-
question_answer1)
A carnots reversible engine converts \[\frac{1}{6}th\] of heat input into work. When the temperature of sink is reduced 62 K, the efficiency of carnotss cycle, becomes \[\frac{1}{3}.\] Calculate temperature of source and sink
A)
372K, 310K done
clear
B)
772K, 312K done
clear
C)
672K, 610K done
clear
D)
None of these done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer2)
A monatomic gas undergoes a process given by \[2dU+3dW=0,\] then the process is
A)
isobaric done
clear
B)
adiabatic done
clear
C)
isothermal done
clear
D)
none of these done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer3)
A diesel engine takes in 5 moles of air at \[20{}^\circ C\] and 1 atm, and compresses it adiabatically to \[\frac{1}{10}\text{th}\] of the original volume. If air is diatomic then work done and change in internal energy is
A)
- 46 kJ, 46 kJ done
clear
B)
36 kJ, - 36 kJ done
clear
C)
46 kJ, - 46 kJ done
clear
D)
- 36 kJ, 36 kJ done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer4)
A gas undergoes a process in which its pressure p and volume V are related as \[V{{p}^{n}}=\] constant the bulk modulus for the gas in the process is
A)
np done
clear
B)
\[{{p}^{1/n}}\] done
clear
C)
\[\frac{p}{n}\] done
clear
D)
\[{{p}^{n}}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
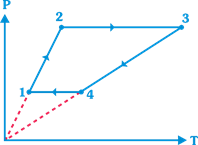
question_answer5)
Three moles of an ideal monoatomic gas perform a cycle shown in figure. The gas temperatures in different states are \[{{T}_{1}}=200K,{{T}_{2}}=400K,{{T}_{3}}=1600K\] and \[{{T}_{4}}=800K.\] The work done by the gas during the cycle is (Take \[R=25/3\text{ }J/mol\text{-}K\])
A)
5 kJ done
clear
B)
25 kJ done
clear
C)
15 kJ done
clear
D)
20 kJ done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer6)
The molar heat capacity of a certain substance varies with temperature according to the given equation, \[C=27.2+(4\times {{10}^{-3}})T.\] The heat necessary to change the temperature of 2 mol. of the substance from 300K to 700K is
A)
\[3.46\times {{10}^{4}}J\] done
clear
B)
\[2.33\times {{10}^{3}}J\] done
clear
C)
\[12\times {{10}^{5}}\] done
clear
D)
\[2.33\times {{10}^{4}}J\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
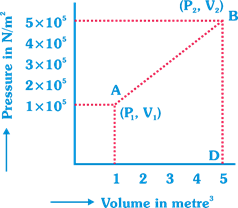
question_answer7)
A system changes from the state \[({{P}_{1}},\,\,\,{{V}_{1}})\] to \[({{P}_{2}},\,\,\,{{V}_{2}})\] as shown in the figure below. What is the work done by the system?
A)
\[7.5\times {{10}^{5}}\] joule done
clear
B)
\[7.5\times {{10}^{5}}\] ergs done
clear
C)
\[12\times {{10}^{5}}\] joule done
clear
D)
\[6\times {{10}^{5}}\] joule done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer8)
A diatomic ideal gas is heated at constant volume until the pressure is doubled and again heated at constant pressure until volume is doubled. The average molar heat capacity for whole process is:
A)
\[\frac{13R}{6}\] done
clear
B)
\[\frac{19R}{6}\] done
clear
C)
\[\frac{23R}{6}\] done
clear
D)
\[\frac{17R}{6}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
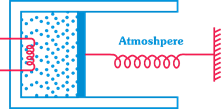
question_answer9)
An ideal monoatomic gas is confined in a cylinder, fitted with piston, which is connected to spring as shown in figure. The gas is heated by a-small electric heater until the piston moves out slowly by 0.1 m. Find the work done by the gas. Spring constant = 8000 N/m,-piston area \[=8\times {{10}^{-3}}{{\text{m}}^{2}}\] atmospheric pressure \[={{10}^{5}}Pa\].
A)
40 J done
clear
B)
80 J done
clear
C)
120 J done
clear
D)
60 J done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer10)
Two carnots engines A and B are operated in series. The first one A receives heat at 1200 K and rejects to a reservoir at T and K. The second engine B receives the heat rejected by the first engine and in turn rejects to a heat reservoir at 300 K. Calculate the value of T, when work outputs of the two engines are equal.
A)
600 K done
clear
B)
750 K done
clear
C)
450 K done
clear
D)
900 K done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer11)
Choose the correct statement for an isolated system.
