| 8 | Y | |
| X | ||
| 4 | 9 | 2 |
| 8 | Y | |
| X | 7 | |
| 4 | 9 | 2 |
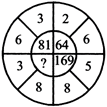 (a) 121 (b) 61
(c) 74 (d) 101
Solution:
(a) Here \[{{\left( 6+3 \right)}^{2}}={{9}^{2}}=81\]
\[{{\left( 2+6 \right)}^{2}}={{8}^{2}}=64\]
\[{{\left( 5+8 \right)}^{2}}={{13}^{2}}=169\]
\[\therefore \]\[{{\left( more...
(a) 121 (b) 61
(c) 74 (d) 101
Solution:
(a) Here \[{{\left( 6+3 \right)}^{2}}={{9}^{2}}=81\]
\[{{\left( 2+6 \right)}^{2}}={{8}^{2}}=64\]
\[{{\left( 5+8 \right)}^{2}}={{13}^{2}}=169\]
\[\therefore \]\[{{\left( more...  Example 1:
A cube of each side 4 cm, has been painted black, red and green on pairs of opposite faces. It is then cut into small cubes of each side 1 cm.
Example 1:
A cube of each side 4 cm, has been painted black, red and green on pairs of opposite faces. It is then cut into small cubes of each side 1 cm.
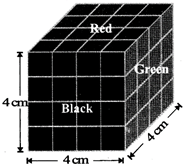 Solve the following questions based on the information given above.
1. How many small cubes will be there?
(a) 16 (b) 64
(c) 24 (d) 8
2. How many small cubes will have three faces painted?
(a) 16 (b) 8
(c) 4 (d) 24
3. How many small cubes will have two faces painted?
(a) 8 (b) 16
(c) 24 (d) None of these
4. How many small cubes will have only one face painted?
(a) 8 (b) 16
(c) 24 (d) None of these
5. How many small cubes will have no face painted?
(a) 8 (b) 16
(c) 24 (d) Nil
6. How many small cubes will have only two faces painted in green and black and all other faces not painted?
(a) 8 (b) 16
(c) 24 (d) None of these
Solutions
1. (b) 64
Total number of small cubes\[=4\times 4\times 4=64\]
2. (b) 8
From the figure it is clear that the small cubes having three faces painted are situated at the comers of the big cube, because at these comers only three faces of the big cube meet.
\[\therefore \] Required number of such cubes = 8
(Because there are 8 comers).
3. (c) 24
From the figure it is clear that to each edge of the big cube 4 small cubes are connected and two out of them are situated at the comers of the big cube which have three faces painted.
Solve the following questions based on the information given above.
1. How many small cubes will be there?
(a) 16 (b) 64
(c) 24 (d) 8
2. How many small cubes will have three faces painted?
(a) 16 (b) 8
(c) 4 (d) 24
3. How many small cubes will have two faces painted?
(a) 8 (b) 16
(c) 24 (d) None of these
4. How many small cubes will have only one face painted?
(a) 8 (b) 16
(c) 24 (d) None of these
5. How many small cubes will have no face painted?
(a) 8 (b) 16
(c) 24 (d) Nil
6. How many small cubes will have only two faces painted in green and black and all other faces not painted?
(a) 8 (b) 16
(c) 24 (d) None of these
Solutions
1. (b) 64
Total number of small cubes\[=4\times 4\times 4=64\]
2. (b) 8
From the figure it is clear that the small cubes having three faces painted are situated at the comers of the big cube, because at these comers only three faces of the big cube meet.
\[\therefore \] Required number of such cubes = 8
(Because there are 8 comers).
3. (c) 24
From the figure it is clear that to each edge of the big cube 4 small cubes are connected and two out of them are situated at the comers of the big cube which have three faces painted.
 Thus, to an edge two small cubes are left which have two faces painted. As the total edges in a cube are 12, the number more...
Thus, to an edge two small cubes are left which have two faces painted. As the total edges in a cube are 12, the number more...  INTRODUCTION
Wastewater needs to be treated before it can be reused, or released into a water body. Wastewater has many impurities and these impurities should be removed by water treatment. Wastewater from households is treated at a treatment plant to remove the physical, biological and chemical matter. In the physical process, wastewater is filtered to remove large impurities. For example: Take a funnel. Place a filter paper in the funnel and wet it with water. Then add some sand, fine gravel and medium gravel into the funnel. These are layers for the filtration of water. Now pour wastewater into the funnel and collect clean water. Repeat the same process several times till the collected water looks clean.
Do you know?
INTRODUCTION
Wastewater needs to be treated before it can be reused, or released into a water body. Wastewater has many impurities and these impurities should be removed by water treatment. Wastewater from households is treated at a treatment plant to remove the physical, biological and chemical matter. In the physical process, wastewater is filtered to remove large impurities. For example: Take a funnel. Place a filter paper in the funnel and wet it with water. Then add some sand, fine gravel and medium gravel into the funnel. These are layers for the filtration of water. Now pour wastewater into the funnel and collect clean water. Repeat the same process several times till the collected water looks clean.
Do you know?
