Category : Teaching
Animals
In our surrounding, we find different type of animals ranging from mammals, reptiles, birds, amphibian, insects and many other smaller forms.
Animals may live on land or in water or fly in air depending upon its ability and nature,
Scientists divide animals into groups, depending upon how they are alike and different.
Six common groups of animals are
1. Fishes 2. Amphibians
3. Reptiles 4. Insects
5. Birds 6. Mammals
3.1 Habitat of Animals
A habitat is a place where living things live and they survive in that area. Animals have basic needs; air, water, food, shelter and space.
Animals live in habitats all over where they are adapted most. Grasslands, rivers, ponds, trees, forests, deserts and Arctic tundra are used as habitat of animals.
Habitat of the animal can also be classified as follow
Land Animals reside on the land and trees, e.g. mammals, birds, reptiles etc.,
Water Animals reside in the water or water body. e.g. fishes, insects, crabs, sponges, snakes etc.
Land and Water Animals which resides and are able to reside in both land and water is called amphibian, e.g. frog, tortoise, snakes, crocodile etc.
Animals of Air Habitat Birds and insects.
3.2 Classification of Animals
Animals are mostly multicellular organism present in kingdom Animalia or Metazoa.
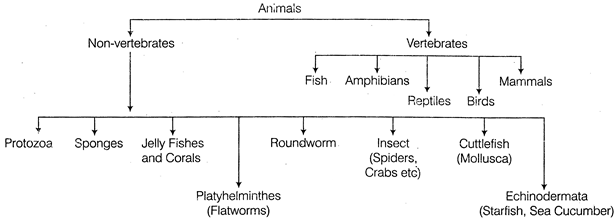
Classification Based on Body Structure
Animals are categorised on the presence of vertebral column into vertebrates
(i) Vertebrates animal having vertebral column/backbone e.g. Mammals, birds, fish, reptiles and amphibian are included in the category of vertebrates,
(ii) Non-vertebrates i.e. absence of vertebrates/back bone e.g. insects, crabs, snails, starfish are examples of invertebrates.
Classification Based on Nutrition
Autotrophs These are organisms that produces complex organic compounds (carbohydrates) from carbon dioxide and water present in atmosphere with the help of chlorophyll and sunlight.
Heterotrophs These are those organisms that cannot produce their own food but depend upon plants and other organisms to survive.
Classification Based on Cell
· Unicellular organisms have single cell and rely over only cell for life processes. These are also called single cell organism e.g. Amoeba, by Paramecium, Englena (they can be seen by micro scope).
· Multicellular organisms are organisms that consist of more than one cell, in contrast to unicellular organisms. All species of animals, land plants and most fungi are multicellular.
Classification Based on Reproduction
Viviparous Animals These are those animals which give birth to their live youngones zygote develop into youngones inside the ovary of the female body, so chances of survival of youngone is more due to proper embaryonic care and protection inside the mother's body e.g. whale, dolphins, dog, cat, human beings etc.
Oviparous Animals These lay fertilised or unfertilised eggs, after a period of incubation youngones hatch out.
Chances of survival of youngones is less because female lay eggs into the open environment, e.g. fishes; amphibians, reptiles all birds, most insects etc.
Classification Based on Habitat
These are those animals that live predominately or entirely on land.
Terrestrial Animals Terrestrial habitat types include forests, grasslands, wetlands and deserts, e.g. bear, cat, dog, deer, ants, snails etc.
Aquatic Animals Animals who can only live in water. It may be freshwater habitats include rivers, streams, lakes, ponds. Marine habitats include brackish water mashes, estuaries, bays, the open sea etc. e.g. fish; octopus; lobsters; seahorse.
Amphibians Animals who can live both on land and in water. They have moist, slimy and soft skin. They mainly live in moist places or close to water to keep their body from drying. A desert is not the kind of habitat that favours the presence of amphibians, with their requirement for water to keep their skins moist and for the development of their young, e.g. frogs, toads, salamanders.
