 To know about the working of a computer, first need to understand various terms such as Data, Processing and Information. First of all, let’s start with three basic terms:-
To know about the working of a computer, first need to understand various terms such as Data, Processing and Information. First of all, let’s start with three basic terms:-
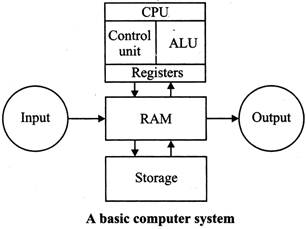
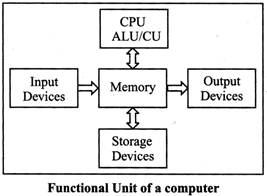 BASIC COMPONENTS OF COMPUTER SYSETEMS
Following are the various components of a computer system-
Input Unit
Data and instructions must enter the computer system before any computation can be performed on the supplied data. The input unit that links the external environment with the computer system performs this task. An input unit performs the following functions:
BASIC COMPONENTS OF COMPUTER SYSETEMS
Following are the various components of a computer system-
Input Unit
Data and instructions must enter the computer system before any computation can be performed on the supplied data. The input unit that links the external environment with the computer system performs this task. An input unit performs the following functions:
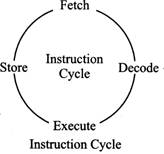 A simple instruction cycle consists of the following steps
A simple instruction cycle consists of the following steps
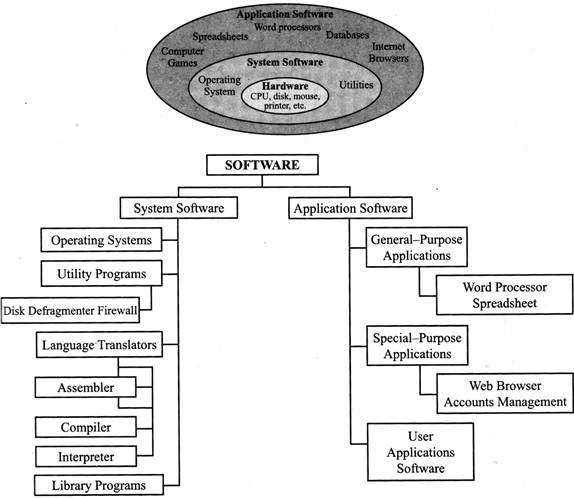 (A) System Software
System software is the software which manages and controls the hardware components and allows interaction between the hardware and the other different types of software. The computer's operating system is a type of system software. Device drivers are also a part of this category.
System software can be separated into two different categories: Operating systems and Utility software.
OPERATING SYSTEM:
A program that acts as an intermediary between a user of a computer and the computer hardware is called an operating system. The operating system is an essential component of the system software in a computer system. Application programs usually require an operating system to function.
Operating systems can be found on almost any device that contains a computer—from cellular phones and video game consoles to supercomputers and web servers. For example: UNIX, MS-DOS, WINDOWS, 98/2000/xp/7.
Functions of an operating system -
The basic functions of an operating system are:
(A) System Software
System software is the software which manages and controls the hardware components and allows interaction between the hardware and the other different types of software. The computer's operating system is a type of system software. Device drivers are also a part of this category.
System software can be separated into two different categories: Operating systems and Utility software.
OPERATING SYSTEM:
A program that acts as an intermediary between a user of a computer and the computer hardware is called an operating system. The operating system is an essential component of the system software in a computer system. Application programs usually require an operating system to function.
Operating systems can be found on almost any device that contains a computer—from cellular phones and video game consoles to supercomputers and web servers. For example: UNIX, MS-DOS, WINDOWS, 98/2000/xp/7.
Functions of an operating system -
The basic functions of an operating system are:
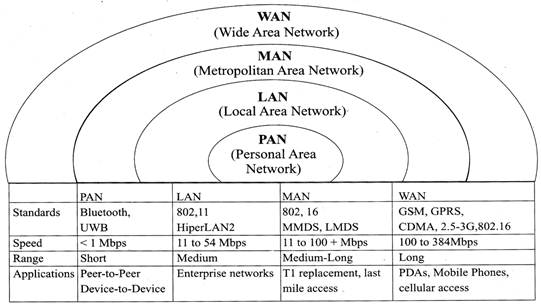 There are many types of Networks including:
There are many types of Networks including:
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