 A forest
INTRODUCTION
The forest is a complex ecosystem consisting mainly of trees that have formed a buffer for the earth to protect life forms. The trees which make up the main area of the forest create a special environment which, in turn, affects the kinds of animals and plants that can exist in the forest. Forests can be broadly classified into many types, some of which are the Taiga type (consisting of pines, spruce, etc.) the mixed temperate forests with both coniferous an deciduous trees, the temperate forests, the sub tropical forests, the tropical forests, and the equatorial rainforests.
In India it is believed that organized exploitation of forest wealth began with an increase in hunting. Ashoka the Great is said to have set up the first sanctuary to protect the forests and all life in it. The Mughal rulers were avid hunters and spent a great deal of time in the forests.
Do you know?
A forest
INTRODUCTION
The forest is a complex ecosystem consisting mainly of trees that have formed a buffer for the earth to protect life forms. The trees which make up the main area of the forest create a special environment which, in turn, affects the kinds of animals and plants that can exist in the forest. Forests can be broadly classified into many types, some of which are the Taiga type (consisting of pines, spruce, etc.) the mixed temperate forests with both coniferous an deciduous trees, the temperate forests, the sub tropical forests, the tropical forests, and the equatorial rainforests.
In India it is believed that organized exploitation of forest wealth began with an increase in hunting. Ashoka the Great is said to have set up the first sanctuary to protect the forests and all life in it. The Mughal rulers were avid hunters and spent a great deal of time in the forests.
Do you know?
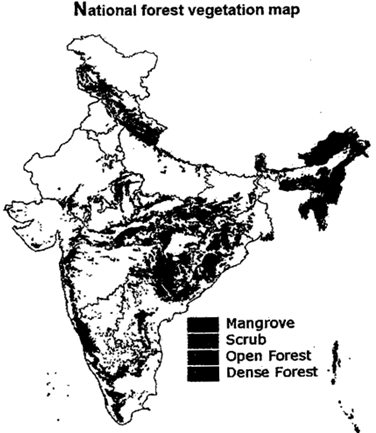 DIFFERENT TYPES OF FORESTS IN INDIA
DIFFERENT TYPES OF FORESTS IN INDIA
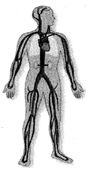 TRANSPORTATION IN UNICELLULAR ORGANISMS
In unicellular organisms, transportation of substances happens through diffusion and osmosis. Gases move in and out of the cell by diffusion. Other substances move by osmosis.
Diffusion
Random motion of particles in order to attain equilibrium of concentration is called diffusion. Diffusion can be observed in many aspects of day to day life. The aroma of food comes from the kitchen because of diffusion. A pleasant smell of flowers comes because of diffusion. Bad odour of garbage RE comes because of diffusion. Particles move from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration.
TRANSPORTATION IN UNICELLULAR ORGANISMS
In unicellular organisms, transportation of substances happens through diffusion and osmosis. Gases move in and out of the cell by diffusion. Other substances move by osmosis.
Diffusion
Random motion of particles in order to attain equilibrium of concentration is called diffusion. Diffusion can be observed in many aspects of day to day life. The aroma of food comes from the kitchen because of diffusion. A pleasant smell of flowers comes because of diffusion. Bad odour of garbage RE comes because of diffusion. Particles move from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration.
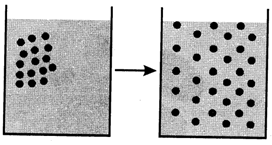 Osmosis
Movement of water through a semi-permeable membrane from high water concentration to low water concentration is called osmosis. Osmosis is a type of diffusion. Cell membrane is a semi-permeable membrane. Substances move across the cell membrane because of osmosis. Seeds swell up; when soaked in water; because of osmosis.
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM IN HUMANS
Diffusion and osmosis can result in transportation of substances to short distances only. For bigger and complex organisms, there is a need of a more complex system for transportation of substances. The circulatory system in humans is composed of three main components, viz. heart, blood vessels and blood.
Do you know?
Blood surges out into the main arteries at a speed of 16 inches per second. If it were to pass through a hole the size of a pinhead at this speed and pressure it would spurt more than 10 feet.
Blood
Blood is a type of tissue which is responsible for transportation of substances. Blood works as the carrier of various substances. Blood performs many very important functions in the body
Osmosis
Movement of water through a semi-permeable membrane from high water concentration to low water concentration is called osmosis. Osmosis is a type of diffusion. Cell membrane is a semi-permeable membrane. Substances move across the cell membrane because of osmosis. Seeds swell up; when soaked in water; because of osmosis.
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM IN HUMANS
Diffusion and osmosis can result in transportation of substances to short distances only. For bigger and complex organisms, there is a need of a more complex system for transportation of substances. The circulatory system in humans is composed of three main components, viz. heart, blood vessels and blood.
Do you know?
Blood surges out into the main arteries at a speed of 16 inches per second. If it were to pass through a hole the size of a pinhead at this speed and pressure it would spurt more than 10 feet.
Blood
Blood is a type of tissue which is responsible for transportation of substances. Blood works as the carrier of various substances. Blood performs many very important functions in the body
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
