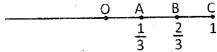
 In the above figures point A represents \[\frac{1}{3},\] point B represents \[\frac{2}{3},\] and point C represents 1.
Line Segment
Line segment is defined as the shortest distance between two fixed points. For example
In the above figures point A represents \[\frac{1}{3},\] point B represents \[\frac{2}{3},\] and point C represents 1.
Line Segment
Line segment is defined as the shortest distance between two fixed points. For example
 (a) 2 (b) 4
(c) 8 (d) 16
(e) None of these
Answer (c)
Ray
It is defined as the extension of a line segment in one infinitive direction. For example:
(a) 2 (b) 4
(c) 8 (d) 16
(e) None of these
Answer (c)
Ray
It is defined as the extension of a line segment in one infinitive direction. For example:
 (a) 2 (b) 4
(c) 12 (d) 16
(e) None of these
Answer (c)
Line
Line is defined as the extension of a line segment infinitive in either direction.
(a) 2 (b) 4
(c) 12 (d) 16
(e) None of these
Answer (c)
Line
Line is defined as the extension of a line segment infinitive in either direction.
 (a) 2 (b) 4
(c) 8 (d) 16
(e) None of these
Answer (a)
Angle
Inclination between two rays having common end point is called angle.
(a) 2 (b) 4
(c) 8 (d) 16
(e) None of these
Answer (a)
Angle
Inclination between two rays having common end point is called angle.
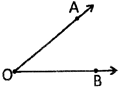 Angle is measured in degree. Symbol of the degree is \[\,{}^\circ \,\]and written as \[a{}^\circ ,\]where a is the measurement of the angle.
Types of Angle
There are different types of angles.
Right Angle
An angle whose measure is exactly \[90{}^\circ \]is a right angle.
Angle is measured in degree. Symbol of the degree is \[\,{}^\circ \,\]and written as \[a{}^\circ ,\]where a is the measurement of the angle.
Types of Angle
There are different types of angles.
Right Angle
An angle whose measure is exactly \[90{}^\circ \]is a right angle.
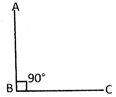 \[\angle \] ABC is a right angle.
Acute Angle
An angle whose measure is less than \[90{}^\circ \]is an acute angle.
\[\angle \] ABC is a right angle.
Acute Angle
An angle whose measure is less than \[90{}^\circ \]is an acute angle.
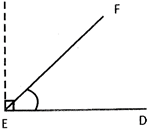 \[\angle \] DEF is an acute angle.
Obtuse Angle
An angle whose measure is greater than \[90{}^\circ \]but less than \[180{}^\circ \]is a obtuse angle.
\[\angle \] DEF is an acute angle.
Obtuse Angle
An angle whose measure is greater than \[90{}^\circ \]but less than \[180{}^\circ \]is a obtuse angle.
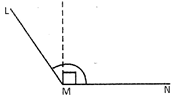 more...
more... 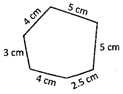 Solution:
Perimeter of the figure = 4 cm + 3 cm + 4 cm + 2.5 cm+ 5 cm + cm = 23.50.
Perimeter of the Triangle
A triangle has three sides. Perimeter of a triangle is the sum of its all the three sides.
Solution:
Perimeter of the figure = 4 cm + 3 cm + 4 cm + 2.5 cm+ 5 cm + cm = 23.50.
Perimeter of the Triangle
A triangle has three sides. Perimeter of a triangle is the sum of its all the three sides.
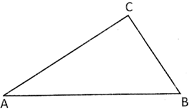 Perimeter of the triangle ABC = AB + BC + CA
Perimeter of the triangle ABC = AB + BC + CA
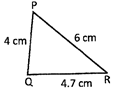 Solution:
Perimeter of the triangle PQR = 4 cm + 4.7 cm + 6 cm= 14.7 cm
Perimeter of the Quadrilateral
Perimeter of a quadrilateral is the sum of the length of its four sides.
Solution:
Perimeter of the triangle PQR = 4 cm + 4.7 cm + 6 cm= 14.7 cm
Perimeter of the Quadrilateral
Perimeter of a quadrilateral is the sum of the length of its four sides.
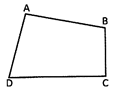 In quadrilateral ABCD, perimeter = AB + BC + CD + DA
In quadrilateral ABCD, perimeter = AB + BC + CD + DA
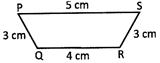 Solution:
Perimeter of the quadrilateral = 5 cm + 3 cm + 4 cm + 3 cm = 15 cm
Perimeter of Rectangles
Perimeter of a rectangle = 2 (Length + Breadth).
Solution:
Perimeter of the quadrilateral = 5 cm + 3 cm + 4 cm + 3 cm = 15 cm
Perimeter of Rectangles
Perimeter of a rectangle = 2 (Length + Breadth).

