
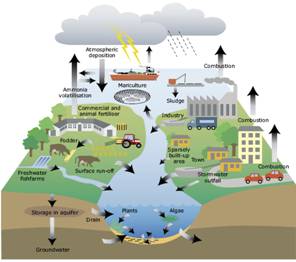
 The amount has not changed at all in the million year of earth's existence. There is plenty of water on our planet, but its distribution is not uniform. About 97.4% of the total water on the earth is present in oceans. Of the remaining 2.6%, only is in liquid form, the rest is frozen in polar caps and glaciers like those of the HIMALAYAS. If the surface of India were flat, and all the ice was packed on the surface of India, it would reach an incredible height of 9 km . thus, only 0.01% of the total water on the earth, which is available freshwater, is used by us and other living beings. The water in the oceans is so salty that it cannot be used for most purposes.
The amount has not changed at all in the million year of earth's existence. There is plenty of water on our planet, but its distribution is not uniform. About 97.4% of the total water on the earth is present in oceans. Of the remaining 2.6%, only is in liquid form, the rest is frozen in polar caps and glaciers like those of the HIMALAYAS. If the surface of India were flat, and all the ice was packed on the surface of India, it would reach an incredible height of 9 km . thus, only 0.01% of the total water on the earth, which is available freshwater, is used by us and other living beings. The water in the oceans is so salty that it cannot be used for most purposes.



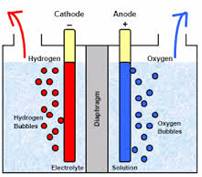 Electroplating: The process of covering a more reactive metal with a less reactive metal with the help of electricity is known as electroplating. Material to be plated should be connected as cathode while anode usually loses material.
Electroplating: The process of covering a more reactive metal with a less reactive metal with the help of electricity is known as electroplating. Material to be plated should be connected as cathode while anode usually loses material.
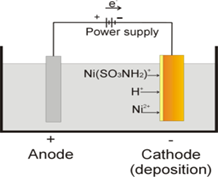
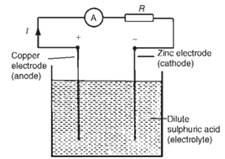
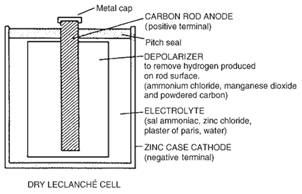 There are more dry cell technologies that enables to remain EMF constant for longer times. Ones are Mercury cells. These cells provide 1.3V for longer time than Lechlanche cells.
There are more dry cell technologies that enables to remain EMF constant for longer times. Ones are Mercury cells. These cells provide 1.3V for longer time than Lechlanche cells.
 Substances that do not allow electric current to flow through them are called insulators, nonconductors, or dielectrics. Rubber, glass, and air are common insulators. Electricians wear rubber gloves so that electric current will not pass from electrical equipment to their bodies. However, if an object contains a sufficient amount of charge, the charge can arc, or jump, through an insulator to another object. For example, if you shuffle across a wool rug and then hold your finger very close to, but not in contact with, a metal doorknob or radiator, current will arc through the air from your finger to the doorknob or radiator, even though air is an insulator. In the dark/ the passage of the current through the air is visible as a tiny spark.
Substances that do not allow electric current to flow through them are called insulators, nonconductors, or dielectrics. Rubber, glass, and air are common insulators. Electricians wear rubber gloves so that electric current will not pass from electrical equipment to their bodies. However, if an object contains a sufficient amount of charge, the charge can arc, or jump, through an insulator to another object. For example, if you shuffle across a wool rug and then hold your finger very close to, but not in contact with, a metal doorknob or radiator, current will arc through the air from your finger to the doorknob or radiator, even though air is an insulator. In the dark/ the passage of the current through the air is visible as a tiny spark.

You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
