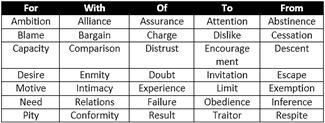
 The following adjectives always take the prepositions: 'to', 'in', 'with', 'of, 'for', respectively.
The following adjectives always take the prepositions: 'to', 'in', 'with', 'of, 'for', respectively.
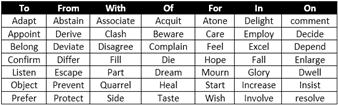
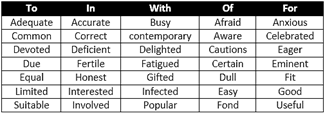 The following verbs always take the prepositions: ?to?, ?from?, ?with?, ?of?, ?for?, ?in?, ?on? respectively.
The following verbs always take the prepositions: ?to?, ?from?, ?with?, ?of?, ?for?, ?in?, ?on? respectively.
 PLAY TIME (DUMB CHARADES)
Your teacher will create slips of paper with prepositions written on them and mix them up in a hat or other container. Each of you will come up and pick a slip from the hat. You will then attempt to convey the meaning of the preposition through actions and gestures without using any words. Teacher may split the class into teams and award more...
PLAY TIME (DUMB CHARADES)
Your teacher will create slips of paper with prepositions written on them and mix them up in a hat or other container. Each of you will come up and pick a slip from the hat. You will then attempt to convey the meaning of the preposition through actions and gestures without using any words. Teacher may split the class into teams and award more...  BOY SAT (with) BEN
But
Or
So
And
Then
Both..... and
Either......or
Neither......nor
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
This lesson will help you to:
BOY SAT (with) BEN
But
Or
So
And
Then
Both..... and
Either......or
Neither......nor
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
This lesson will help you to:
 There are conjunctions that join independent sentences and are called Coordinating Conjunctions. They connect similar kind or group of words. Some of them are:
And
There are conjunctions that join independent sentences and are called Coordinating Conjunctions. They connect similar kind or group of words. Some of them are:
And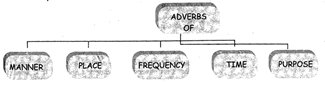 KINDS OF ADVERBS
Adverbs of Manner She moved slowly and spoke quietly. Adverb of Place She has lived on the island all her life. She still lives there now. Adverbs of Frequency She takes the boat to the mainland every day. She often goes by herself. Adverbs of Time She tries to get back before dark. It?s starting to get dark now. She finished her tea first. She left early.
Misconcept/ Concept
Misconcept: an adverb says more about (modifies) a verb.
Concept: Although adverbs do indeed modify verbs, they can also modify an adjective, another adverb, a pronoun, or a noun more...
KINDS OF ADVERBS
Adverbs of Manner She moved slowly and spoke quietly. Adverb of Place She has lived on the island all her life. She still lives there now. Adverbs of Frequency She takes the boat to the mainland every day. She often goes by herself. Adverbs of Time She tries to get back before dark. It?s starting to get dark now. She finished her tea first. She left early.
Misconcept/ Concept
Misconcept: an adverb says more about (modifies) a verb.
Concept: Although adverbs do indeed modify verbs, they can also modify an adjective, another adverb, a pronoun, or a noun more... 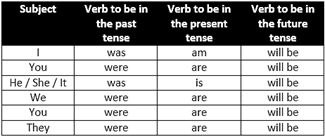 LOTS OF VERB EXPRESS PHYSICAL ACTIONS
Here are some sentences with the verbs highlighted. (These verbs express physical actions.) Examples:
She sell leather bags. (In this example, the word sells is a verb. It express the physical activity to sell.)
The doctor wrote the prescription. (In this example, the word wrote is a verb. It expresses the physical activity to write.)
Alison bought a ticket. (The word bought is a verb. It expresses the physical activity to buy.)
