LEARNING OBJECTIVES
This lesson will help us to:-
- Define fractions numerator and denominator.
- Identify a fraction using object and shapes.
- Understand equivalent fraction.
- Compare fractions.
- Add unit fractions with like denominators.
REAL IF EXAMPLES
- An hour is divided in fraction of hours. Half\[\left( \frac{1}{2} \right)\] and hour; quarter of an hour.
.

- Sport like football, have half time in the game. Half time shows a break marking the completion of half of a game.

QUICK CONCEPT REVIEW
When a whole object or group is divided into equal parts, then each part is called a fraction of that whole.

Suppose, there is an apple and you want to divide it equally among 2 friends then equal pieces of the apple form fractions.
A fraction is a part of a whole divided in equal parts.
PROPERTIES OF FRACTION
- A fraction is written in the form of \[\frac{N}{D};D\ne 0.\]Here N is called the numerator and D is called the denominator. For example; \[\frac{1}{3}\] means one part out of 3 equal parts.
- When a whole is divided in 2 equal parts, then each part is called a half and is written as\[\frac{1}{2}\]

- When a whole is divided in 4 equal parts, then each part is called quarter or one-fourth and is written as \[\frac{1}{4}\].
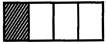
- Fractions that appear differently but have the same value are called equivalent fractions. For example \[\frac{2}{4}\] ,\[\frac{1}{2}\]and\[\frac{3}{6}\].
- In a fraction, multiply the numerator and denominator by the same number to get an equivalent fraction.
For example: \[\frac{1}{4}=\frac{1}{4}\times \frac{3}{3}=\frac{3}{12}\]
So, \[\frac{1}{4}\] and\[\frac{3}{12}\]are equivalent fractions.
TYPES OF FRACTIONS
Let us now understand different kinds of fractions. Fractions can be divided into two categories:
Like and unlike fractions.
Proper and Improper fractions.
Like Fractions are those fractions which have the same denominators.
\[\frac{1}{9},\frac{2}{9},\frac{3}{9},\frac{5}{9},\frac{6}{9}\]Etc. is all like fractions
Unlike Fractions are those fractions which have different denominators.
\[\frac{1}{3},\frac{2}{13},\frac{4}{9},\frac{5}{8},\frac{6}{11}\] are all unlike fractions.
Proper Fractions are those fractions in which the numerator is less than the denominator.
\[\frac{1}{2},\frac{2}{3},\frac{4}{5},\frac{6}{7},\frac{8}{9},\frac{9}{11}\]are all proper fractions.
Improper Fractions are those fractions in which the numerator is greater than the denominator,
\[\frac{3}{2},\frac{8}{5},\frac{7}{4},\frac{12}{10}\] are improper fractions.
Games
Take paper cut outs of basic shapes like circle, square and rectangle. Now fold the paper to get equal parts. It's time to cooer. Color half quarter, one third of different shapes
HISTORICAL PREVIEW
- The egyptions were one of the first groups to study fractions. It evolved from problems like division of food as there was no money to make payment.
- The arabs introduced the fractional bar in the 12th century
AMAZING FACTS
- The word fraction is originated from a Latin word fraction, which more...


 AMAZING FACTS
AMAZING FACTS

 QUICK CONCEPT REVIEW
When a whole object or group is divided into equal parts, then each part is called a fraction of that whole.
QUICK CONCEPT REVIEW
When a whole object or group is divided into equal parts, then each part is called a fraction of that whole.
 Suppose, there is an apple and you want to divide it equally among 2 friends then equal pieces of the apple form fractions.
A fraction is a part of a whole divided in equal parts.
PROPERTIES OF FRACTION
Suppose, there is an apple and you want to divide it equally among 2 friends then equal pieces of the apple form fractions.
A fraction is a part of a whole divided in equal parts.
PROPERTIES OF FRACTION

