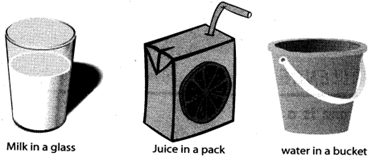
 LIQUID
A liquid is anything that has size or volume, but does not have a shape. Liquids must be contained in a cup, bottle, or some container in order to have a shape. Milk, water, and juice are liquids. When you pour milk into a glass, it takes the shape of the glass. If you spill the glass of milk on the floor, it will spread quickly as it takes the shape of the floor.
LIQUID
A liquid is anything that has size or volume, but does not have a shape. Liquids must be contained in a cup, bottle, or some container in order to have a shape. Milk, water, and juice are liquids. When you pour milk into a glass, it takes the shape of the glass. If you spill the glass of milk on the floor, it will spread quickly as it takes the shape of the floor.
 Particles of liquid are not as close together as particles in a solid, and move around much more freely. They have no regular shape or arrangement and move freely.
GAS
Gases are hard to identify because they have no colour, size or shape. When we take deep breath our lungs fill up with air. Air is a combination of many gases.
The particles in a gas move freely at high speeds. There is a lot of free space in between the particles, and they take the shape of any container.
Particles of liquid are not as close together as particles in a solid, and move around much more freely. They have no regular shape or arrangement and move freely.
GAS
Gases are hard to identify because they have no colour, size or shape. When we take deep breath our lungs fill up with air. Air is a combination of many gases.
The particles in a gas move freely at high speeds. There is a lot of free space in between the particles, and they take the shape of any container.
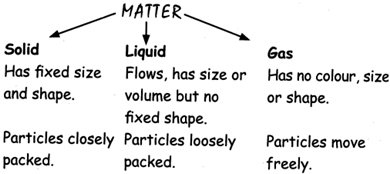 Matter Changes from One State to Another
Matter Changes from One State to Another

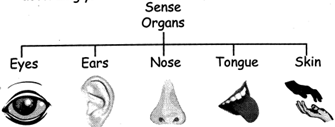 2. Skeletal system; Ail the bones of our body together form skeletal system and form the framework of the body. It gives the shape of the body and support the body to stand, sit, and walk.
2. Skeletal system; Ail the bones of our body together form skeletal system and form the framework of the body. It gives the shape of the body and support the body to stand, sit, and walk.
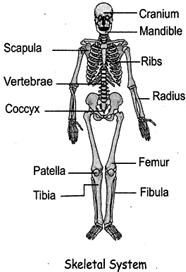 The adult human skeletal system consists of 206 bones. Human infants are born with 300 to 350 bones, some of which fuse together as the body develops. By the time most children reach the age of 9 they have 206 bones. The skeletal system performs vital functions — support, movement, protection, blood cell production, calcium storage.
3. Nervous system: Nervous system consists of brain and nerves. Made up of your brain, your spinal cord, and an enormous network of nerves that thread throughout your body, the nervous system is the control center for your entire body. Your brain uses information it receives from your nerves to coordinate all of your actions and reactions. It controls all your actions of seeing, hearing, speaking, thinking etc.
The adult human skeletal system consists of 206 bones. Human infants are born with 300 to 350 bones, some of which fuse together as the body develops. By the time most children reach the age of 9 they have 206 bones. The skeletal system performs vital functions — support, movement, protection, blood cell production, calcium storage.
3. Nervous system: Nervous system consists of brain and nerves. Made up of your brain, your spinal cord, and an enormous network of nerves that thread throughout your body, the nervous system is the control center for your entire body. Your brain uses information it receives from your nerves to coordinate all of your actions and reactions. It controls all your actions of seeing, hearing, speaking, thinking etc.
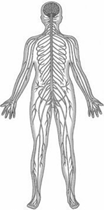 4. Muscular system: Muscular system is made up of muscles. On average, probably 40% of your body weight is in muscles. You have over 630 muscles that move you. Without muscles you couldn't open your mouth, speak, shake hands, walk, talk, or move your food more...
4. Muscular system: Muscular system is made up of muscles. On average, probably 40% of your body weight is in muscles. You have over 630 muscles that move you. Without muscles you couldn't open your mouth, speak, shake hands, walk, talk, or move your food more... 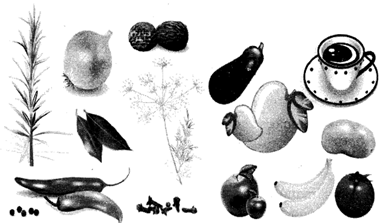 PARTS OF PLANTS THAT ARE EATEN
Almost every part of a plant is eaten. But there is hardly any plant that is eaten whole.
Different parts of a plant that are eaten are- roots (carrot, radish, turnip etc), stems (celery, lotus-stem etc), leaves (cabbage, spinach, coriander etc), seeds (ex. peas), fruit (cherry, mango, apple, pear etc), flower (ex. Rose, saffron etc).
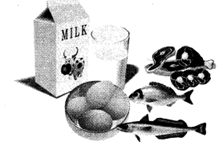
FOOD FROM ANIMALS
PARTS OF PLANTS THAT ARE EATEN
Almost every part of a plant is eaten. But there is hardly any plant that is eaten whole.
Different parts of a plant that are eaten are- roots (carrot, radish, turnip etc), stems (celery, lotus-stem etc), leaves (cabbage, spinach, coriander etc), seeds (ex. peas), fruit (cherry, mango, apple, pear etc), flower (ex. Rose, saffron etc).
FOOD FROM ANIMALS
 2. A baby chicken grows into a hen/cock.
2. A baby chicken grows into a hen/cock.
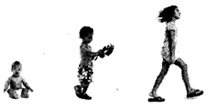
 3. A baby grows into an adult man/women.
3. A baby grows into an adult man/women.
 There are many things which remain same in size even after so many years. For example, you cannot wear the same clothes of your childhood days now, as you have grown up but your clothes haven't.
Thus the things which don't grow with time are called non-living things.
Examples: Your school, tap, door and pencil donot grow and remain same in size. So they are non-living things.
Examples:
There are many things which remain same in size even after so many years. For example, you cannot wear the same clothes of your childhood days now, as you have grown up but your clothes haven't.
Thus the things which don't grow with time are called non-living things.
Examples: Your school, tap, door and pencil donot grow and remain same in size. So they are non-living things.
Examples:
 2. Living things can move from place to place but non-living things can't move.
You can get up, walk, run and move from one place to another on your own. Similarly, birds fly, fishes swim, animals walk and run. Plants also show movement. For example sunflower moves in the direction of sun. All these are living things.
So, all living things can move from one place to another
1. Children run while playing.
2. Living things can move from place to place but non-living things can't move.
You can get up, walk, run and move from one place to another on your own. Similarly, birds fly, fishes swim, animals walk and run. Plants also show movement. For example sunflower moves in the direction of sun. All these are living things.
So, all living things can move from one place to another
1. Children run while playing.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