Arboreal Animals Animals who 'live primarily on trees. They eat, sleep and play in the tree canopy. e.g. squirrel; chameleon; monkeys; various rodents; parrots etc.
Classification Based on Body Temperature
· Warm blooded animal are able to regulate the temperature of body. e.g. mammals and birds. But animals like reptiles, fishes, amphibians and insects are cold blooded animals as they are unable to regulate their body temperature.
· These animals show hibernation (winter sleep) and aestivation (summer sleep) e.g. fish, reptilia (frogs and lizard).
Classification Based on Food Habits
Animals also have different food habits.
On this basis, animals can also be classified into following categories
Carnivores Animals Which feeds on another animals or flesh, e.g. lion, tiger, shark, whale, eagle, vulture etc have sharp, pointed and curved front teeth. They also have strong grinding teeth in the back of their mouth.
Herbivores Animals Which feeds on plants and leafy materials, e.g. elephant, cow, rabbit etc. Herbivores have sharp, flat and broad front teeth. They have sharp front teeth to pluck and bite leaves of plants.
These animals also have strong and flat back teeth to chew the food.
Omnivores Animals Which feeds on both plants and flesh, e.g. dog, cat, hen, mynah, bear etc.
Decomposers It is break down dead decaying organisms. Decomposer help in forming humus layer of the soil. They are heterotrophic in nature.
A vulture is a large bird, eats the flesh of dead animals.
3.3 Relationships between Organisms
Different organisms have relationship with others organisms, where one organism benefits from the other without affecting it. Such type of relationships are explained below
Commensalism
In this type of relationship, one organism benefited from a relationship and other one is neutral i.e. not harmed or benefited, e.g. Egret bird and grazing cattle in close association, orchids growing as an epiphyte on a mango branch and barnacles growing on whale back.
Mutualism/Symbiosis
In this relationship, both organisms benefit from each other, e.g. Lichens represent an symbiotic relationship between fungus any photosynthesising algae or cyanobacteria. Mycorrizae are symbiotic relation of fungi and roots of higher plant.
Parasitism
In this type of relationship, one species benefits and other organism is harmed, e.g. human liver fluke, malaria parasite, lice on human.
Predation
It is when one organism eats another organism to obtain nutrients. One organism is prey that is eaten.
In this relationship and other one is predator e.g. pitcher plant.
Competition
In this relationship, organisms compete for same resource e.g. flamingoes and fishes compete for zooplankton in the lake.
3.4 Respiration in Animals
Respiration is the process by which animals take in oxygen and exchange it for carbon dioxide and water as waste products.
Animals need oxygen and energy to survive. Human and territorial mammals, birds, reptiles breath with the help of lungs.
Fishes and amphibians breath with the gills.
Earthworm breath with the help of moist skin.
Various other micro-organism, animals breathe through specific pore, opening or through body surface.
|
Animals |
Respiratory Organ |
|
Frog |
Lung and Skin |
|
Earthworm |
Skin |
|
Flies |
Haikia |
|
Human, Lion, Snakes, Birds |
Lungs |
|
Octopus, Fish |
Gills |
|
Whale, Dolphin |
Lungs, Nose |
3.5 Reproduction in Animals
On the basis of reproduction, animals are of two types
1. Oviparous Animals Which lays eggs, e.g. birds, reptiles, amphibian, fish etc.
2. Viviparous Animals Which give birth to their
youngones e.g. mammals.
There are two kinds of fertilisation in animals
1. External Fertilisation Fertilisation of ovum and sperm outside body of females, e.g. fish, frog etc.
2. Internal Fertilisation Fertilisation of ovum and sperm inside the body of females, e.g. reptiles, mammals, birds etc.
Development of embryo after the fertilisation will occur inside female body if animals is viviparous otherwise embryo will develop outside. Most of the viviparous animal have mammary glands, hair on the skin and visible ears.
3.6 Locomotion in Animals
Different animals have different structure to facilitate the locomotion. Animals translocate from one place to another in search of safety, shelter, food and mate. Mammals usually move with the help of legs, fish uses fins to swim from one place to another, birds flies with the help of wings to reach one place to another.
