CHAPTER-9 INDUSTRIES
The industries of Madhya Pradesh provide a firm basis to the economy of Madhya Pradesh. According to Economic Survey 2018-19, the contribution of industries in the state's GDP is 23.87% in 2016-17. Madhya Pradesh is on 7th place in terms of industrial development. Madhya Pradesh has a strong base of mineral resources and accounts for 14%
of India's total cement production. The state has an oil refinery at Bina with an annual capacity of 6 MMT. The installed power capacity of the state is over 23,400 MW; 35% of which is contributed by renewable energy sources. The state is a leading producer of a variety of horticulture crops and offers lucrative opportunities for food processing industries. The state also offers opportunities in textile manufacturing, automobiles, food processing, soya processing, engineering and agriculture equipment manufacturing, among others. According to the Ease of Doing business report published by World Bank and DIPP 2019 MP Stands on 4th Position.
On the basis of the raw material used, the various industries can be categorized as follows:-
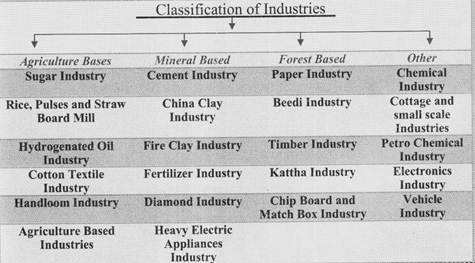
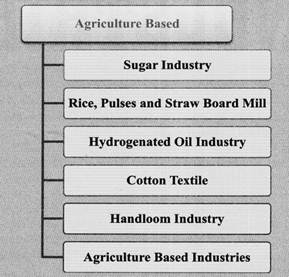
Agriclture Based Industries
The agriculture based industries are dependent on the agriculture for their raw material. These industries are the most crucial in the initial phase of development and have highest access among people as they fulfill the basic needs of a common man. In Madhya Pradesh major agriculture based industries are:
Sugar Industry
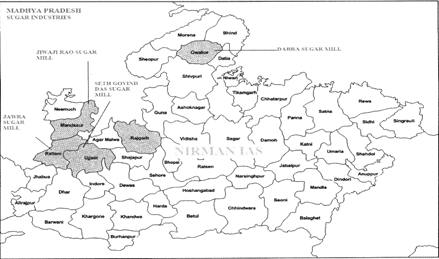
- The first sugar mill in the state was established at Jawra (Ratlam) in 1934, since, sugarcane is cultivated majorly in the Western districts of the state, and major sugar mills are situated in the Western districts of the state.
- The largest sugar mill of the state is at Bariai in Sehore. Others are Dabra Sugar Mill (Gwalior), Jiwajirao Sugar Co. (Mandsaur), Jawra Sugar Mill (Ratlam), Seth Govind Das Sugar Mill (Ujjain), Sarangpur, Balsai and Aalot Sugar Mill. There are 27 sugar mills If Madhya Pradesh.
Locational Factors
- Raw Material: Sugarcane is a perishable and weight losing raw material about 90 percent of the material is wasted and only 10 percent sugar is produced. Hence Sugar industries are located near the sugarcane producing areas.
- Transportation: Location of sugar mills closer to the farmers enables the farmers to bring their produce to the mills easily using transportation like bullock carts, tractors etc.
- Availability of labour: Cheap labor should be available at local level.
- Availability of Capital- Growth of any Industry depends on low interest loan with supporting policies of Government and same are the case for sugar industry.
- Power-Constant supply of electricity in extremely needed for industrial growth.
- Market availability: Sufficient level of market is available for the consumption of the sugar in the state.
Problems with sugar industry in Madhya Pradesh
- The low yield of sugarcane leads to short supply to sugar mills.
- Short crushing season varying normally from 4 to 6 months in a year after that the mills and their workers remain ideal during remaining period of the year.
- Financial condition of sugar factories are poor and this resulted in delay payments to fanners.
- Unsatisfactory locations of the industry.
- Inadequate supply of sugarcane; sugarcane supply fluctuate every year according to its production.
- Low milling efficiency and recovery of sugar from sugarcane is very low.
- Factories do not have control over the quantity and quality of sugarcane supplied by me innumerable cane growers.
- Limited utilization of sugarcane byproducts specially bagasse and molasses.
- Political interference over sugar co-operatives. Eg- Dabra sugar mill.