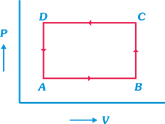
A)
\[\Delta U(C\to D)=\] negative done
clear
B)
\[\Delta Q(A\to B)=\] positive done
clear
C)
\[\Delta U=(A-B-C-D-A)\ne 0\] done
clear
D)
\[\Delta Q(D\to A)=0\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
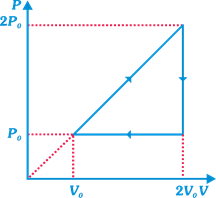
question_answer12)
An imaginary ideal gas with adiabatic exponent \[\gamma =2\] goes through a cycle as shown in figure. Find efficiency of cycle:
A)
\[\frac{1}{9}\] done
clear
B)
\[\frac{1}{8}\] done
clear
C)
\[\frac{1}{6}\] done
clear
D)
\[\frac{1}{5}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer13)
| DIRECTION: Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follows: |
| In the figure n mole of a monoatomic ideal gas undergo the process ABC as shown in the P-V diagram. The process AB is isothermal and BC is isochoric. The temperature of the gas at A is \[{{T}_{0}}\]. Total heat given to the gas during the process ABC is measured to be Q. |
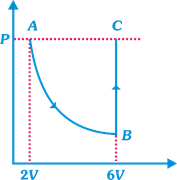 |
| Temperature of the gas at C is equal to |
A)
\[{{T}_{0}}\] done
clear
B)
\[3{{T}_{0}}\] done
clear
C)
\[6{{T}_{0}}\] done
clear
D)
\[2{{T}_{0}}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer14)
| DIRECTION: Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follows: |
| In the figure n mole of a monoatomic ideal gas undergo the process ABC as shown in the P-V diagram. The process AB is isothermal and BC is isochoric. The temperature of the gas at A is \[{{T}_{0}}\]. Total heat given to the gas during the process ABC is measured to be Q. |
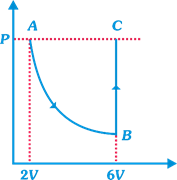 |
| Heat absorbed by the gas in the process BC |
A)
\[3nR{{T}_{0}}\] done
clear
B)
\[nR{{T}_{0}}\] done
clear
C)
\[2nR{{T}_{0}}\] done
clear
D)
\[6nR{{T}_{0}}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer15)
| DIRECTION: Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follows: |
| In the figure n mole of a monoatomic ideal gas undergo the process ABC as shown in the P-V diagram. The process AB is isothermal and BC is isochoric. The temperature of the gas at A is \[{{T}_{0}}\]. Total heat given to the gas during the process ABC is measured to be Q. |
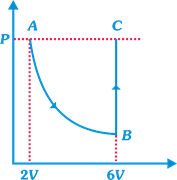 |
| The average molar heat capacity of the gas in process ABC |
A)
\[\frac{Q}{n{{T}_{0}}}\] done
clear
B)
\[\frac{Q}{2n{{T}_{0}}}\] done
clear
C)
\[\frac{Q}{3n{{T}_{0}}}\] done
clear
D)
\[\frac{2Q}{n{{T}_{0}}}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer16)
P-V plots for two gases during adiabatic process are shown in figure. Plots 1 and 2 should correspond, respectively, to
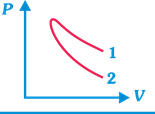
A)
He and \[{{O}_{2}}\] done
clear
B)
\[{{O}_{2}}\] and He done
clear
C)
He and Ar done
clear
D)
\[{{O}_{2}}\] and \[{{N}_{2}}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer17)
From the following V-T diagram as shown in the figure. What is true about pressure?
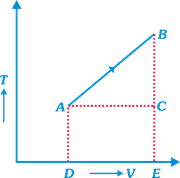
A)
\[{{p}_{1}}<{{p}_{2}}\] done
clear
B)
\[{{p}_{1}}>{{p}_{2}}\] done
clear
C)
\[{{p}_{1}}={{p}_{2}}\] done
clear
D)
Cannot predict done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer18)
A gas expands adiabatically at constant pressure such that its temperature \[T\,\propto \,a/\sqrt{V}.\] The value of \[\gamma =({{C}_{p}}/{{C}_{V}})\] of the gas is
A)
1.30 done
clear
B)
1.50 done
clear
C)
1.67 done
clear
D)
2.00 done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer19)
For a certain process the molar heat capacity of an ideal gas is found to be \[\left( {{C}_{v}}+\frac{R}{2} \right).\] For the given process it can be concluded that
A)
PV = constant done
clear
B)
\[\frac{P}{V}=\] constant done
clear
C)
\[\frac{{{V}^{2}}}{P}=\] constant done
clear
D)
none of these done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer20)
2 moles of a mono-atomic gas undergo isobaric expansion as shown in figure. The efficiency for the process is found to be \[\frac{x}{10}\]. Find the value of\[x\].
