SERIES
In series (numbers, letters, combination of numbers and letters, figures) completion, student is required to study the given series, identify the pattern followed by the terms of the series either to find missing term or to identify the wrong term.
COMPLETION OF FIGURE PATTERN
In this type of questions, a figure pattern is given, in which a part is missing, followed by the four options. A student has to select the best option amongst the given options which completely fits in the pattern or completes the pattern.
INSERTING THE MISSING CHARACTER
In this type of questions, a set of terms following a certain pattern is given. The student is required to identify the relation or pattern followed in the given terms and find the missing character.
FIGURE MATRIX
In this type of questions, sets of figures follows the same rule either row-wise or column-wise. A student has to analyse the set of figures and identify the rule and then find the missing figure from the set of options.
EXAMPLE
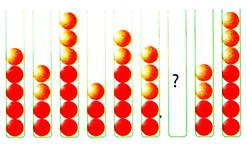
1. Which is the missing figure?
(a)

(b)

(c)

(d)

Explanation (a):
Number of balls changes from 1 to 3, 3 to 5, 5 to 7 boxes and 2 to 4, 4 to 6, ....... boxes
Pattern followed:
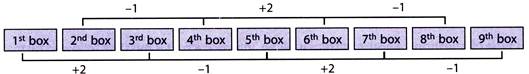
Number of balls in 7th box is 8.
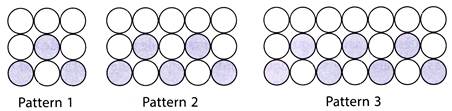
2. How many shaded circles will be there in pattern 81?
(a) 161
(b) 162
(c) 163
(d) 160
Explanation (c):
Number of shaded circles in Pattern 1 = 3
Number of shaded circles in Pattern 2 = 5
Number of shaded circles in Pattern 3 = 7
Pattern followed is
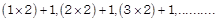
i.e., 3, 5, 7..........
Number of shaded circles in Pattern

