
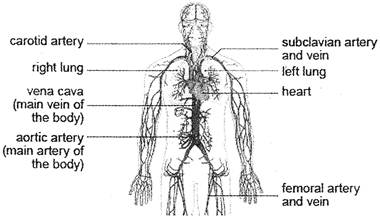
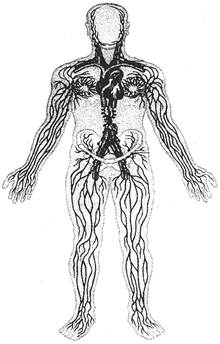
 Blood vessels are the tubular path through which blood keeps on circulating. There are three types of blood vessels, that is, arteries, veins, and capillaries. Together they form a net of blood vessels, which reaches every part of the body, making the blood to reach every parts. Blood, for reaching from heart to other parts of the body and for returning into heart from other parts of the body, use two different vessels system. The blood vessels called arteries are used by the blood to reach from heart to other parts of body .And the vessels called veins are used by the blood for coming back into heart from other parts of the body. Capillaries connect the arteries with veins. Thus blood vessels, by connecting with each other, form a tubular pathway through which blood could circulate throughout the body and can perform its functions. Blood rich in oxygen is called oxygenated blood and the blood rich in carbon dioxide is called deoxygenated blood. Arteries carry oxygenated blood and veins carry deoxygenated blood.
But one artery named pulmonary artery carries deoxygenated blood from heart to the lung and one vein name pulmonary vein carries oxygenated blood from lung to the heart.heart.
Blood vessels are the tubular path through which blood keeps on circulating. There are three types of blood vessels, that is, arteries, veins, and capillaries. Together they form a net of blood vessels, which reaches every part of the body, making the blood to reach every parts. Blood, for reaching from heart to other parts of the body and for returning into heart from other parts of the body, use two different vessels system. The blood vessels called arteries are used by the blood to reach from heart to other parts of body .And the vessels called veins are used by the blood for coming back into heart from other parts of the body. Capillaries connect the arteries with veins. Thus blood vessels, by connecting with each other, form a tubular pathway through which blood could circulate throughout the body and can perform its functions. Blood rich in oxygen is called oxygenated blood and the blood rich in carbon dioxide is called deoxygenated blood. Arteries carry oxygenated blood and veins carry deoxygenated blood.
But one artery named pulmonary artery carries deoxygenated blood from heart to the lung and one vein name pulmonary vein carries oxygenated blood from lung to the heart.heart.
| Aerobic respiration | Anaerobic respiration |
| Respiration which is performed in the presence of oxygen | Respiration which is performed in the absence of oxygen |
| Production of more energy | Production of comparatively more...
 Let understand the whole process with the help of following points:
First, the air enters through nose or mouth into pharynx, as both nasal and oral cavity opens into it.
Pharynx leads to two path. One goes to lungs and another to the stomach, named wind pipe and food pipe respectively
Air enters into lung through wind pipe.
Lung acts as a junction of two systems, respiratory system and circulatory system, where respiratory gasses (carbon dioxide and oxygen) are exchanged from one to another system.
Only oxygen is allowed to enter into circulatory system (blood stream).
Blood receives the oxygen and enters into heart.
Heart pumps this blood throughout the body so that each cell can be supplied with oxygen.
Cells receive this oxygen and perform oxidation (burning of glucose).
Carbon dioxide produced during oxidation inside the cells are expelled into circulatory system.
Blood receives this carbon dioxide and reaches to the heart.
Heart pumps this blood to the lungs.
In lungs, \[C{{O}_{2}}\] enters into respiratory system from circulatory system.
Now this \[C{{O}_{2}}\] more...
Let understand the whole process with the help of following points:
First, the air enters through nose or mouth into pharynx, as both nasal and oral cavity opens into it.
Pharynx leads to two path. One goes to lungs and another to the stomach, named wind pipe and food pipe respectively
Air enters into lung through wind pipe.
Lung acts as a junction of two systems, respiratory system and circulatory system, where respiratory gasses (carbon dioxide and oxygen) are exchanged from one to another system.
Only oxygen is allowed to enter into circulatory system (blood stream).
Blood receives the oxygen and enters into heart.
Heart pumps this blood throughout the body so that each cell can be supplied with oxygen.
Cells receive this oxygen and perform oxidation (burning of glucose).
Carbon dioxide produced during oxidation inside the cells are expelled into circulatory system.
Blood receives this carbon dioxide and reaches to the heart.
Heart pumps this blood to the lungs.
In lungs, \[C{{O}_{2}}\] enters into respiratory system from circulatory system.
Now this \[C{{O}_{2}}\] more... 


