 QUICK CONCEPT REVIEW
An angle is a measure of a turn. It is measured in degrees (°). There are different types of angles:
Acute angle: If the measure of an angle is less than\[{{90}^{0}}\], then it is called an acute angle.
QUICK CONCEPT REVIEW
An angle is a measure of a turn. It is measured in degrees (°). There are different types of angles:
Acute angle: If the measure of an angle is less than\[{{90}^{0}}\], then it is called an acute angle.
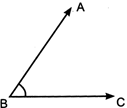 \[\angle ABC\] is an acute angle.
Right angle: If the measure of an angle is 90°, then it is called a right angle.
Amazing Facts
\[\angle ABC\] is an acute angle.
Right angle: If the measure of an angle is 90°, then it is called a right angle.
Amazing Facts
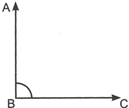 \[\angle ABC\] is a right angle.
Obtuse angle: If the measure of an angle is greater than\[{{90}^{0}}\], then it is called an obtuse angle.
\[\angle ABC\] is a right angle.
Obtuse angle: If the measure of an angle is greater than\[{{90}^{0}}\], then it is called an obtuse angle.
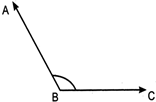 \[\angle ABC\]is an obtuse angle.
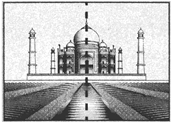
Symmetry is when one shape becomes exactly like another if it is rotated, reflected or translated.
\[\angle ABC\]is an obtuse angle.
Symmetry is when one shape becomes exactly like another if it is rotated, reflected or translated.
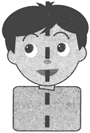 The vertical line in the figure above is called line of symmetry.
3D shapes have faces, edges and vertices. A net of a
3D shape is a figure which folds up to form a 3D shape.
For example:
The vertical line in the figure above is called line of symmetry.
3D shapes have faces, edges and vertices. A net of a
3D shape is a figure which folds up to form a 3D shape.
For example:
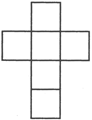
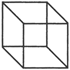 Net of a cube folds up to form a cube.
Net of a cube folds up to form a cube.
 Historical preview
Historical preview
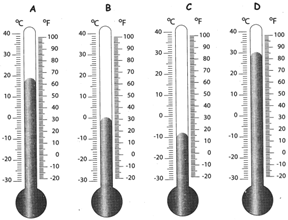 Temperature Conversion
By looking at the diagram, it can be seen that:
Temperature Conversion
By looking at the diagram, it can be seen that:
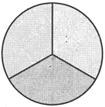 Part of a whole
Part of a whole
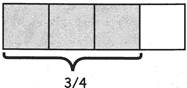 √ the top number (the numerator) says how many parts the whole is divided into.
√ the bottom number (the denominator) says how many you have.
Comparing fractions: Fractions are compared to see if one fraction is equal to (=), greater than (>) or smaller than (<) the other fraction.
√ the top number (the numerator) says how many parts the whole is divided into.
√ the bottom number (the denominator) says how many you have.
Comparing fractions: Fractions are compared to see if one fraction is equal to (=), greater than (>) or smaller than (<) the other fraction.
 The ratio of checkered ball: striped balls is 3:1.
Amazing Facts
The ratio of checkered ball: striped balls is 3:1.
Amazing Facts
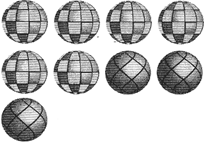 The ratio of checkered ball: striped balls is 9: 3 = 3:1, even thought there are more balls.
The ratio of checkered ball: striped balls is 9: 3 = 3:1, even thought there are more balls. 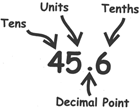
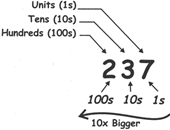
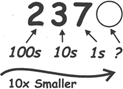
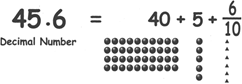 Place of a decimal: In a decimal number, position or "place" of each digit is important.
In the number 237,
Place of a decimal: In a decimal number, position or "place" of each digit is important.
In the number 237,
 "Two Hundred Thirty Seven"
(iv) As we move left, each position is 10 times bigger,
Hundreds are 10 times bigger than Tens.
"Two Hundred Thirty Seven"
(iv) As we move left, each position is 10 times bigger,
Hundreds are 10 times bigger than Tens.
 Expanded form of decimals
\[315.162=300+10+5+\frac{1}{10}+\frac{6}{100}+\frac{2}{1000}\]
(vi) Like more...
