determine the properties of a compound is known as functional group. e.g. \[-OH\] (alcohol), -CHO (aldehyde), > C = C < (alkene), \[-C\equiv C-\] (alkyne), etc.
- Homologous Series: A series of compounds in which the same functional group substitute’s hydrogen in a more...
 The existence of two or more chemical compounds with the same molecular formula but having different properties owing to different arrangement of atoms within the molecule is termed as isomerism
The existence of two or more chemical compounds with the same molecular formula but having different properties owing to different arrangement of atoms within the molecule is termed as isomerism