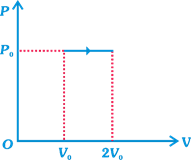
A)
2 done
clear
B)
3 done
clear
C)
4 done
clear
D)
5 done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer21)
A 100 kg piston encloses 32 g of oxygen gas at a temperature of \[{{27}^{o}}C\] in a vertical cylinder of base area of \[4\text{ }d{{m}^{2}}\]. The air pressure outside is \[1\times {{10}^{5}}Pa\]. The axis of the cylinder is vertical, and the piston can move in it without friction. How much heat is to be transferred to the gas to raise the piston by 20 cm. Use \[R=\frac{25}{3}J/mol/K\]
A)
3500 J done
clear
B)
350 J done
clear
C)
7000 J done
clear
D)
750 J done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer22)
An ideal refrigerator has a freezer at a temperature of \[-13{}^\circ C\]. The coefficient of performance of the engine is 5. The temperature of the air (to which heat is rejected) is.
A)
\[320{}^\circ C\] done
clear
B)
\[39{}^\circ C\] done
clear
C)
325 K done
clear
D)
\[325{}^\circ C\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer23)
P.T graph of an ideal gas of equal number of moles of different volumes are plotted as shown. Choose the correct answer
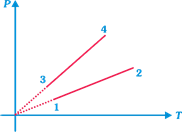
A)
\[{{V}_{1}}={{V}_{2}}>{{V}_{3}}={{V}_{4}}\] done
clear
B)
\[{{V}_{1}}={{V}_{2}}<{{V}_{3}}={{V}_{4}}\] done
clear
C)
\[{{V}_{1}}={{V}_{2}}={{V}_{3}}={{V}_{4}}\] done
clear
D)
\[{{V}_{4}}>{{V}_{3}}>{{V}_{2}}>{{V}_{1}}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer24)
The degrees of freedom per molecule of an ideal gas is 5. Work done by the gas is 100 J when it expands isobarically. The heat absorbed by the gas will be
A)
250 J done
clear
B)
150 J done
clear
C)
350 J done
clear
D)
200 J done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer25)
Two rigid boxes containing different ideal gases are placed on a table. Box A contains one mole of nitrogen at temperature \[{{T}_{0}},\] While Box B contains one mole of helium at temperature (7/3) \[{{T}_{0}}\]. The boxes are then put into thermal contact with each other and heat flows between them until the gases reach a common final temperature (Ignore the heat capacity of boxes). Then, the final temperature of the gases, \[{{T}_{f}},\] in term of \[{{T}_{0}}\] is
A)
\[{{T}_{f}}=\frac{7}{3}{{T}_{0}}\] done
clear
B)
\[{{T}_{f}}=\frac{3}{2}{{T}_{0}}\] done
clear
C)
\[{{T}_{f}}=\frac{5}{2}{{T}_{0}}\] done
clear
D)
\[{{T}_{f}}=\frac{3}{7}{{T}_{0}}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer26)
743 J of heat energy is added to raise the temperature of 5 mole of an ideal gas by 2 K at constant pressure. How much heat energy is required to raise the temperature of the same mass of the gas by 2 K at constant volume?
A)
826 J done
clear
B)
743 J done
clear
C)
660 J done
clear
D)
620 J done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer27)
A gas expands with temperature according to the relation \[V=k{{T}^{2/3}}\]. Calculate work done when the temperature changes by 60 K?
A)
10 R done
clear
B)
30 R done
clear
C)
40 R done
clear
D)
20 R done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer28)
For a cyclic process \[A\to B\to C\to A,\] the following information is given
| Path | \[\Delta Q\](Heat supplied) | \[\Delta U\] (Increase in internal energy) | Work done by system on surrounding |
| \[A\to B\] | 600 J | 200 J | 400 J |
| \[B\to C\] | - 100 J | 100 J | - 200 J |
| \[C\to A\] | - 100 J | - 300 J | 200 J |
Calculate the heat of the cycle and efficiency of cycle.