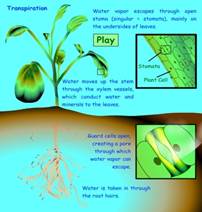
 To be alive, protection and energy are the first and basic requirement. And preparation of food is the first stage in the way of obtaining energy. It is the carbon, hydrogen and oxygen that make us enable to utilize the sunlight to get energy. Therefore these elements play very important role in sustaining life on the Earth. Without them we cease to exist.
To be alive, protection and energy are the first and basic requirement. And preparation of food is the first stage in the way of obtaining energy. It is the carbon, hydrogen and oxygen that make us enable to utilize the sunlight to get energy. Therefore these elements play very important role in sustaining life on the Earth. Without them we cease to exist.

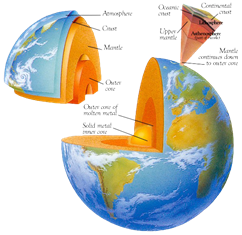 Look at the following picture of the Inner layer of the Earth
Look at the following picture of the Inner layer of the Earth
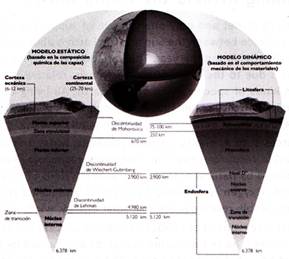 The mantle layer of the earth is mainly composed of elements like, magnesium, iron, silicon and oxygen. Temperature of the mantle layer is about 3000°C Outer mantle of the Earth is thinner than the inner mantle. The upper layer (crust) is made up of rocks, which are again made up of amino silicates.
The mantle layer of the earth is mainly composed of elements like, magnesium, iron, silicon and oxygen. Temperature of the mantle layer is about 3000°C Outer mantle of the Earth is thinner than the inner mantle. The upper layer (crust) is made up of rocks, which are again made up of amino silicates.
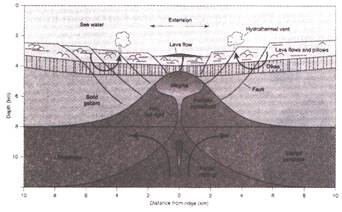 The outermost layer of the Earth is called crust. The average thickness of the continental crust is about 30 to 50/km and mostly contains granite. The average thickness of the oceanic crust is about 10 km and mostly contains basalt.
Continental crust is formed by the movement and colliding of the plates.
The outermost layer of the Earth is called crust. The average thickness of the continental crust is about 30 to 50/km and mostly contains granite. The average thickness of the oceanic crust is about 10 km and mostly contains basalt.
Continental crust is formed by the movement and colliding of the plates.

 Sand is the larger particle found in soil. It is easily available on the surface of the earth. Sandy soil contains very little humus and of low fertility. The size of the particle of the sandy soil is bigger than that of particle size of the other soil.
The size of the particle of the silt soil is smaller than sands soil and bigger than clayey soil. Silt soil can easily transported from one place to another through the movement of the air.
Look at the following picture of the silt soil
Sand is the larger particle found in soil. It is easily available on the surface of the earth. Sandy soil contains very little humus and of low fertility. The size of the particle of the sandy soil is bigger than that of particle size of the other soil.
The size of the particle of the silt soil is smaller than sands soil and bigger than clayey soil. Silt soil can easily transported from one place to another through the movement of the air.
Look at the following picture of the silt soil
 The particle size of the clayey soil is very small. The formation of clayey soil is the gradual chemical weathering of rocks.
Look at the following picture of the clayey soil
The particle size of the clayey soil is very small. The formation of clayey soil is the gradual chemical weathering of rocks.
Look at the following picture of the clayey soil


Current Affairs CategoriesArchive
Trending Current Affairs
You need to login to perform this action. |