Reptiles either have legs to move or it crawls with the help of body surface. Frog has webbed feet to move, penguin uses its flippers to move and insects have many legs to move.
Description of some animals are as follow
1. Pedestal Animals These animals walk as 1 locomotive action e.g. human, lion, dog, cat, cow etc.
2. Creeping Animals These animals move by creeping e.g. snakes, worms caterpillars, earthworms. Snake move with the help of muscles and their scales. Earthworm move with the help of bristle by repeated contractions and relaxations of their muscles in the skin.
3. Flying Animals Aves are the flying animals.
Animals have very light weight as the adaptation for flight. Ostrich and emu are non- flight animals, they run instead of flying.
Owl can almost fully rotate their heads because its has fixed eye sockets, i. e. their eyeballs cannot rotate.
4. Swimming Animals Fishes, frogs are swimming animals, swan and ducks are also prefer to swim.
Frogs are leaping animal.
3.7 Sense Organs and Stimulation in Animals
There are 5 senses in animals in the Earth. These are; syes, ears, nose, tongue and skin. These sense organs help in performing various activities.
These activities are as follow
· Some special birds like kites, eagles and vultures
· can see things four time more than humans so that they can recognise their prey from the distance.
· Ants recognise their group by a special kind of odour released by ants themselves.
· Some insect are attracted towards their mate because of their smell, e.g. Silkworm.
· Mosquito can even find a human in dark by odour of body and heat of the body and smell of sole of the feet.
· Birds can see at different direction at a time because they have eyes on the left and right of the face.
· Elephants also blow air in their ears along with listening. Ear is also known as temperature stabiliser for elephant.
· Dog, lion and tiger can identify their area or den by smell of their excreta.
· Frog and lizard use their tongue to catch their prey.
· Nocturnal animals can only see white and black colour, e.g. owl, raccoon.
· Snakes don't have noses so snakes smell with their tongues. Also snakes don't have ears, so they absorb vibrations of Earth to determines the prey or danger.
· Bats are mammals because they give birth to their youngones.
· Squirrels are rodents. Like other rodents, squirrel have four front teeth that never stop growing so they don't wear down from the constant gnawing.
· Tiger can make difference between rustling of
· leaves arid sound of animal moving on the grass
· Cockroach is the organism which can walk and fly.
3.8 Benefits with Animals
Animals have great impact on environment.
Some animals are very beneficial for us, here some beneficial animals described below
|
Animals' Name |
Uses |
|
Bees |
Honey and Wax |
|
Silkworm |
Silk |
|
Lac/Lakhworm |
Lakh |
|
Cow, Buffalo, Goat, Hen, Duck, Fish |
Milk, Meat, Egg |
|
Sheep, Goat, Camel, Rabbit |
Knitting yarn |
|
Cow, Bull, Buffalo, Sheep |
Leather |
|
Farmer's Friend |
Earthworm |
|
Crow, Dog, Kite, Vulture, Eagle. |
Cleaning Animals |
3.8.1 Specific Features of Specific Class of Animals
Specific class of animals have some specific features. These are as follow
Pisces/Fishes
They have scales on the body. They have invisible ears and have only two chambered heart. Fishes are oviparous animal.
Amphibians
They don't have scales on their body but they possess invisible ear. Amphibians have three chambered heart, breathe through gills, lungs and skin, and amphibians as like fishes also reproduces by external fertilisation so it is also oviparous animal, e.g. frog, tadpole, crocodiles etc.
Reptiles
· They have scales on their body. They also possess invisible ear like birds and fishes. Reptiles breathe by lungs and it has three chambered heart. It also reproduces by oviparous method, e.g. snakes, lizards, tortoise etc.
