
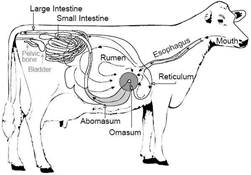
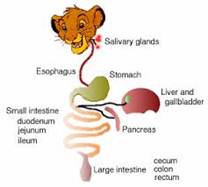
 Digestive system of a cow Digestive system of a lion
Digestive system of a cow Digestive system of a lion



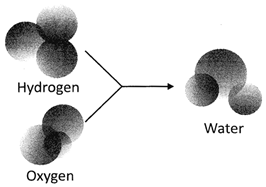 In the above picture, molecules of hydrogen and oxygen combine together to form molecules of water.
In the above picture, molecules of hydrogen and oxygen combine together to form molecules of water.



 Sodium metal Chlorine Gas Formation of slat Table salt
Sodium metal Chlorine Gas Formation of slat Table salt

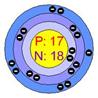 Atomic structure of sodium Atomic structure of chloride
Atomic structure of sodium Atomic structure of chloride
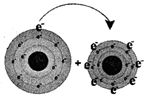
 Sodium loses one electron Sodium chloride (table salt)
In the picture (1), sodium loses its one valance electron and gives it to chlorine. In the picture (2) the atoms of the resulting elements are positively charged sodium ions and negatively charged chlorine ions. The bond, between sodium and chlorine is called ionic bond. Because, in this reaction, one reactant is in metallic form and another is in nonmetallic form. The atomic number of sodium is 11 and the valance electron in outer most orbits is 1. The atomic number of chlorine is 17 and the number of valance electrons in outer most orbits is 7.
For the classification of atomic structure of known elements a table has been introduced, which is called periodic table.
Periodic Table
In the periodic table the elements have been arranged according to their atomic number. The atomic number of an element is the number of protons in its nucleus.
The columns of periodic table signify the group of the elements. The elements more...
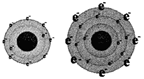
Sodium loses one electron Sodium chloride (table salt)
In the picture (1), sodium loses its one valance electron and gives it to chlorine. In the picture (2) the atoms of the resulting elements are positively charged sodium ions and negatively charged chlorine ions. The bond, between sodium and chlorine is called ionic bond. Because, in this reaction, one reactant is in metallic form and another is in nonmetallic form. The atomic number of sodium is 11 and the valance electron in outer most orbits is 1. The atomic number of chlorine is 17 and the number of valance electrons in outer most orbits is 7.
For the classification of atomic structure of known elements a table has been introduced, which is called periodic table.
Periodic Table
In the periodic table the elements have been arranged according to their atomic number. The atomic number of an element is the number of protons in its nucleus.
The columns of periodic table signify the group of the elements. The elements more...  The dissolution of sugar in water is also dissolution of solid in liquid. The solid can also be a solvent and its solutes are gas, liquid and solid. The dissolution of hydrogen in palladium is the dissolution of gas in liquid.
The dissolution of sugar in water is also dissolution of solid in liquid. The solid can also be a solvent and its solutes are gas, liquid and solid. The dissolution of hydrogen in palladium is the dissolution of gas in liquid.

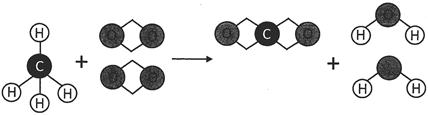 In the above picture, methane and oxygen are reactants and carbon dioxide and water are products. An arrow mark between the reactants and the products is used to denote the forward direction of the reaction. In the above reaction, one molecule of methane and two molecules of oxygen react together and form two molecules of water and one molecule of carbon dioxide.
Look at the following picture of chemical equation
In the above picture, methane and oxygen are reactants and carbon dioxide and water are products. An arrow mark between the reactants and the products is used to denote the forward direction of the reaction. In the above reaction, one molecule of methane and two molecules of oxygen react together and form two molecules of water and one molecule of carbon dioxide.
Look at the following picture of chemical equation
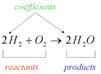 Reactants Products
In the picture above, the coefficient of the molecule is shown. Reactants in the given equation are hydrogen and oxygen whereas product is water.
Look at the following chemical equation
Reactants Products
In the picture above, the coefficient of the molecule is shown. Reactants in the given equation are hydrogen and oxygen whereas product is water.
Look at the following chemical equation
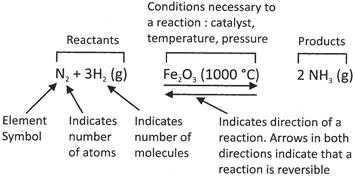 In the above chemical equation, N, is symbolic representation of nitrogen, and 2 in front of N represent the number of atoms. H is the symbolic representation of hydrogen and 3 behind H is representing the number of molecule of hydrogen. In the parenthesis, g represents the gas form of hydrogen. Arrows in the both= direction indicates the reversible reaction. 1000°C (Ferric oxide above the arrow) indicates the necessity of resistive components during the reaction. The product of the reaction is ammonia in the form more...
In the above chemical equation, N, is symbolic representation of nitrogen, and 2 in front of N represent the number of atoms. H is the symbolic representation of hydrogen and 3 behind H is representing the number of molecule of hydrogen. In the parenthesis, g represents the gas form of hydrogen. Arrows in the both= direction indicates the reversible reaction. 1000°C (Ferric oxide above the arrow) indicates the necessity of resistive components during the reaction. The product of the reaction is ammonia in the form more... 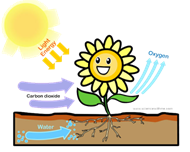 The following reaction takes place between the reactants during the process of photosynthesis.
The following reaction takes place between the reactants during the process of photosynthesis.
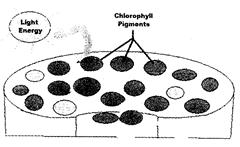 Chlorophyll transfers absorbed solar energy into the centre of the cell where, exchange of electrons between the water molecules and solar energy takes place. The result of the exchange of these electrons is the production of oxygen gas and hydrogen ions. ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is an enzyme. The function of ATP is to transport the energy within the cell for metabolism which is produced during the exchange of these more...
Chlorophyll transfers absorbed solar energy into the centre of the cell where, exchange of electrons between the water molecules and solar energy takes place. The result of the exchange of these electrons is the production of oxygen gas and hydrogen ions. ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is an enzyme. The function of ATP is to transport the energy within the cell for metabolism which is produced during the exchange of these more...  Monotropa
Monotropa
 Cuscuta
Cuscuta
 Pitcher Plant
Pitcher Plant
 Symbiotic plants
Symbiotic plants

You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