 I How many groups do you get?
How many 3's are in 12?
The answer is 4. So. 12 - 3 = 4.
The symbol'\[\div \]' indicates Division.
Think: If you DIVIDE 10 into groups of two, how many groups are there?
How many groups of two are there in 10? How many two’s are there in 10?
Since 2+2+2+2+2= 10, there are FIVE twos in 10; 10 \[\div \] 2 = 5
Division is the equal distribution of a given quantity. The number to be divided is called the dividend. The number which divides is called the divisor. The answer is called the quotient. The number left after the division is called the remainder.
Chunmun bought 15 apples from fruit market. She placed 15 apples equally in 3 baskets.
I How many groups do you get?
How many 3's are in 12?
The answer is 4. So. 12 - 3 = 4.
The symbol'\[\div \]' indicates Division.
Think: If you DIVIDE 10 into groups of two, how many groups are there?
How many groups of two are there in 10? How many two’s are there in 10?
Since 2+2+2+2+2= 10, there are FIVE twos in 10; 10 \[\div \] 2 = 5
Division is the equal distribution of a given quantity. The number to be divided is called the dividend. The number which divides is called the divisor. The answer is called the quotient. The number left after the division is called the remainder.
Chunmun bought 15 apples from fruit market. She placed 15 apples equally in 3 baskets.
 Divide 15 into equal groups.
There are 5 apples in each group.
Therefore, 15 - 3 = 5
Divide 15 into equal groups.
There are 5 apples in each group.
Therefore, 15 - 3 = 5
 1. Mrs. Khanna got 35 flowers on her wedding anniversary.
1. Mrs. Khanna got 35 flowers on her wedding anniversary.
 She placed them equally in 5 vases.
She placed them equally in 5 vases.
 There were 7 flowers in each vase.
So, 35 - 5 = 7 or
"Thirty five divided by five is seven."
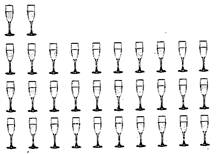
2. Minki arranged 32 glasses on the dining table for guests.
There were 7 flowers in each vase.
So, 35 - 5 = 7 or
"Thirty five divided by five is seven."
2. Minki arranged 32 glasses on the dining table for guests.
 Amazing Facts
Amazing Facts
 This is a tray with Ladoos (sweet). It has 9 Ladoos. How many Ladoos are there in 6 trays?
This is a tray with Ladoos (sweet). It has 9 Ladoos. How many Ladoos are there in 6 trays?
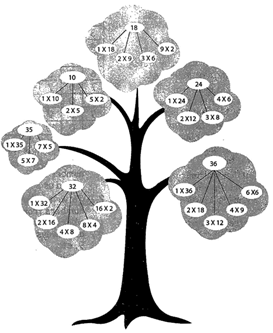 10 \[\Rightarrow \]1X 10 =2X5=5X2
35 \[\Rightarrow \]1X 35 =5X7=7X5
24 \[\Rightarrow \]1X24=2X12=3X8 more...
10 \[\Rightarrow \]1X 10 =2X5=5X2
35 \[\Rightarrow \]1X 35 =5X7=7X5
24 \[\Rightarrow \]1X24=2X12=3X8 more...  MORE ABOUT SUBRTACTION
MORE ABOUT SUBRTACTION
 More about Addition
Addition is one of the basic four operations.
More about Addition
Addition is one of the basic four operations.
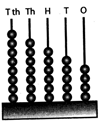 Face Value
Face value of a digit in a number is the digit itself. For example- Face value of 9 in 1892 is 9.
more...
Face Value
Face value of a digit in a number is the digit itself. For example- Face value of 9 in 1892 is 9.
more...  We should not waste water. It is very valuable for all the living things. While using water we should keep following things in mind:
We should not waste water. It is very valuable for all the living things. While using water we should keep following things in mind:
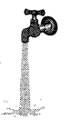
 Soil or earth is also a renewable resource. We live on it. It supports the trees and gives us shelter. Below earth's surface there are sources of water. The land also provides us with minerals like copper and iron etc. We should try not more...
Soil or earth is also a renewable resource. We live on it. It supports the trees and gives us shelter. Below earth's surface there are sources of water. The land also provides us with minerals like copper and iron etc. We should try not more... 
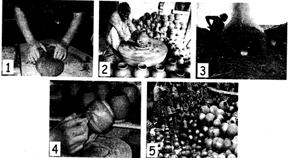 1. Kneading clay
2. Making pots
3. Baking the pots in kiln
4. Decorating Pots
5. Selling different pottery more...
1. Kneading clay
2. Making pots
3. Baking the pots in kiln
4. Decorating Pots
5. Selling different pottery more... 
 Non- Uniform Motion
Non- Uniform Motion
 more...
more... 