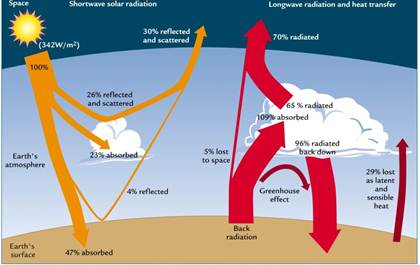
 Solar Radiation
In the figure below, a bundle of wood stick burns and radiates heat energy.
Solar Radiation
In the figure below, a bundle of wood stick burns and radiates heat energy.
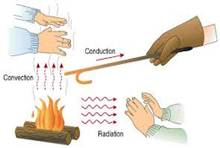 Radiation
Air around the fire gets heated first and moves upward. To fill the air gap, cold air comes around the fire and gets heated too. Our hands near the fire feel heat due to the radiation of heat.
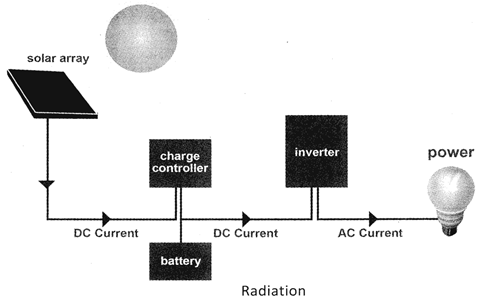
Radiation of heat energy is useful for the human being. The temperature of the human body is 98.4°F and should be constant. Air, around the fire, is heated due to convection of heat. Other end of the iron rod, which is away from fire, is heated by the conduction of heat. In the following figure, a solar plate converts solar radiation into electrical energy.
Look at the following picture of radiation of heat
Radiation
Air around the fire gets heated first and moves upward. To fill the air gap, cold air comes around the fire and gets heated too. Our hands near the fire feel heat due to the radiation of heat.
Radiation of heat energy is useful for the human being. The temperature of the human body is 98.4°F and should be constant. Air, around the fire, is heated due to convection of heat. Other end of the iron rod, which is away from fire, is heated by the conduction of heat. In the following figure, a solar plate converts solar radiation into electrical energy.
Look at the following picture of radiation of heat

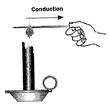
 An iron rod is heated Copper wire
An iron rod is heated Copper wire

 Steel Aluminum
Steel Aluminum
 Knife
In the above figure (1), an iron rod is heated by a burning candle. Iron rod is a good conductor of heat because heat is transferred from one end to other end. The property of the conductor is called conduction. In the figure (2), copper wire is the conductor of heat because, it transfers heat from one end to other.
In the figure (3), alloy steel is the conductor of heat, therefore, utensils made of steel are widely used for the preparation of food. Aluminum is also a good conductor of heat and therefore, used as utensils for the food preparation.
Knife
In the above figure (1), an iron rod is heated by a burning candle. Iron rod is a good conductor of heat because heat is transferred from one end to other end. The property of the conductor is called conduction. In the figure (2), copper wire is the conductor of heat because, it transfers heat from one end to other.
In the figure (3), alloy steel is the conductor of heat, therefore, utensils made of steel are widely used for the preparation of food. Aluminum is also a good conductor of heat and therefore, used as utensils for the food preparation.

 In the above picture an iron rod has been heated and heat is transferred from its rounded part to whole part. The rate of transfer of heat depends on the length of the rod and the amount of heat received by the rod from heat producing elements. The other parts of the rod gets heated by conduction. And the rods around the heated rod get heat by radiation.
Look at the following picture of the method of heat transfer from one object to another
In the above picture an iron rod has been heated and heat is transferred from its rounded part to whole part. The rate of transfer of heat depends on the length of the rod and the amount of heat received by the rod from heat producing elements. The other parts of the rod gets heated by conduction. And the rods around the heated rod get heat by radiation.
Look at the following picture of the method of heat transfer from one object to another
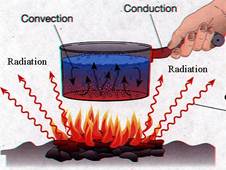 In the above picture a pan filled with water is heated by the radiation of heat from a stove. Water, at the lower level of the pan gets heated first because of its closeness with the heat radiating stove. Heated water goes upward and cold water comes down ward. Water inside the pan is heated by convection method. The whole part of the pan is heated by conduction of heat.
In the above picture a pan filled with water is heated by the radiation of heat from a stove. Water, at the lower level of the pan gets heated first because of its closeness with the heat radiating stove. Heated water goes upward and cold water comes down ward. Water inside the pan is heated by convection method. The whole part of the pan is heated by conduction of heat.




 Cold water Water evaporates
Cold water evaporates slowly. Evaporation of cold water depends on the temperature of the atmosphere, when external heat is not applied. Water evaporates fast when heat is applied. Rate of evaporation of water will increase if applied heat is increased. Some solid converted into liquid and then gas, when heat is applied. For example ice (solid) converts to water (liquid) and then into water vapor (gas) with the application of heat.
Cold water Water evaporates
Cold water evaporates slowly. Evaporation of cold water depends on the temperature of the atmosphere, when external heat is not applied. Water evaporates fast when heat is applied. Rate of evaporation of water will increase if applied heat is increased. Some solid converted into liquid and then gas, when heat is applied. For example ice (solid) converts to water (liquid) and then into water vapor (gas) with the application of heat.





 Yak Sheep
Yak Sheep

 Goat Alpaca
During the winter season, thin hairs on animal’s body keep them warm. After winter, these hairs are shaved off, which again start growing during non-winter season.
Goat Alpaca
During the winter season, thin hairs on animal’s body keep them warm. After winter, these hairs are shaved off, which again start growing during non-winter season.
 Dust particles are present on haired skin of sheep, therefore, fleece of sheep must be scoured by soap or detergent.
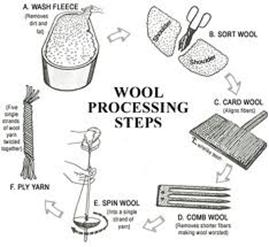
Look at the following picture of process of making Wool from fleece of sheep
Dust particles are present on haired skin of sheep, therefore, fleece of sheep must be scoured by soap or detergent.
Look at the following picture of process of making Wool from fleece of sheep
 more...
more... 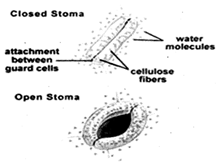 Open and closed stomata are shown in the picture above. Carbon dioxide and water enters and oxygen is released, when stomata is open.
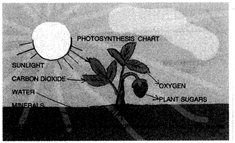
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a process by which all the green plants prepare their own food . In this process, complex organic material is synthesized using carbon dioxide, water, and inorganic salts, in the presence of sunlight. Oxygen is produced during photosynthesis as by-product.
Open and closed stomata are shown in the picture above. Carbon dioxide and water enters and oxygen is released, when stomata is open.
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a process by which all the green plants prepare their own food . In this process, complex organic material is synthesized using carbon dioxide, water, and inorganic salts, in the presence of sunlight. Oxygen is produced during photosynthesis as by-product.

You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
