Programming Concepts
Category : Railways
Programming Concepts
It is the sequence of instructions in which the problems of computer tasks and steps are performed with the help of computer. A person who writes or performs the program is known as programmer. Programmer uses some specific languages to write program which is known as programming languages e.g. C++, Java, etc.
Programming Language
It is a set of keywords, symbols and a system of rules for constructing statements by which humans can communicate instructions to be executed by a computer.
Programming languages are mainly categorised into three parts which are as follows
Low Level Language
These programming languages are more arcane and difficult to understand. It is designed to operate and handle the entire instruction set of a computer system directly which are generally used to write the system software, e.g. Machine language and Assembly language.
Machine Language
It is the only language understood by the computers. Sometimes, it referred to as machine code or object code or binary language. It is a collection of binary digits (0 or 1) or bits that the computer reads and interprets.
Assembly Language
It is a low level programming language which is used as an interface with computer hardwares. It uses structured commands as substitutions for numbers, allowing humans to read the code easier than looking at binary codes.
Medium Level Language
It serves as the bridge between raw hardware and programming layer of a computer system. It is designed to improve the translated code before it is executed by the processor. C language is known as medium level language.
High Level Language (HLL)
It is an advanced computer programming language that is not limited to one computer, designed for a specific job and is easier to understand. The main advantage of high level languages over low level languages is that they are easier to read, write and understand, e.g. BASIC, C, FORTRAN, Java, Pascal, etc.
Some High Level Languages and Their Application Areas
|
Language |
Year |
Developer |
Application Area |
Nature |
|
FORTRAN (Formula Translation) |
1957 |
a team of programmers at IBM |
Calculation |
Compiled |
|
ALGOL (Algorithmic Language) |
1958 |
A commitee of European and American computer scientists |
Scientific purpose |
Compiled |
|
LISP (List Processing) |
1958 |
John McCarthy at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) |
Artificial intelligence |
Compiled and Interpreted |
|
COBOL (Common Business Oriented Language) |
1959 |
Grace Hopper |
Business management. string oriented |
Compiled |
|
BASIC (Beginner's All purpose Symbolic Instruction Code) |
1964 |
John G. Kemeny and Thomas E. Kurtz at Dartmouth college in New Hampshire |
Programming for educational purpose |
Interpreted |
|
Pascal |
1970 |
Niklaus Wirth |
Education |
Compiled |
|
C |
1972 |
Dennis Ritchie at Bell Labs |
System programming |
Compiled |
|
C++ |
1983 |
Bjarne Stroustrup at Bell Labs |
System object programming |
Compiled |
|
Java |
1995 |
James Gosling at Sun Microsystems |
Internet oriented programming |
Compiled and Interpreted |
|
Program Documentation It is a kind of documentation that gives a comprehensive procedural description of a program. It shows as to how software is written. The program documentation describes what exactly a program does by mentioning about the requirements of the input data and effect of performing a programming task. De-Bugging It is the process of locating and fixing or bypassing bugs (errors) in computer program code. To debug any program, first separate the source of problem and then correct it. |
Language Translator
It helps in converting programming languages to machine language.
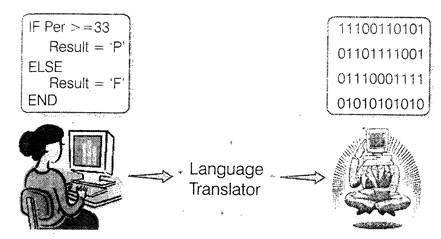
The translated program is called the object code. Depending upon used programming languages, language translator are divided into three categories which are as follows
Assembler
It converts a program written in assembly language into machine language. Assembly language consists of mnemonic codes, which are difficult to learn and are machine dependent.
Some basic functions of an assembler are as follows
(a) Replaces mnemonic codes by machine codes.
(b) Replaces symbolic addresses by numeric addresses.
(c) Determines machine representation for constants.
Interpreter
It converts a HLL program into machine language by converting it line-by-line. If there is any error in any line, it stops the execution of the program
immediately and reports the user at the same time and program execution cannot resume until the error is rectified by the user. Interpreter is very useful for debugging and suitable for novice programmer. This is a slow process and consumes less memory space.
Compiler
It converts HLL program into machine language, which can be understood by the processor. For each high level language, the machine requires a separate compiler. A compiler creates a unique object program, i.e. if a source program is compiled, there is no need of that source program because output can be obtained by executing that object program (copy created by the compilation of source code). Compiler converts the entire HLL program in one go and reports all the errors of the program along with the line numbers.
Algorithm
It is an effective method that can be expressed within a finite amount of space and time and in a well-defined formal language for calculating a function.
The desirable features of an algorithm are
(i) Each step of algorithm should be simple.
(ii) It must and in a finite number of steps.
(iii) It should be as efficient as possible.
(iv) It should be unambiguous in the sense that the logic should be crisp and clear.
(v) It should be effective, i.e. it must lead to a unique solution of the problem.
Flowchart
It is a type of diagram that represents an algorithm work flow or process, showing the steps as boxes of various kinds, and their order by connecting them with arrows. Flowcharts are used in analysing, designing, documenting or managing a process or program in various fields. The two most common types of boxes in a flowchart are
(i) A processing step, usually called activity and denoted as a rectangular box.
(ii) A decision, usually denoted as a diamond.
Tit-Bits
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