Expanded form of decimals
\[315.162=300+10+5+\frac{1}{10}+\frac{6}{100}+\frac{2}{1000}\]
(vi) Like more... 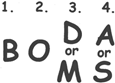
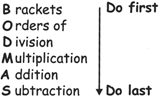 Steps to simplify the order of operation using BODMAS rule:
Steps to simplify the order of operation using BODMAS rule:


 This way also all the students were not fitting in the frame.
Then she made 4 lines of 5 each. Now all the students could fit in the frame.
This way also all the students were not fitting in the frame.
Then she made 4 lines of 5 each. Now all the students could fit in the frame.
 So here we saw three different ways to make 20 students stand in lines.
The first way is \[1\times 20\]
The second way is \[2\times 10\]
& the third way is \[5\times 4\]
Therefore, we can say that 1,20,2, 5 & 4 are the factors of 20.
Definition of factors: The factors of a number are thosewhich divide the number without leaving any remainder.
Thus, factors of a number divide the number completely,
Note: A number can have many factors.
So here we saw three different ways to make 20 students stand in lines.
The first way is \[1\times 20\]
The second way is \[2\times 10\]
& the third way is \[5\times 4\]
Therefore, we can say that 1,20,2, 5 & 4 are the factors of 20.
Definition of factors: The factors of a number are thosewhich divide the number without leaving any remainder.
Thus, factors of a number divide the number completely,
Note: A number can have many factors.
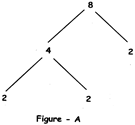 figure - A. Therefore, the factors of 8 are 2, 2 A 2.
Example 2: We can make factor trees of a same number 60 in different ways as shown in figures - B, C and D:
figure - A. Therefore, the factors of 8 are 2, 2 A 2.
Example 2: We can make factor trees of a same number 60 in different ways as shown in figures - B, C and D:
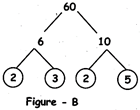 Fig.-B: This is a factor tree of 60. Here 60 has been broken into two factors 6 & 10. But 6 & 10 are not prime numbers. 6 & 10 are again broken into two factors each. 6 is broken in 2 & 3 more...
Fig.-B: This is a factor tree of 60. Here 60 has been broken into two factors 6 & 10. But 6 & 10 are not prime numbers. 6 & 10 are again broken into two factors each. 6 is broken in 2 & 3 more... | Symbol | Words Used |
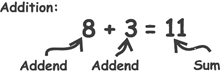
| + | Addition, Add, Sum, Plus, Increase, Total |
| - | Subtraction, Subtract, Minus, Less, Difference, Decrease, Take Away, Deduct |
| \[\times \] | Multiplication, Multiply, Product, By, Times, Lots of |
| \[\div \] | Division, Divide, Quotient, Goes Into, How Many Times |
 Properties for Addition
Properties for Addition
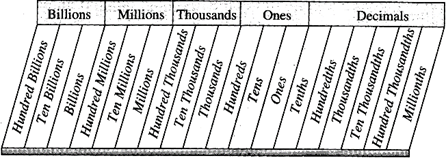 The concept of place value is as follows:
Beginning with the ones place at the right, each place value is multiplied by increasing powers of 10. For example, the value of the first place on the right is "one" the value of the place to the left of it is "ten," which is 10 times 1. The place to the left of the tens place is hundreds, which is 10 times 10, and so forth.
The place value of number goes beyond 1000 with the next place value being 10 times greater. The place values after thousand are ten thousands (10,000), hundred thousand (1,00,000), millions (10,00,000) and so on.
For easier readability, commas are used to separate each group of three digits, which is called a period. When a number is written in this form, it is said to be in "standard form" Example: four hundred sixteen thousand, seven hundred thirty-one can be written as 416,731.
The role of place value in addition, subtraction and multiplication algorithms.
The concept of place value is as follows:
Beginning with the ones place at the right, each place value is multiplied by increasing powers of 10. For example, the value of the first place on the right is "one" the value of the place to the left of it is "ten," which is 10 times 1. The place to the left of the tens place is hundreds, which is 10 times 10, and so forth.
The place value of number goes beyond 1000 with the next place value being 10 times greater. The place values after thousand are ten thousands (10,000), hundred thousand (1,00,000), millions (10,00,000) and so on.
For easier readability, commas are used to separate each group of three digits, which is called a period. When a number is written in this form, it is said to be in "standard form" Example: four hundred sixteen thousand, seven hundred thirty-one can be written as 416,731.
The role of place value in addition, subtraction and multiplication algorithms.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
