Mensuration-I
Category :
Mensuration I (Area and Perimeter)
AREA
Total space inside the boundary of a 2-Dimensional finger is called the area of that particular figure. It is measured in square unit.
PERIMETER
Perimeter is the length of border around any enclosed plane. Therefore, sum of the sides of a plane figure is the perimeter of that particular figure, It is measured on particular unite, i.e., meter, centimeter, decimeter.
TRIANGLE
A figure enclosed by three sides is known as triangle. A triangle has three angles with total sum of \[180{}^\circ \]and sum of its any two sides is more than the third side.
Equilateral Triangle
It has all three sides equal.
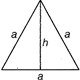
It has all three sides equal.
Area\[=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{4}{{a}^{2}};\]height \[=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}a\]
Perimeter\[=3a\]
Where, a = Side, Each angle \[=60{}^\circ \]
In radius of equilateral triangle\[=\frac{\text{side}}{\text{2}\sqrt{\text{3}}}\text{=}\frac{\text{1}}{\text{3}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ Height}\]
Circumradius of equilateral triangle \[=\frac{\text{side}}{\sqrt{3}}=\frac{1}{3}\times \text{Height}\]
Isosceles Triangle
It has any two sides and two angles equal and its altitude bisects the base.

Area \[=\frac{b}{4}\sqrt{4{{a}^{2}}-{{b}^{2}}}\]
Height \[=\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}-\left( \frac{b}{2} \right)}=\frac{1}{2}\sqrt{4{{a}^{2}}-{{b}^{2}}}\]
Perimeter \[=a+a+b=2a+b\]
Where, a = Each of two equal sides
b = Third side
Scalene Triangle
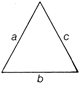
It has three unequal sides
Area \[=\sqrt{s\,(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)}\]
[Heron's formula]
Where, Semi-perimeter \[s=\frac{a+b+c}{2}\]
and a, b and c are the sides of the triangle.
Perimeter \[=a+b+c\]
Right Angled Triangle
It is a triangle with one angle is equal to \[90{}^\circ \]
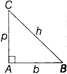
Area \[=\frac{1}{2}\times b\times p\]
Perimeter\[=p+b+h\]
Relation between p, h, and b by Pythagoras Theorem
\[{{h}^{2}}={{p}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}\]
Where, p = Perpendicular
b = Base and h = Hypotenuse
Area \[=\frac{1}{2}\times \]Product of two sides \[\times \] Sine included angle \[=\frac{1}{2}bh\,\sin \,C=\frac{1}{2}pb\,\sin A\]
Radius of incircle of triangle \[r=\sqrt{\frac{(s\,-a)(s\,-b)(s\,-c)}{s}}\]
Area of triangle if medians are given.
Let length of medians of \[\Delta ABC\]be u, v and w.
\[\therefore \] Area of triangle\[=\frac{4}{3}\sqrt{s(a-u)(s-u)(s-w)}\]
Where, Semi-perimeter \[s=\frac{u+v+w}{2}\]
QUADRILATERAL
A figure enclosed by four sides is called a quadrilateral. A quadrilateral has four angles and sum of these angles is equal to\[360{}^\circ .\]
Square
It is a quadrilateral with all 4 sides equal and each angle is equal to \[90{}^\circ .\]
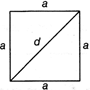
Area \[={{(side)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}\]or \[\frac{1}{2}{{d}^{2}}\]
Perimeter \[=4\times \]side \[=4\,a\]
Diagonal \[(d)=a\sqrt{2}\]
Where, a = Side, d = Diagonal
Rectangle
It is a quadrilateral with equal opposite sides and each angle is equal to \[90{}^\circ .\]
Area= Length x Breadth
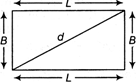
\[=L\times B\]
Perimeter \[=2\,\,(L\times B)\]
Diagonal (d) \[=\sqrt{{{L}^{2}}+{{B}^{2}}}\]
Area of walls of rectangular room \[=2\times (L+B)\times h\]
Where, L = Length,
B = Breadth,
h = Height
Parallelogram
It is a quadrilateral with opposite sides parallel and equal.
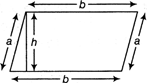
Area = Base \[\times \]Height \[b\times h\]
Perimeter \[=2\,(a+b)\]
Trapezium
It is a quadrilateral with anyone pair of opposite sides parallel.

Area \[=\frac{1}{2}\](Sum of parallel sides \[\times \]Height)\[=\frac{1}{2}(a+b)h\]
Where, a and b are parallel sides and h is the height or perpendicular distance between a and b.
Rhombus
It is parallelogram with all 4 sides equal. The opposite angles in a rhombus are equal but they are not right angle.
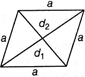
Area \[=\frac{1}{2}\times {{d}_{1}}\times {{d}_{2}},\]
Side (a) \[=\frac{1}{21}\sqrt{d_{1}^{2}+d_{2}^{2}}\]\[\Rightarrow \]\[{{4}^{2}}=d_{1}^{2}+d_{2}^{2}\]
Perimeter = 4 a
Where, a = side, \[{{d}_{1}}\]and \[{{d}_{2}}\] are diagonals.
REGULAR POLYGON
In regular polygons all sides and all interior angles are equal. A polygon is called pentagon, hexagon, heptagon, octagon, nonagon and decagon according as it contains 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 and 10 sides, respectively.
If each side of a regular polygon of n sides = a, then
Area of regular pentagon \[=5\,{{a}^{2}}\frac{\sqrt{3}}{4}\]
Area of regular hexagon \[=6{{a}^{2}}\frac{\sqrt{3}}{4}\]
Area of regular octagon \[=2\,(\sqrt{2}+1){{a}^{2}}\]
CIRCLE
It is a plane figure enclosed by a line on which every point is equally distant from a fixed point (centre) inside the curve.
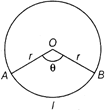
Area \[=\pi \,{{r}^{2}}\]
Circumference (perimeter)\[=2\pi \,r\]
Diameter \[=2r\]
Length of the arc \[(l)=\frac{\pi r\theta }{180{}^\circ }\]
Area of sector\[AOB=\frac{\pi {{r}^{2}}\theta }{360{}^\circ }\]
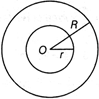
In ease of circular ring,
Area\[=\pi \,({{R}^{2}}-{{r}^{2}})\]
Difference in circumference of both the rings \[(2\pi R-2\pi {{r}^{2}})\]
Where,
R = 'Radius of bigger ring
r = Radius of smaller ring
Quicker One
Ø If all the measuring sides of any two-dimensional figure are changed (increased or decreased) by a%, then its perimeter also changes by a% In case of circle such change takes place because of the change in radius (or diameter).
Ø If the length and breadth of a rectangle are increased by a% and b%, respectively, then area will be increased by \[\left( a+b+\frac{ab}{100} \right)%\]
Ø Area of a square inscribed in a circle of radius r is equal to \[2{{r}^{2}}.\]
Ø If a pathway of width x is made inside or outside a rectangular plot of length / and breadth b, then area of pathway is
(i) \[2x\,\,(\text{l}+b+2x),\] if path is made outside the plot.
(ii) \[2x\,(\text{l}+b-\text{ }2x),\]if path is made inside the plot.
Ø If two paths, each of width x are made parallel to length \[(l)\] breadth (b) of the rectangular plot is the middle of the plot, then area of the paths is \[x\,\,(l+b-x).\]
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
