Category : 11th Class
![]()
(1) Cockroach belong to the class insecta of the phylum Arthropoda.
(2) Two species of cockroaches commonly found in India are? Periplaneta americana and Blatta orientalis. Periplaneta americana is the largest and most common species. The generic name periplaneta was given by Burmeister in 1838.
(3) Cockroaches are nocternal and cursorial (running). It is cosmopolitan in distribution, but cockroach are more abundant in warm, humid areas.
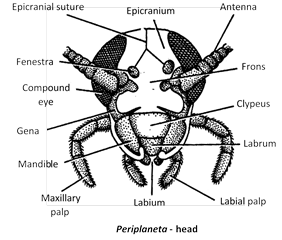
(4) Body is divided into head, thorax and abdomen. Head is derived by the fusion of six embryonic segments. The part of head between and behind the eyes is epicranium (vertex). The front of head capsule is made up of three unpaired flattened sclerites called frons, clypeus and labrum.
(5) The thorax consists of three segments-prothorax, mesothorax and metathorax. Thorax bears three pairs of jointed appendages and two pairs of wings on mesothorax and metathorax.
(6) Exoskeleton of each segment consists of four chitinous plates called sclerites. The dorsal sclerite is called tergum or tergite, ventral sclerite is sternum or sternite and two lateral sclerites are called pleura or pleurites. The dorsal plate of the thorax is called notum
(7) The antenna is made of many segments, podomeres. The first segment is scape (largest), second pedicel and rest many jointed flagellum. Antenna is a thigmoreceptor sensitive to touch.
(8) Mouthparts of cockroaches are mandibulate type or cutting and chewing type. Mouthparts consists of labrum (upper lip), labium (lower lip), maxillae (segmented and resemble to a leg), mandibles and hypopharynx (tongue).
(9) The main structures of mastication (chewing) are mandibles which are short with teeth.
(10) Maxilla consists of cardo, stipes, galea, lacinia and 5-segmented maxillary palp.
(11) Labium (= second maxilla) consists of submentum, mentum, prementum, palpiger, paraglossa, glossa and three jointed labial palp.
(12) Glossa and paraglossa are together called lingula. They push the masticated food into buccal cavity.
(13) A common salivary duct opens at the base of the hypopharynx.
(14) Each leg is formed by five segments, viz, coxa, trochanter, femur, tibia and tarsus (tarsus is made by five tarsomeres). Attached to the last tarsomere called pretarsus and it bears, a soft lobe called arolium or pulvilus and a pair of claws is present. They are helpful in moving on smooth surfaces. Plantulae are present on tarsus and act as thermoreceptors.
(15) The most swollen segment in the leg of cockroach is coxa. The longest segment in the leg of cockroach is tibia.
(16) In adult cockroach abdomen is made up of ten segments. But in embryonic stage eleven segments are present. The 11 segment of embryo is represented in adult by podical plates.
(17) In male cockroach, eighth and ninth terga are overlapped by seventh tergum. In female seventh, eighth and ninth sterna are fused to form a brood pouch. Seventh sternum of brood pouch forms a pair of gynavalvular plates.
(18) Anal cerci bear minute sensory hairs which are sensitive to sound and other vibrations.
(19) Anal cerci, a pair of many jointed structures are present on the tergite of 10th segment in both sexes.
(20) Anal styles, a pair of small, spine-like unjointed structures are present on sternite of 9th segment in males only.
(21) Cockroach has two pairs of wings. The first pair (mesothoracic) are thick, hard and leathery, protective in function called tegmina (= elytra). Second pair (metathoracic) are thin, soft and membranous.
(22) Cockroach does not fly, but the wings help in escaping from danger.
(23) Body wall of cockroach is made up of two layers, outer cuticle and inner hypodermis.
(24) Cuticle is invaginated forming endoskeletal elements like tentorium in head and apodemes in thorax. They provide sites for attachment of muscles. The cuticle has three distinct layers, outer primary cuticle or epicuticle, middle thick exocuticle and inner thick endocuticle.
(25) Hypodermis is a single layered epithelium. Some of its cells are modified into large oval trichogen cells concerned with secretion of movable bristles on the body of cockroach.
(26) The body cavity of cockroach is a haemocoel, filled with blood.
(27) The alimentary canal of cockroach is divisible into three parts, viz, foregut, midgut and hindgut.