- Faulty government policies.
- Old and obsolete machinery in most of the factories. This affects Ae capacity of sugar production.
- Inefficient technology, unprofitable process of production, high cost of sugarcane and large excise duty result in high cost of manufacturing.
Rice, Pulses and Straw Board Mill
- Rice mills are located in Indore, Bhopal, Jabalpur and Rewa district.
- Pulses mills are located in Indore, Ujjain and Sagar district.
- Straw Board mills are located in Shajapur district.
Hydrogenated Oil Industry
- Oilseeds and soybean are cultivated in the state on a mass scale. Hence, the production hydrogenated oil is popular here.
- Most of the factories are situated in me oil producing belts of the state like Malwa Plateau, Betul-Chhindwara Plateau, Central Narmada Valley and Chambal Valley area.
- Major oil mills in the state are in GanjBasoda (Vidisha), Jabalpur, Khandwa, GwaIior, Indore and Morena.
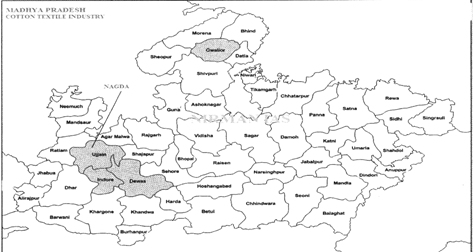
Cotton Textile Industry
- MP ranks fifth (m Lakh bales) in the production of cotton. 18.69 lakh bales in 2018.
- First cotton mill of the state was established in 1906 at Burhanpur. This remained unsuccessful then after Malwa Mill established in Indore in 1907.
- There are about 70 textile mills, thousands of looms and millions of spindles are operating in the state.
- Indore is the largest centre of production of cotton textile in the state.
- The other cotton textile producing centres are at Gwalior, Bhopal, Ujjain, Pithampur, Dhar, Khargone, Burhanpur, Dewas, Khandwa and Chhindwara.
- The state is natural choice for textile related investments due to easy availability of raw materials like cotton well established ecosystem and progressive policy framework.
- 100% FDI to boost the textile sector, state government facilitating textile parks.
- Major companies are Aditya Birla group. Trident group, Vardhaman textiles, Raymond and Century textiles.
Factors for localization of Textile Industry
- Raw material- It is an agro-based Industry and variability in the supply of raw cotton affects me production, their it requires constant supply of raw material. Western Madhya Pradesh been an important area of cotton production.
- Means of transport-Cotton cloth factories are usually in big cities which are connectd to the markets by rail and roadways. Due to this there is no difficulty in sending the cloth to various market centers.
- Availability of cheap labour-It is a labour intensive Industries requires cheap labour. Workers of western Madhya Pradesh and Rajasthan work in these factories, efficiency in this work comes in a short time, so unskilled labours become skilled in the industrial process after short time.
- Climate- Cotton requires black soil and hot and humid climate. Cotton yam cannot be spun successfully under dry condition. Soils of Madhya Pradesh and its hot and its hot and humid climate greatly suitable for this industry.
- Availability of capital and land-One of the main reasons for the distribution of cotton textile in Madhya Pradesh is that it is one of the industries which started in princely states. The princely capitals of central India were their main place of establishment. The kings gave land without value, taxes were reduced, electric power was managed which give protection to this industry. Now in modem times State government also provide basic structures like land, electricity etc at cheap prices.
- Market proximity- Due to the large population in Madhya Pradesh, the market is available in large quantities.
- Availability of energy and Water-Adequate energy is being made available in Madhya Pradesh, factories get water from the water supply of the cities, lakes and tube wells.
Problems with cotton textile industry
- Shortage of raw cotton in Madhya Pradesh.
- Obsolete machinery in large number of mills. This results in low productivity and inferior quality.
- Insufficient Power supply to mills which adversely affects the production.
- Low productivity of labour. Labour strikes are common in textile industry of M.P.
- State cotton industry faces stiff competition from other states like Maharashtra and Gujarat.
- Local level politics also adversely affected textiles mills in M.P.
Silk Textile or Artificial Thread Industry
- This is comparatively a recent industry in the state. For these, the raw material is procured from Gwalior and Dewas mills.
- In Madhya Pradesh, Major artificial thread cloth producing centers are at Indore, Gwalior, Nagda (Ujjain) and Dewas.
- Grasim mill in Nagda is the biggest mill of artificial thread in the state.
