Sexual Reproduction
The method of reproduction, in which both male and female are involved, is called sexual reproduction. The male and female mate with each other, and their egg fertilized to produce the new offspring. Each of the two parents contributes half of the offspring genetic makeup by creating the haploid gametes. In these anisogamous species, the male produces sperm and female produces ova. In isogamous species, the gametes are similar, but they have separable properties. For example, the green algae, chlamydomonas, reinhardtii. There are many animals and plants, which reproduce sexually. The new offspring inherit the trait of both the parents. In plants, Bryophytes reproduces sexually; but they are normally haploid which produce gametes.

Allogamy
In this method, the ovum of one individual fertilized with the spermatoza of another individual.

Autogamy
It is also known as self fertilization, which occurs in hermaphrodite organisms. In this organisms, both the male and female sex are present in the same individual.

Mitosis and Meiosis
There are the two methods of cell division, mitosis and meiosis. The mitosis occurs in somatic cells, where as meiosis occurs in reproductive cell orgametes. In mitosis, the number of cell after the cell division is doubled, but the number of chromosomes remains the same as in the parent cell. In meiosis, the number of cell becomes four times, but the number of chromosomes is reduced to half. This process occurs in two phase, meiosis I and meiosis II.


There are different methods of cell division in the multicellular organisms, which helps in its growth and development. The method of cell division, which takes place in the reproductive cell for reproductions is?
(a) Mitosis
(b) Meiosis
(c) Prophase
(d) Anaphase
(e) None of these
Answer: (b)
Explanation
The cell division in the reproductive cell is by the method of meiosis and cell division in rest of the body parts is through mitosis.

Some organisms have both the sex, while, most of the other multicellular organisms have male and female on different organisms. The organisms, in which have both male and female sex are present is called hermaphrodite. Which one of the following organisms given below is hermaphrodite?
(a) Leach
(b) Earthworm
(c) Tapeworm
(d) Silkworm
(e) None of these
Answer: (b)

Asexual vs. Sexual Reproduction
The organisms, which reproduces sexually tend to grow exponentially in numbers, but rely on mutation for variations in DNA. They have similar vulnerabilities. The organisms that reproduce sexually, yield less
more...

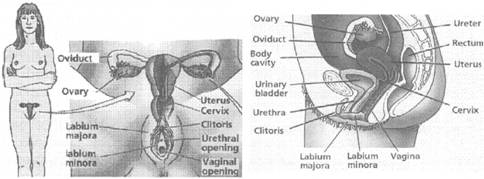
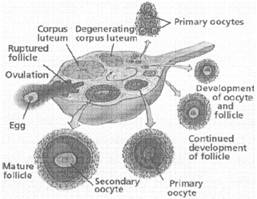 The Female Reproductive System
The Female Reproductive System

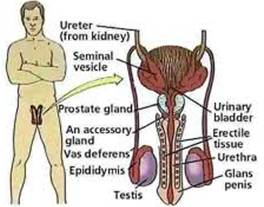
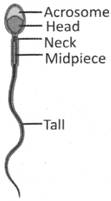
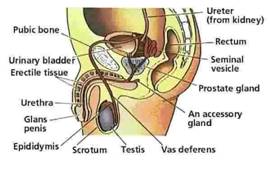 The Male Reproductive System
The Male Reproductive System

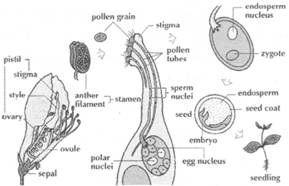
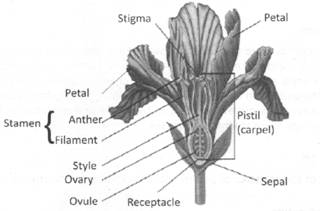 The reproductive part of the flowers
The reproductive part of the flowers
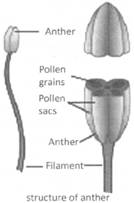
 more...
more... 



 Bryophyllum Tuber Potato
Bryophyllum Tuber Potato



 Multicellular Organism
Multicellular Organism