(28) Foregut (stomodaeum) is differentiated into five parts - buccal chamber, pharynx, oesophagus, crop and gizzard. Gizzard is muscular and internally provided with six cuticular teeth which crush the food.
(29) Midgut (mesenteron or ventriculus) is short, tubular, lined with glandular endoderm. At anterior end of mesenteron there are eighth blind glandular hepatic caecae which secrete digestive enzymes. Internally mesenteron is not lined by cuticle but it is covered by a very thin and transparent peritrophic membrane formed of chitin and proteins.
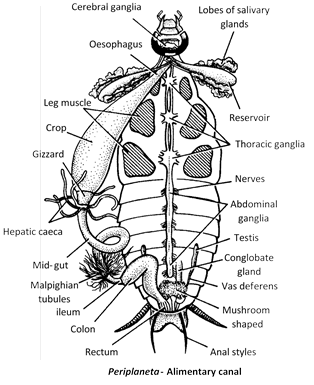
(30) A stomodaeal valve is present between gizzard and mesenteron.
(31) Hindgut (proctodaeum) comprises ileum, colon and rectum. The wall of rectum is provided with six rectal papillae, which help in the absorption of water and salts.
(32) At the junction of foregut and midgut seven or eight finger like structure are present called hepatic caecae.
(33) Cockroach is omnivorous, feeds on all sorts or organic debris. The digestive enzymes of saliva are mainly zymase and amylase. Most of the nutrients of food are digested in the crop Digested food is absorbed in the mesenteron and hepatic caecae.
(34) Circulatory system in cockroach is of open type or lacunar type. In this type blood is always in direct contact with tissues. The blood flow through haemocoelic system.
(35) The heart is situated in pericardial sinus over the dorsal diaphragm.
(36) Heart of cockroach is neurogenic and longitudinaly beaded with 13 chambers perforated by ostia having valves.
(37) The blood circulation is maintained by 13 pairs of wing-shaped involuntary alary muscles.
(38) Blood (or haemolymph) is colourless due to the absence of respiratory pigment. Hence it does not take part in respiration. Blood is composed of plasma and colourless blood cells called haemocytes.
(39) In cockroach oxygen is carried to individual cell without participation of blood. All body tissue receive oxygen directly.
(40) Respiratory system of cockroach consists of tracheal system. The tracheal system opens outside by ten pairs of spiracles (two pairs thoracic and eight pairs of abdominal. The spiracles are with valves.
(41) The first thoracic and first abdominal spiracles remain open all the times. The trachea is lined with spiral thickening of cuticle called intima which prevents the tracheal tubes from collapsing.
(42) Excretory organs of cockroach are Malpighian tubules open at the junction of midgut and hindgut (ileum).
(43) Malpighian tubules absorb excretory substances from haemolymph and fat bodies and pass into the proctodaeum.
(44) In cockroach chief excretory product is uric acid (uricotelism).
(45) Fat body of cockroach contains mainly four types of cells. viz., trophocytes, mycetocytes, oenocytes and urate cells. The fat body is functionally analogous to liver of vertebrates. Mycetocytes contain symbiotic bacteria which help in synthesis of some amino acids, vitamins and of glycogen from glucose.
(46) Nervous system of cockroach consists of a nerve ring (in the head) and a double ventral nerve cord. The total number of ganglia in ventral nerve cord of cockroach is nine (Three thorasis and six abdominal).
(47) Sense organs in cockroach are ? Photoreceptors (compound and simple eyes), thigmoreceptors (antennae), chemoreceptors (on maxillary and labial palps, labium and hypopharynx) and auditory receptors on anal cerci.
(48) Each compound eye is made up of about 2000 functional units called ommatidia.
(49) Each ommatidium is composed of a cuticular lens, two corneagen cells, a crystalline cone surrounded by four cone cells, a rhabdome surrounded by seven retinular cells and a basement membrane.
(50) There are two types of vision in insects, mosaic vision or apposition image during day time and superposition or dull image in dim light.
(51) The vision in cockroach is called mosaic vision because in cockroach, pigment sheath of ommatidia is non-contractile so capable of only mosaic vision even during night.
(52) Simple eye of cockroach is mainly concerned with light collecting rather than image forming.
(53) In cockroach the endocrine organs are cardiac, corpora allata and prothoracic glands.
(54) Corpora cardica and corpora allata are attached to the brain. Corpora allata is neurosecretory and secretes juvenile hormone or neotinin.
