Results on Area of Quadrilateral
Category : 9th Class
(i) Any diagonal of a parallelogram divides it into two triangles of equal area.
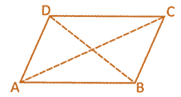
In the above given figure,
\[\text{ar(}\Delta \text{ABC})=\text{ar}(\Delta \text{ACD)}\]
Similarly
\[\text{ar(}\Delta \text{ABD})=\text{ar}(\Delta \text{BCD)}\]
(ii) Parallelograms which are on the same base and between the same parallel lines are equal in area.
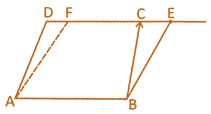
In the above given figure,
\[ar(l{{l}^{gm}}ABCD)=ar(l{{l}^{gm}}ABEF)\]
(iii) Triangles which are on the same base and between the same parallel lines are equal in area.
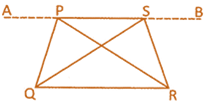
In the above given figure \[QR|\,\,|AB\]
Then \[~\text{ar(}\Delta \text{PQR)}=\text{ar(}\Delta \text{QRS)}\]
(iv) Area of trapezium= \[\frac{1}{2}\] (sum of parallel sides) \[\times \] (distance between them)

![]()

![]() In the figure given below shows a pentagon in which TU drawn parallel to SP meet at QP produced at U and RV parallel to SQ, meet PQ produced at V then:
In the figure given below shows a pentagon in which TU drawn parallel to SP meet at QP produced at U and RV parallel to SQ, meet PQ produced at V then:
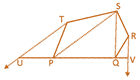
(a) ar(pentagon PQRST) \[=\text{ar(}\Delta \text{STU)}+\text{ar(}\Delta \text{QRV)}\]
(b) ar(pentagon PQRST) \[~=\text{ar(}\Delta \text{SUV)}\]
(c) ar(pentagon PQRST) \[~=\text{ar(}\Delta \text{SUV)}+\text{ar(}\Delta \text{TUP)}\]
(d) ar(pentagon PQRST) \[=\text{ar}(\Delta \text{SUV})+\text{ar(}\Delta \text{QRV)}\]
(e) None of these
Answer: (b)
Explanation:
Since \[RV|\,|SQ\] \[\Rightarrow \] \[~\text{ar(}\Delta \text{SPT)}=\text{ar}(\Delta \text{TUP)}\]
\[\text{ar(}\Delta \text{SQR)}+\text{ar(}\Delta \text{SPT)}+\text{ar(}\Delta \text{SPQ)}=\text{ar(}\Delta \text{SRV)}+\]\[\text{ar(}\Delta \text{SUP)}+\text{ar(}\Delta \text{BPQ)}\]
\[\Rightarrow \] \[\text{ar(pentagon PQRST)}=\text{ar(}\Delta \text{SUV)}\]
![]() In a trapezium non-parallel sides are equal. When we join the midpoint of diagonals and parallel sides a quadrilateral is formed, the quadrilateral formed is.....
In a trapezium non-parallel sides are equal. When we join the midpoint of diagonals and parallel sides a quadrilateral is formed, the quadrilateral formed is.....
(a) Rhombus
(b) Rectangle
(c) Trapezium
(d) Square
(e) None of these
Answer: (b)
![]() For a trapezium which one of the following statements is correct?
For a trapezium which one of the following statements is correct?
(a) Adjacent sides are parallel
(b) Vertically opposite sides are parallel
(c) The line joining the mid points of the diagonal is parallel to the parallel side and equal to half their differences
(d) The line joining the mid points of the diagonal is parallel to the parallel side and equal to their differences
(e) None of these
Answer: (b)
![]() If the length of the diagonals of rhombus are 30 cm and 16 cm respectively then the perimeter of rhombus is_____.
If the length of the diagonals of rhombus are 30 cm and 16 cm respectively then the perimeter of rhombus is_____.
(a) 17cm
(b) 69cm
(c) 63cm
(d) 68cm
(e) None of these
Answer: (d)
![]() In the adjoining figures which have equal value of angle\[x\]? [Every quadrilateral is rhombus]
In the adjoining figures which have equal value of angle\[x\]? [Every quadrilateral is rhombus]
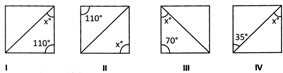
(a) I and II
(b) II and III
(c) III and IV
(d) I and IV
(e) None of these
Answer: (d)
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