A)
400 J, 100% done
clear
B)
600 J, 66.67% done
clear
C)
400 J, 66.67% done
clear
D)
600 J, 100% done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer29)
| A certain mass of gas is taken from an initial thermodynamic state A to another state B by process I and II. In process I the gas does 5 joules of work and absorbs 4 joules of heat energy. In process II, the gas absorbs 5 joules of heat. The work done by the gas in process II (see figure) is |
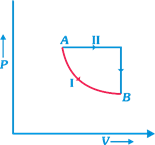 |
A)
+6 joules done
clear
B)
- 6 joules done
clear
C)
+4 joules done
clear
D)
- 4 joules done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer30)
Two vessels A and B contain water at temperature \[{{T}_{A}}\] and \[{{T}_{B}},\] at \[10{}^\circ C\] and \[2{}^\circ C\] respectively. If the water in both the vessels were compressed adiabatically and if we take into account the finite bulk modulus of elasticity of water, then \[{{T}_{A}}\] and \[{{T}_{B}}\]
A)
increase and decrease respectively done
clear
B)
decrease and increase respectively done
clear
C)
both increase done
clear
D)
both decrease done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer31)
| An ideal gas can be expanded from an initial state to a certain volume through two different processes |
| (i) \[P{{V}^{2}}=\] constant and |
| (ii) \[P=K{{V}^{2}}\] where K is a positive constant. Then |
A)
Final temperature in (i) will be greater then in (ii) done
clear
B)
Final temperature in (ii) will be equal to (i) done
clear
C)
Total heat given to the gas in (i) case is greater than in (ii) done
clear
D)
Total heat given to the gas in (ii) case is greater than in (i) done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer32)
| Direction: An ideal diatomic gas is confined in a cylinder A of volume \[{{V}_{0}},\] this cylinder is connected to another cylinder B with the help of tube of a negligible volume. The cylinder B is fitted with a movable piston which can be adjusted from outside. Initially, the piston is adjusted so that volume of B is the same as volume of A i.e., \[{{V}_{0}}\]. B is evacuated and the stopcork is opened so that gas expands and occupies the volume \[2{{V}_{0}}\]. [System is thermally isolated from the surroundings]. |
| |
 |
| During this free expansion, the internal energy of the system. Now with the stop-cork open, the piston is slowly moved to compress the gas back to cylinder A at temperature T. For this |
A)
increases done
clear
B)
decreases done
clear
C)
remains constant done
clear
D)
nothing can be said done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer33)
| Direction: An ideal diatomic gas is confined in a cylinder A of volume \[{{V}_{0}},\] this cylinder is connected to another cylinder B with the help of tube of a negligible volume. The cylinder B is fitted with a movable piston which can be adjusted from outside. Initially, the piston is adjusted so that volume of B is the same as volume of A i.e., \[{{V}_{0}}\]. B is evacuated and the stopcork is opened so that gas expands and occupies the volume \[2{{V}_{0}}\]. [System is thermally isolated from the surroundings]. |
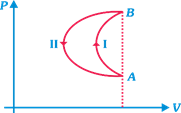 |
| Work done on the gas is [for n moles of gas] |
A)
\[nRT\text{ }\ln \text{ }2\] done
clear
B)
\[-nRT\text{ }\ln \text{ }2\] done
clear
C)
\[nRT\] done
clear
D)
\[-nRT\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer34)
| Direction: An ideal diatomic gas is confined in a cylinder A of volume \[{{V}_{0}},\] this cylinder is connected to another cylinder B with the help of tube of a negligible volume. The cylinder B is fitted with a movable piston which can be adjusted from outside. Initially, the piston is adjusted so that volume of B is the same as volume of A i.e., \[{{V}_{0}}\]. B is evacuated and the stopcork is opened so that gas expands and occupies the volume \[2{{V}_{0}}\]. [System is thermally isolated from the surroundings]. |
| |
 |
| The heat absorbed by the gas is |
A)
\[nRT\text{ }\ln \text{ }2\] done
clear
B)
\[-nRT\text{ }\ln \text{ }2\] done
clear
C)
nRT done
clear
D)
\[-nRT\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer35)
In a cyclic process, a gas is taken from state A to B via path-I as shown in the indicator diagram and taken back to state A from state B via path-II. In the complete cycle:
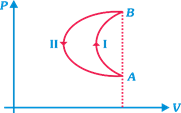
A)
work is done by the gas done
clear
B)
heat is ejected by the gas done
clear
C)
no work is done by the gas done
clear
D)
nothing can be said about work as data is insufficient done
clear
View Solution play_arrow