(55) Intercerebral glands in brain secrete the brain hormone. Brain hormone stimulates the prothoracic glands to secrete a moulting hormone called ecdysone.
(56) In cockroach, sexes are separate, so dioecious or unisexual animal.
(57) Male organs consist of testes, vasa deferentia, ejaculatory duct, mushroom or utricular gland, phallic or conglobate gland and male gonaphophysis.
(58) Testes of cockroach are located in the abdominal segments 4, 5 and 6. They produce sperms.
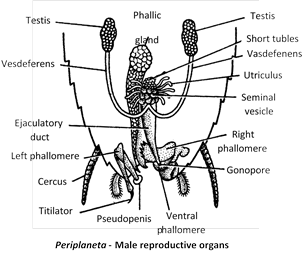
(59) All sperms of a seminal vesicle are glued together into a large bundle called spermatophore. Spermatophore has three-layered wall. Inner layer secreted by utriculi majores; middle layer secreted by ejaculatory duct and outer layer secreted by phallic gland.
(60) There are three asymmetrical chitinous structures called male gonapophyses or phallomeres. Right phallomere has serrated edges and a hook; left phallomere has an asperate lobe, pseudopenis and a hooked titillator and ventral phallomere is simple.
(61) Female organs consist of ovaries, oviducts, vagina, genital chamber, spermathecae, colleterial glands and female gonapophysis (ovipositor processes). Ovaries of cockroach are located in the abdominal segments 2 to 6. Each ovary is made up of eight ovarioles.
(62) Oviducts fuse to form a common oviduct or vagina. It opens into gynatrium. Gynatrium opens out through female gonopore.
(63) Collaterial glands are opens into gynatrium through a common pore. Left collecterial gland secrete HCI and scleroprotein and right gland secrete hydroxy phenol. Ootheca of cockroach is formed of a protein secreted by collaterial glands.
(64) A pair of spermathecae (left larger pyriform sac) are present near female genital pore. They store spermatophores received during copulation.
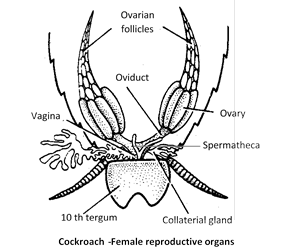
(65) Near the female gonopore three pairs of gonapophyses are present. They are helpful in copulation and in oviposition.
(66) Ootheca of cockroach contains 16 fertilized eggs in two rows (8 + 8). The egg of cockroach is centrolecithal type.
(67) Nymph of cockroach emerges out from ootheca.
(68) Metamorphosis in cockroach is incomplete or paurometabolous type. Metamorphosis is regulated by two hormones, ecdysone secreted by prothoracic glands and juvenile hormone secreted by corpora allata.
![]()
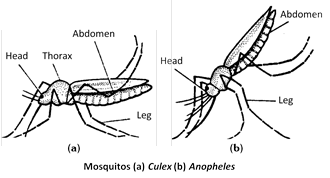
(1) Mosquito are inhabitants of damp and marshy places.
(2) The common genera of mosquito are -
Culex (body held parallel to surface while sitting),
Aedes (= Stegomyia) (body held parallel to surface while sitting, with black and white striped body),
Anopheles (Body held at an angle to the surface, dark spotted wing).
(3) The body of mosquito is divided into head, thorax and abdomen. Head bears a pair of antennae, compound eyes and mouth parts.
(4) In adult mosquito, ocelli (simple eyes) are totally absent (in cockroach and housefly, ocelli are present).
(5) Thorax is three-segmented with only one pair of wings (mesothoracic). Metathoracic wings are modified into halteres which are balancing and sound producing structures.
(6) Mosquito shows sexual dimorphism. Sex differentiation can be done on the basis of antennae and maxillary palps. Antenna of a male mosquito is plumose (more hairy or brushy) and female is pilose (with few short hairs).
(7) Female mosquitoes are blood suckers. They have piercing and sucking mouthparts. Males feed on nectar and have only sucking mouthparts.
(8) Mouthparts found in both sexes are ? Labrum, epipharynx forming upper lip and labium and proboscis.
(9) The puncturing elements in the mouthparts of female mosquito are maxillae and mandibles.
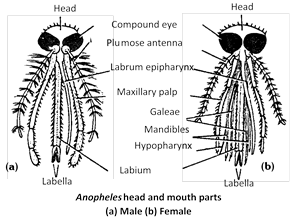
(10) Mandible are totally absent in male mosquito.