3. Which number will replace the question mark in the number pattern given below?

(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Explanation (d):
Pattern followed is:
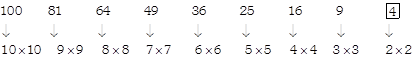
4. What is the missing number in the series given below?
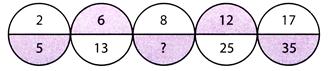
(a) 17
(b) 27
(c) 35
(d) 41
Explanation (a):
Pattern followed in
? is
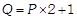
Hence, number in lower part of third circle is:
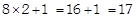
5. Which figure will replace the question mark in
more...  (a)
(a)  Number of balls in 7th box is 8.
2. How many shaded circles will be there in pattern 81?
Number of balls in 7th box is 8.
2. How many shaded circles will be there in pattern 81?
 (a) 161
(b) 162
(c) 163
(d) 160
Explanation (c):
Number of shaded circles in Pattern 1 = 3
Number of shaded circles in Pattern 2 = 5
Number of shaded circles in Pattern 3 = 7
Pattern followed is
(a) 161
(b) 162
(c) 163
(d) 160
Explanation (c):
Number of shaded circles in Pattern 1 = 3
Number of shaded circles in Pattern 2 = 5
Number of shaded circles in Pattern 3 = 7
Pattern followed is  (a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Explanation (d):
Pattern followed is:
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Explanation (d):
Pattern followed is:
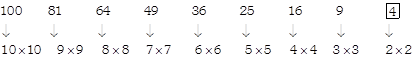 4. What is the missing number in the series given below?
4. What is the missing number in the series given below?
 (a) 17
(b) 27
(c) 35
(d) 41
Explanation (a):
Pattern followed in
(a) 17
(b) 27
(c) 35
(d) 41
Explanation (a):
Pattern followed in  ? is
? is  (b)
(b)  (c)
(c)  (d)
(d)  Explanation (b):
The figure in option (b) is made up of both straight and curved lines.
2. There is a certain relationship between the pair of figures given on either side of : Identify the relationship of the given pair and find the missing term in the other pair.
Explanation (b):
The figure in option (b) is made up of both straight and curved lines.
2. There is a certain relationship between the pair of figures given on either side of : Identify the relationship of the given pair and find the missing term in the other pair.
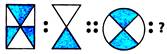 (a)
(a) 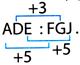 So, if we follow the same rule
So, if we follow the same rule 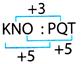 4. In the given question, four numbers are given. Out of these, three are alike in a certain way but the rest one is different. Choose the one which is different from rest of the three.
(a) 6 (b) 12 (c) 18 (d) 9
Explanation (d):
Except (d), all others are multiples of 6 or, except (d) all are even numbers.
4. In the given question, four numbers are given. Out of these, three are alike in a certain way but the rest one is different. Choose the one which is different from rest of the three.
(a) 6 (b) 12 (c) 18 (d) 9
Explanation (d):
Except (d), all others are multiples of 6 or, except (d) all are even numbers. 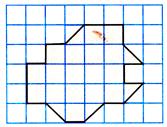 Number of complete squares =17
Number of half squares = 5
Area of figure is
Number of complete squares =17
Number of half squares = 5
Area of figure is 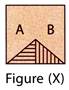 (a)
(a) 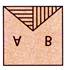 (b)
(b)  (c)
(c)  (d)
(d) 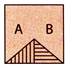 Explanation (b)
Explanation (b)
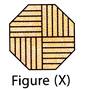
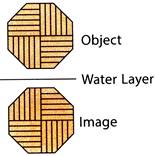
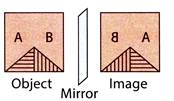 2. Find the water image of figure (X).
2. Find the water image of figure (X).
 (a)
(a)  (b)
(b)  (c)
(c)  (d)
(d)  Explanation (a)
Explanation (a)
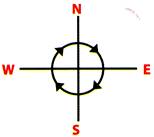
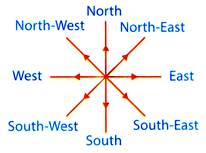 Clockwise turn (Right turn): When somebody moves in direction which is same as the moving direction of clock-hands is called clockwise turn.
Clockwise turn (Right turn): When somebody moves in direction which is same as the moving direction of clock-hands is called clockwise turn.
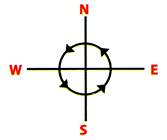
 Anticlockwise turn (Left turn): Moving in the opposite direction of the clockwise direction is called anticlockwise direction.
Anticlockwise turn (Left turn): Moving in the opposite direction of the clockwise direction is called anticlockwise direction.
 EXAMPLE
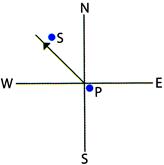
1. John is facing the community centre. What will he be facing if he turns
EXAMPLE
1. John is facing the community centre. What will he be facing if he turns 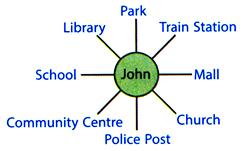 (a) Library (b) School (c) Police Post (d) Church
Explanation (c):
(a) Library (b) School (c) Police Post (d) Church
Explanation (c):
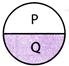
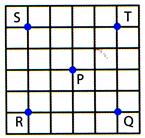 (a) P (b) Q (c) R (d) S
Explanation (d):
(a) P (b) Q (c) R (d) S
Explanation (d):
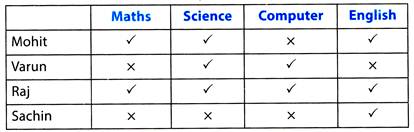 Raj is good in all subjects.
Raj is good in all subjects.
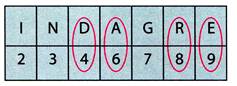 DEAR: 4968
2. If the code of PRESENT is TNESERP and code of PAPER is REPAP, then what will be the code of MONDAY?
(a) YADNOM (b) YADOMN (c) YADMNO (d) YADMON
Explanation (a):
Letters of word are written in reverse order to get their code.
So, code for MONDAY is YADNOM.
DEAR: 4968
2. If the code of PRESENT is TNESERP and code of PAPER is REPAP, then what will be the code of MONDAY?
(a) YADNOM (b) YADOMN (c) YADMNO (d) YADMON
Explanation (a):
Letters of word are written in reverse order to get their code.
So, code for MONDAY is YADNOM.