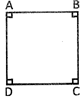 Perimeter of the square ABCD = 4 \[\times \]AB
Perimeter of the square ABCD = 4 \[\times \]AB
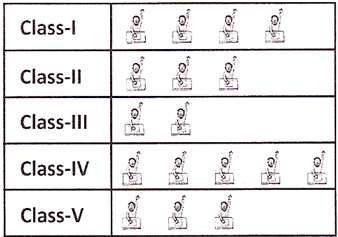 Key: One boy represents 8 students.
(a) How many students were present in class III?
(b) In which class least number of students were present?
(c) How many students were present in class IV and class V together?
(d) How many more students was present in class IV in comparison of class III
Solution:
(a) 16 (b) Class III (c) 64 (d) 24
Barograph
When the data is represented on the graph with the help of bars, it is known as Barograph.
Key: One boy represents 8 students.
(a) How many students were present in class III?
(b) In which class least number of students were present?
(c) How many students were present in class IV and class V together?
(d) How many more students was present in class IV in comparison of class III
Solution:
(a) 16 (b) Class III (c) 64 (d) 24
Barograph
When the data is represented on the graph with the help of bars, it is known as Barograph.
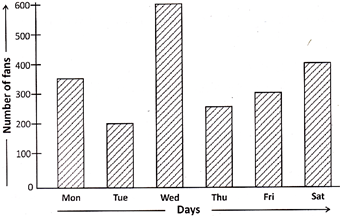 (a) How many fans were sold by the shop during the week?
(b) On which day, maximum number of fans were sold?
(c) How many more fans were sold on Wednesday in comparison to Tuesday?
(d) On which day 400 fans were sold?
Answer:
(a) 2100
(b) Wednesday
(c) 400
(d) Saturday
(a) How many fans were sold by the shop during the week?
(b) On which day, maximum number of fans were sold?
(c) How many more fans were sold on Wednesday in comparison to Tuesday?
(d) On which day 400 fans were sold?
Answer:
(a) 2100
(b) Wednesday
(c) 400
(d) Saturday
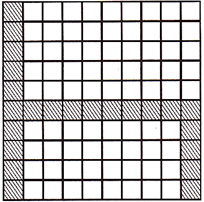 Since, 23 out of 100 squares are shaded, we can say \[\frac{23}{100}\] of the whole part (large square) is shaded. Here, \[\frac{23}{100}\] has 100 as its denominator, we call it a percentage. \[\frac{23}{100}\] can be named as 23 percent of 23% So, \[\frac{23}{100}\]= 23% and 23% = \[\frac{23}{100}\]. Remember that the numerator of a fraction with denominator 100 will be percentage.
Since, 23 out of 100 squares are shaded, we can say \[\frac{23}{100}\] of the whole part (large square) is shaded. Here, \[\frac{23}{100}\] has 100 as its denominator, we call it a percentage. \[\frac{23}{100}\] can be named as 23 percent of 23% So, \[\frac{23}{100}\]= 23% and 23% = \[\frac{23}{100}\]. Remember that the numerator of a fraction with denominator 100 will be percentage.
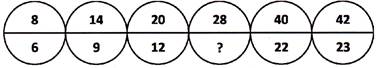 (a) 18 (b) 22
(c) 16 (d) 14
(e) None of these
Answer (c)
Explanation: Pattern followed in
(a) 18 (b) 22
(c) 16 (d) 14
(e) None of these
Answer (c)
Explanation: Pattern followed in 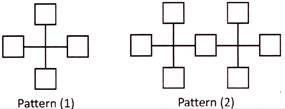
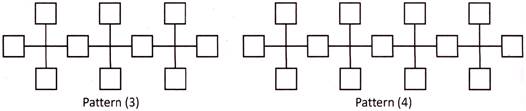 (a) 103 (b) 94
(c) 98 (d) 89
(e) None of these
Answer (b)
Explanation: Number of squares in Pattern \[(1)\,\,=\,\,(3\,\times \,1)\,\,+\,\,1\,\,=\,\,4\]
Number of squares in Pattern \[(2)\,\,=\,\,(3\,\times \,2)\,\,+\,\,1\,\,=\,\,7\]
Number of squares in Pattern \[(3)\,\,=\,\,(3\,\times \,3)\,\,+\,\,1\,\,=\,\,10\]
Number of squares in Pattern \[(4)\,\,=\,\,(3\,\times \,4)\,\,+\,\,1\,\,=\,\,13\]
Therefore, Number of squares in Pattern \[(31)\,\,=\,\,(3\,\times \,31)\,\,+\,\,1\,\,=\,\,93\,\,+\,\,1\,\,=\,\,94\]
Problems Based on Alphabet Test and Word Formation
Alphabet test is one of the most common topic of reasoning where we come across various types of problems as follows:
(a) 103 (b) 94
(c) 98 (d) 89
(e) None of these
Answer (b)
Explanation: Number of squares in Pattern \[(1)\,\,=\,\,(3\,\times \,1)\,\,+\,\,1\,\,=\,\,4\]
Number of squares in Pattern \[(2)\,\,=\,\,(3\,\times \,2)\,\,+\,\,1\,\,=\,\,7\]
Number of squares in Pattern \[(3)\,\,=\,\,(3\,\times \,3)\,\,+\,\,1\,\,=\,\,10\]
Number of squares in Pattern \[(4)\,\,=\,\,(3\,\times \,4)\,\,+\,\,1\,\,=\,\,13\]
Therefore, Number of squares in Pattern \[(31)\,\,=\,\,(3\,\times \,31)\,\,+\,\,1\,\,=\,\,93\,\,+\,\,1\,\,=\,\,94\]
Problems Based on Alphabet Test and Word Formation
Alphabet test is one of the most common topic of reasoning where we come across various types of problems as follows:
| Period | Kharab |
Operation on Numbers
Operation on Numbers
In the previous chapter we have studied about numbers, way of numeration and some properties of numbers. In this chapter we will study operation on numbers. Addition, subtraction, multiplication and division are four basic arithmetic operations. Let us know about them.