VERBS EXPRESS MENTAL ACTIONS TOO
As discussed in the beginning, verbs not only express physical actions like the ones above, they can express mental actions too: Examples:
She considers the job done. (The word considers is a verb. It expresses the mental activity to consider.)
Peter guessed the right number. (The word guessed is a verb. It expresses the mental activity to guess.)
I thought the same thing. (The word thought is a verb. It express the mental activity to think.)
VERBS EXPRESS A STATE OF BEING
A small, but extremely important, group of verbs do not express any activity at all. The most important verb in this group- arguably of all- is the verb to be. As already mentioned, this is seen in forms like are, were, was, will be, etc.
Examples:
Edwina is the largest elephant in this area. (The word 'is' is a verb from the verb to be.)
It was a joke. (The word was is a verb from the verb to be.)
I am. (The word am is a verb from the verb to be.) (Point of interest: I am is the shortest sentence in English.)
Real - Life Example
Modal verbs, to you, means building upon the knowledge you already have. While most of you are able to explain what most verbs do, such as convey action, movement or behaviour, modal verbs might seem more mysterious. Modal verbs which conveys an attitude or mood. They include can, could, will, would, may, might, must, shall, should and ought. Modal verbs more...
LOTS OF VERB EXPRESS PHYSICAL ACTIONS
Here are some sentences with the verbs highlighted. (These verbs express physical actions.) Examples:
She sell leather bags. (In this example, the word sells is a verb. It express the physical activity to sell.)
The doctor wrote the prescription. (In this example, the word wrote is a verb. It expresses the physical activity to write.)
Alison bought a ticket. (The word bought is a verb. It expresses the physical activity to buy.)
VERBS EXPRESS MENTAL ACTIONS TOO
As discussed in the beginning, verbs not only express physical actions like the ones above, they can express mental actions too: Examples:
She considers the job done. (The word considers is a verb. It expresses the mental activity to consider.)
Peter guessed the right number. (The word guessed is a verb. It expresses the mental activity to guess.)
I thought the same thing. (The word thought is a verb. It express the mental activity to think.)
VERBS EXPRESS A STATE OF BEING
A small, but extremely important, group of verbs do not express any activity at all. The most important verb in this group- arguably of all- is the verb to be. As already mentioned, this is seen in forms like are, were, was, will be, etc.
Examples:
Edwina is the largest elephant in this area. (The word 'is' is a verb from the verb to be.)
It was a joke. (The word was is a verb from the verb to be.)
I am. (The word am is a verb from the verb to be.) (Point of interest: I am is the shortest sentence in English.)
Real - Life Example
Modal verbs, to you, means building upon the knowledge you already have. While most of you are able to explain what most verbs do, such as convey action, movement or behaviour, modal verbs might seem more mysterious. Modal verbs which conveys an attitude or mood. They include can, could, will, would, may, might, must, shall, should and ought. Modal verbs more...  KINDS OF PRONOUN
1. Personal Pronoun: Example:- I ate a chocolate. You ate chocolate. Mrs Roy is shouting. She is angry. Mr Khan is running. He is in a hurry. We were frightened to hear the thunder. They are laughing, at the clown. Here ?I, WE, YOU, HE, SHE, IT, THEY,? are called Personal Pronouns because they stand for the three persons; (i) the person speaking ---?I?, ?we?, denote the first person, (ii) the person spoken to--- ?you? denotes the second person and (iii) the person spoken of--- ?he, she, it, they? denote the third person.
2. Relative Pronoun: I met Suman yesterday who had returned from London. He found the pen, which he thought he had lost. Here is the book that you had lent me. Here the pronouns ?who?, ?which? and ?that? are relating or connecting to the nouns ?Suman?, ?pen? and ?book? respectively. These are called Relative Pronoun.
3. Demonstrative Pronoun: Example:- This is a gift from my aunt. That was just an excuse. These are the places which I always wanted to visit. Bombay mangoes are better than those of Bangalore. Here the pronouns point to the objects to which they refer. These are Demonstrative Pronouns and show clearly or demonstrative Pronouns and show clearly or demonstrate what they are referring to.