· Reptiles such as snakes hears from the vibrations coming out of a surface or land. Snake do not have any external ear. They can only feel vibration from the ground. Snake has two hollow teeth known as fangs. When snake bites/poison enters only through fangs. Medicine for snake bites are made from snake's poison. There are many kinds of snakes in our country, only four of them are poisonous. They are Cobra, Karait, Russel's viper (Duboiya) and Saw-Scale Viper (Afai).
There are numerous animals around us in world.
Some animals have specific characteristics, which are given in the table.
|
Animals |
Specific Characteristics |
|
Elephants |
Elephants are herbivorous, elephants large ear flaps help to control their body temperature. Females tend to live in family groups, which can consist of one female with her calves. Leader of group is often the oldest female elephant (low). Males leave their family groups when they reach puberty. Calves are the centre of attention in their family groups and rely on their mother for as long as 3 years. Elephant's trunk is elongated nose and upper lip. Elephant drinks about 2 gallons (7.5 litres) of water at a time. One elephant can eat 300 pounds (136 kg) of food in one day. They sleep and rest less to maintain their body temperature. |
|
Tiger |
Tiger may consume upto 40 kg (88 pond) of meat at one time. It has two times more sight capacity than humans in night. For hearing they can move their ears in different direction. |
|
Rhino ceros |
It is second longest terrestrial animal after elephant it is herbivorous, weight up 1000 kg. It has around \[1\frac{1}{2}\,cm\]thick skin. It has one horn on nose hence called as rhino. |
|
Ziraffe |
Ziraffe is the tallest mammal of the Earth, it has about 5 meter height. It sleep for very less time (around 2 hours in 24 hours). Its life time is about 25 years. |
|
Chimpanzee |
This is a very clever animal. It lives in group. Group is of about 3 to 80 members. |
|
Sloth |
Sloth are mammals which looks like beer. Sloth make very good habitat for other orgnisms and a single sloth may be home several species of moths, beetles, cockroaches, fungi and algae. It is a nocturnal animal, sleeps around 17 hours in day time. |
|
Dolphin |
Dolphins are mammals. Dolphin live in social groups of 5 to several hundred. They use echolocation to find prey and communicate with each-other in water. Gangetic dolphin is national water animal of India and is said to represent the purity of holy Ganga river as it can only survive impure and fresh water. |
|
Whale |
Blue whale is largest animal of Earth. These are mammals. Its life span is about 90 years. |
|
Earthworm |
An earthworm is a tube shaped segmented worm. Earthworms are commonly found living in soil, feeding on live and dead organic matter. Earthworms improve soil fertility by converting large organic matter into rich humus. Earthworms are used in making vermicompost also. |
Insects live in colony. These organisms recognise their fellow mates and other things mostly through their smell or by specific type of secretion known as pheromones, e.g. ant, bees, silkworm etc. Spider lives alone and it does not form colony.
3.9 Birds
They have feathers on the body, four chambered heart and breathe through lungs like reptiles, fishes and amphibian, it also possess invisible hair and reproduces by oviparous method, e.g. eagle, pigeon, parrot, sparrow etc.
Birds have boat shaped body, hollow bones, wings and feathers to help in flying. It sits on the branches of trees. It's claws are made so that it helps in grasping the branches of trees.
Birds have fixed eye position, so in order to see in different direction birds move their neck in different direction. Among all the birds owl has maximum capacity to rotate its nearly upto \[360{}^\circ \] while mynah can move its neck back and fourth with jerk.
Different birds make their nest in their own way.
Bulbul uses bushes with dried grass and hedges to make nest. Robin nest is made up of soft twigs, roots, wool, hair, cotton wool and grass. Robin's nest is very soft in nature. Crow make its nest using wire, wood, grass and twigs and it makes nest high up on trees.