Addition
Under the operation of addition two or more than two numbers are added with each other.
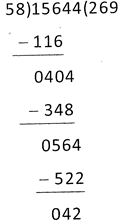 Remainder = 42
Remainder = 42
Categories of Computers
Introduction
Computers are categorized on the basis of types of input signal processed by its peripherals, purpose of their use, physical structure, speed and reliability. Two types of signal are usually processed by the computer, these are digital and analog signal. Some types of computer processes both analog and digital signal. Therefore, depending on the types of input signal processed by computer, they are categorized into three groups.
v Digital computers work on digital signal.
v Analog computers work on analog signal.
v Hybrid computers work on both digital and analog signal.
In this chapter we will study more about these classification.
Digital Computer
A digital computer is a computer that stores data in terms of binary digits (digital) and proceeds in discrete steps from one state to the next. The word 'digital' stands for discrete (step-by-step) and hence, digital computers can take only discrete values. A digital computer gives accurate information than an analog computer.
Types of Digital Computer
Types of Digital computer are based on their size and performance, purpose of their use, etc.
Depending upon the size and performance, digital computers are categorized into five tvpes. They are the followings.
Embedded Computer
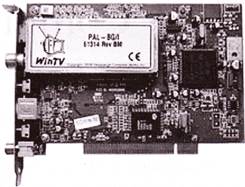
An Embedded computer is one that has computer hardware with software embedded in it as one its important components. Smallest Embedded computers are equipped within the circuit and they are programmed for performing the specific task. An example of embedded computer is soldered on the television circuit which performs the task during the tuning to a particular television frequency.
Look at the following picture of Embedded computers as a TV tuner card:
 Microcomputer
A Microcomputer contain a microprocessor which works as a CPU. It accepts input, stores large quantities of data, execute complex instructions which direct it to perform mathematical and logical operations and outputs the answer in a human readable form. The microcomputers are basically used in educational training, playing games, etc. The microcomputer are further divided into Desktop computer, workstation and PDAs.
Minicomputers
A Minicomputer is midsized computer. A multi-user computer capable of supporting from 10 to 100 of users simultaneously. In terms of size and power, minicomputers lie between microcomputer and mainframe. They have capability to connected more input and output devices than microcomputer and also known as multiuser computer.
Mainframe Computers
A Mainframe computers are large-sized, powerful multi-user computers that can support concurrent programs. It can be used by as many as hundreds or thousands of users at the same time. Large organisations may use a mainframe computer to execute large-scale processes such as processing the organisation's payroll. It is designed to handle large volume of data and information and also has great processing speed as compare to the minicomputer. more...
Microcomputer
A Microcomputer contain a microprocessor which works as a CPU. It accepts input, stores large quantities of data, execute complex instructions which direct it to perform mathematical and logical operations and outputs the answer in a human readable form. The microcomputers are basically used in educational training, playing games, etc. The microcomputer are further divided into Desktop computer, workstation and PDAs.
Minicomputers
A Minicomputer is midsized computer. A multi-user computer capable of supporting from 10 to 100 of users simultaneously. In terms of size and power, minicomputers lie between microcomputer and mainframe. They have capability to connected more input and output devices than microcomputer and also known as multiuser computer.
Mainframe Computers
A Mainframe computers are large-sized, powerful multi-user computers that can support concurrent programs. It can be used by as many as hundreds or thousands of users at the same time. Large organisations may use a mainframe computer to execute large-scale processes such as processing the organisation's payroll. It is designed to handle large volume of data and information and also has great processing speed as compare to the minicomputer. more...
Understanding Windows 10
Introduction
Microsoft windows is a Graphical User Interface operating system. If has features which guides the user to perform the specific task using the operating system. An operating system is a software component of a computer system that is responsible for the management of various activities of the computer and the sharing of computer resources. Generally, a computer uses two types of programs, application and system program users and application programs access the services offered by the operating -system, by means system calls and application programming interfaces. Users interact with a computer operating system though Command Line Interfaces (CLI) or Graphical User Interface (GUI). Some of the common operating systems are Linux, Windows etc.
Start menu
When click on the start button, start menu appears on the screen giving all the available options to start using the Windows. Overview of the options available in the start menu.
| ||