4. Reflexive Pronoun: Example:- I tried to do it myself. You should try to do it yourself. We were very ashamed of ourselves. The students were asked to behave themselves. The action here is turning or reflecting back( reflects) to the person who is performing the action. It is a Reflexive Pronoun.
5. Emphatic Pronoun: Example:- I myself saw her singing at her work. You yourself can answer best. They themselves took part in the show. The city itself fell. In more...
KINDS OF PRONOUN
1. Personal Pronoun: Example:- I ate a chocolate. You ate chocolate. Mrs Roy is shouting. She is angry. Mr Khan is running. He is in a hurry. We were frightened to hear the thunder. They are laughing, at the clown. Here ?I, WE, YOU, HE, SHE, IT, THEY,? are called Personal Pronouns because they stand for the three persons; (i) the person speaking ---?I?, ?we?, denote the first person, (ii) the person spoken to--- ?you? denotes the second person and (iii) the person spoken of--- ?he, she, it, they? denote the third person.
2. Relative Pronoun: I met Suman yesterday who had returned from London. He found the pen, which he thought he had lost. Here is the book that you had lent me. Here the pronouns ?who?, ?which? and ?that? are relating or connecting to the nouns ?Suman?, ?pen? and ?book? respectively. These are called Relative Pronoun.
3. Demonstrative Pronoun: Example:- This is a gift from my aunt. That was just an excuse. These are the places which I always wanted to visit. Bombay mangoes are better than those of Bangalore. Here the pronouns point to the objects to which they refer. These are Demonstrative Pronouns and show clearly or demonstrative Pronouns and show clearly or demonstrate what they are referring to.
4. Reflexive Pronoun: Example:- I tried to do it myself. You should try to do it yourself. We were very ashamed of ourselves. The students were asked to behave themselves. The action here is turning or reflecting back( reflects) to the person who is performing the action. It is a Reflexive Pronoun.
5. Emphatic Pronoun: Example:- I myself saw her singing at her work. You yourself can answer best. They themselves took part in the show. The city itself fell. In more...  1. An umbrella saves us from the scorching heat of the sun and heavy rains.
(C) COLLECTIVE NOUN
1. An umbrella saves us from the scorching heat of the sun and heavy rains.
(C) COLLECTIVE NOUN
 1. Bee hive is reared in large scale production of honey.
(D) MATERIAL NOUN
1. Bee hive is reared in large scale production of honey.
(D) MATERIAL NOUN
 1. Petrol is very precious as it speeds up our mobility from one place to another.
(E) ABSTRACT NOUN
1. Petrol is very precious as it speeds up our mobility from one place to another.
(E) ABSTRACT NOUN
 1. Laughter is the best medicine in a stressful situation.
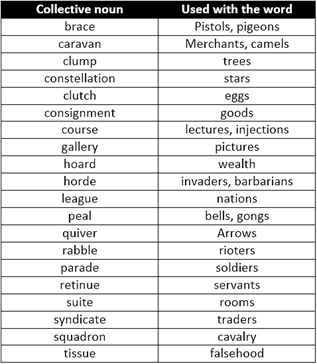
A. Words Showing Collection
1. Laughter is the best medicine in a stressful situation.
A. Words Showing Collection
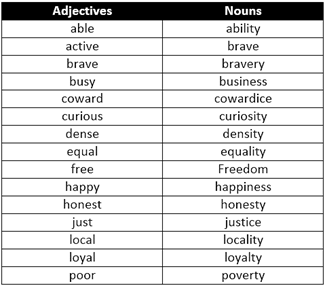
 B. Formation of Nouns from Adjectives
B. Formation of Nouns from Adjectives
 Misconcept / Concept
Misconcept: Collective nouns are plural. more...
Misconcept / Concept
Misconcept: Collective nouns are plural. more... You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