Birds and their Specific Features
|
Characteristics |
Related Bird |
|
Sharp eyesight |
Eagle, Kite, Vulture |
|
Bird neck rotation |
Owls, Mynah |
|
Nest (normal) (Soft) Nest (Soft and Hard) Nest
|
Red-vented bulbuls (in bushes) Robin (soft grasses, fibers, yarn, cotton etc.) · Crow (it makes its nest on highest tree) · Cuckoo (Koel) (Show brood parasitism lay its egg in the nest of crow). · Baya weaver (Soan chidiya)-it makes hanging nest. · Weaver bird (weave the nest) Woodpecker (make their nest in bark of tree with the help of beak, pointed beak act as both chisee and crowbar to remove bark). |
|
Omnivorous bird |
Peacock (National bird of India). |
|
Birds without flight |
Penguin and emu. |
Brood Parasite
These are organisms that rely on others to raise their young. Koel is a brood parasite over crow for development and hatching of its eggs.
|
Herbarium |
Herb |
|
Vivarium |
Butterfly |
|
Aquarium |
Fishes |
|
Terrarium |
Earthworm |
Pet Animals
Those animals which are kept by human beings as a source of companionship protection and pleasure are known as pet animals. They are also considered as part of our family, e.g. dogs, cats, horses, rabbits and parrots.
Animal Husbandry
It is a science of breeding and caring of animals. It is basically management of those animals which are commercially important to human. Animals give many useful products for humans.
|
Animal |
Product |
|
Cow |
Milk, meat |
|
Buffalo |
Milk, meat |
|
Goat |
Milk, meat, wool |
|
Sheep |
Meat, wool |
|
Honey bee |
Honey |
|
Lac insect |
Lac |
|
Silkworm |
Silk fibre |
|
Hen, Chicken |
Egg, meat |
|
Snake |
Leather |
|
Rabbit |
Meat and fur |
Animals are domesticated for various purposes sush as
Dairy Animals These animals have ability to produce large quantities of milk, from which other dairy products like cheese, butter, mava, sweets etc are made. Cows, buffaloes and goats are used reared up as dairy animals. Cows milk has low fat content than buffalo's milk. Goats are called as poor's cow.
Poultry Animals Eggs are rich in proteins. Chicken and ducks are raised for egg production.
To Carry Weight Horses and donkeys are use to carry weight.
For Agriculture Bull are used in agriculture.
Pet Animals A pet or companion animal is an animal kept primarily for a person's company, protectioner, entertainment rather than as a working animal, sport animal and livestock. Pets provide their owners physical and emotional benefits.
|
Aetiology |
It is related with cause and conditions of a disease. |
|
Neiology |
Study of diseases related with nervous system. |
|
Ethology |
Study of animal behaviour. |
|
Animal |
Younganes |
Animal |
Youngones |
|
Bear |
Cab |
Toad |
Tadpole, toadlet |
|
Butterfly |
Caterpillar |
Tiger |
Cub |
|
Frog |
Polliwog, tadpole, froglet |
Swan |
Flapper, cygnet |
|
Eagle |
Eaglet |
Snake |
Snakelet |
|
Kangaroo |
Joey |
Giraffe |
Calf |
|
Monkey |
Infant |
Horse |
Foal, colt (male), filly (female) |
|
Rabbit |
Bunny, kit |
Elephant |
Calf |
|
Sheep |
Lamp |
Bat |
Pup |
|
Yak |
Calf |
Dog |
Whelp, pup, puppy |
|
Zebra |
Foal |
Shark |
Cub |
Bee-Keeping (Apiculture)
· Honey bees are attracted to litchi flower.
Honeybee lay their eggs from October to
December. So, it is the best time to start bee keeping in the state of Bihar.
· Every bee-hive has one queen bee that lay eggs.
Most of the bee in the hive are worker-bees, there are also few male-bee.
3.10 Impact of Animals on Children
Presence of animals in the surrounding influences the behaviour of child. Through studies, it has been known that playing with the pet reduces stress.
Child develops an affection to the animal which is domesticated in house, e.g. dog, cat, cow, rabbit, parrot, pigeon etc. While it develops a sense of fear from animal which it has not seen in daily life or have learnt from surrounding that these animals are dangerous.
By observing the action of several animals like ants, spider, squirrel, sense of curiosity arouses in the child and it tries to find answer for his observation, so in a way it helps in developing thinking skill of child.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