(11) Male and female mosquito copulate while in flight. The eggs are laid by the female in clusters on stagnant water of ponds, ditches, tanks, pools marshy places etc. The eggs developed and from each a small transparent larva called wriggler comes out into the water.
(12) Wriggler is a free swimming, active and aquatic larva performing wriggling movements. The body has head, thorax (without legs) and abdomen (9-segmented). Head bears a pair of compound eyes, a pair of simple eyes (absent in adult mosquito), a pair of small antennae.
(13) Wriggler has a lifespan of 3-4 days. During this period it undergoes four moults to give rise to five instar larva.
(14) 5th instar larva changes into a pupa (nonfeeding), it is comma-shaped. The pupa of mosquito is known as tumbler. It has a pair of respiratory trumpets.
(15) After completion of metamorphosis (complete metamorphosis), it will transform into an adult called 'Imago'.
(16) Johnston's organ lies in the second segment of antennae. In male mosquito, it helps to locate females by flight tone.
(17) Spraying of oil on stagnant water controls malaria because mosquito larvae cannot breath and die.
(18) Fish which can be used in biological control of mosquitoes is Gambusia.
![]()
(1) Housefly belong to the class insecta of the phylum Arthropoda. Musca domestica is the most common housefly in Europe and America. The common Indian species in musca nebulo.
(2) The body of housefly is divided into head, thorax and adbomen.
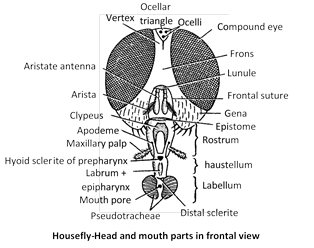
(3) Head is large with a pair of compound eyes, each made up about 4000 ommatidia, three ocelli and two antennae.
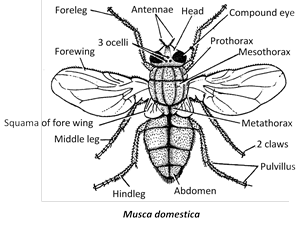
(4) Thorax is three segmented with three pair of legs, one pair of wings (mesothoracic) and a pair of halteres. The halteres are present on metathorax and they are balancing organs during flight and also receive sound stimuli.
(5) Housefly differs from mosquito in having hindlegs resting on surface while sitting.
(6) The mouth parts of the common housefly are sponging type which are adapted for sucking liquid or semiliquid.
(7) Labium is the most developed part of mouthparts forming the proboscis. The proboscis consists of three region - Rostrum, Haustellum, Labellum.
(8) Oral groove is found on haustellum cantaining blade-like hypopharynx and flattened labrum and epipharynx.
(9) Pseudotracheae are found in labellum.
(10) In the mouth parts of housefly, mandibles are totally absent.
(11) House flies are saprophagus, feed upon all shorts of dead organic matter.
(12) The breeding season of housefly lasts from march to october (summer and rainy season).
(13) Housefly lays eggs on decaying organic matter such as cow dung, horse manure, human faeces etc.
(14) A larval stage occurs in housefly that lives in dung and is called maggot. This larva undergoes moulting twice. The period in between two moults is known as stadium while the form of larva are called instar. Thus there are two moult and three instars.
(15) The first instar has only one pair of posterior abdominal spiracles. So it is metapneustic.
(16) The second instar larva of housefly has one pair of abdominal and one pair of prothoracic spiracles. So it is amphipneustic.
(17) Different stages in the life history of housefly are - Egg ® Larva (maggot) ® pupa ® Imago (adult).
(18) Larva of housefly respires by means of tracheae.
(19) An imago (young one of housefly) will come out after 4-5 days.
(20) Housefly shows a complete metamorphosis (holometabolous type).
Common Names
|
Limulus - King carb Palamnaeus - Scorpion Lycosa - Spider Astacus - Crayfish Daphnia - Waterflea Palaemon - Freshwater prawn Palinurus - Lobster Lucifer - Shrimp Carcinus - Crab Eupagurus - Hermit crab Balanus - Rock barnacle Julus - Millipede Scolopendra - Centipede Lepisma - Silverfish Carasius - Stick insect Phyllium - Leaf insect Pediculus - Louse Cimex - Bedbug Xenopsylla - Rat flea Drosophila - Fruitfly Musca - Housefly Phlebotomus - Sandfly Glossina - Testse fly Bombyx - Silkmoth |
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