Handloom Industry
- This industry not only produces traditional and artistic clothes but also provider employment opportunity to weavers.
- The main handloom centers of the state are Sehore, Khargone, Neemuch, Balaghat, Sidhi and Mandala. In 1976 the Directorate of Handloom was established in Madhya Pradesh.
- Under cottage and rural industries, Sant Ravidas Madhya Pardesh Hastashilp and Handloom Corporation is playing role in the development of Handloom areas.
- State Government has started a scheme 'Kabeer Bunkar Puraskaar Yojana' for weavers. In this Yojana, three best weavers will be awarded an amount of Rs. 1,00,000 (1st), 50,000 (2nd) and 25,000(3rd) along with Medal.
Agriculture Based Industries
|
Industry
|
Place and other imporatant Facts
|
|
Woolen Clothes
|
Indore
|
|
Jute
|
Satna and Amlai
|
|
Cotton Mills
|
Madhya Pradesh holds the third place in the country after Maharashtra and Gujarat, Indore is the prime city of producing cotton clothes
|
|
Hydrogenated Vegetable Oil (oil made from vegetable fats)
|
Gwalior, Jabalpur, Indore, GanjBasoda, Khandwa
|
|
Synthetic Fiber
|
Gwalior, Ujjain, Dewas, Indore, Nagda
|
Food Processing Industries
- Food Processing includes process under which any raw product of agriculture, dairy, animal husbandry, meat, poultry or fishing is transformed through a process (involving employees, power, machines or money) in such a way that its original physical properties undergo a change and the transformed product has commercial value and is suitable for human and animal consumption.
- It also includes the process of value addition to produce products through methods such as preservation, addition of food additives, drying etc. with a view to preserve food substances in an effective manner, enhance their shelf life and quality.
- The first food processing industry of Madhya Pradesh is located in Bavai (Hoshangabad). Additionally, Malanpur (Bhind), Pipariya (Hoshanganbad), maneri (Mandal), Jaggakhedi (Mandsaur), Boregaon (Chhindwara), Nimrani (Khargone) have also been developed as food processing units.
- Other agro bassed industries include jute industries in satna and Arnlai (Anuppur), rice miles (Indore, Bhopal, Jabalpur, Rewa), Pules miles (Indore, Ujjain, Bhopal, Sagar) and mustard oil miles in Morena.
- Focus Areas to accomplish the vision and the mission of the food processing sector in the State, highest priority is given to farmers and processors, and entire strategy is based on 'farmers and processors'.
- State government is determined to continuously strive hard to transform the existing food processing environment into a vibrant food processing environment. It would concentrate on the following key areas-
- Promote processing cluster formation to improve farmer income and processing capacity in the state.
- Promote private sector participation through development of processing facilities in PPP mode.
- Promote and assist formation of cooperatives and societies to increase aggregation of produce and farmer income.
- Promote development/up-gradation of marketing infrastructure to assist in better price ; realization to farmers and ensuring better raw material availability to processors.
- Address skill gaps through establishing education institutes imparting education and research.
- The key projects by state govemment-
- Development of Pulses processing cluster in Sagar district.
- Development of Wheat processing cluster in Sehore district.
- Development of Paddy processing cluster in Satna district.
- Establishment of integrated fruit and vegetable processing facility at Ratlam on PPP model.
- Establishment of vegetable dehydration facility at Neemuch on PPP model.
- Establishment of modem slaughter houses on PPP model.
- Marketing Infrastructure Development
- Development/up-gradation of marketing facilities of the APMC's.
- Farmer Linkages and Empowerment
- Formation of commercial poultry development societies/co-operatives.
- Strengthening of FPOs by facilitating me formation, market linkages and capacity building etc.
- Human Resource Development
- Establishment of Food Technology institute at Indore.
- Enhance human resource befitting global competition.
|
1.
|
Dairy
|
Indore, Ujjain, Bhopal
|
|
2.
|
Fruits and vegetables
|
Indore, Ujjain, Bhopal, Gwalior
|
|
3.
|
Flour milling
|
Indore, Bhind, Bhopal, Hoshangabad, Raisen
|
|
4.
|
Rice milling
|
Balaghat, Katni, Raisen, Ujjain, Gwalior
|
|
5.
|
Pulse processing
|
Indore, Katni, Narsimhapur, Sagar
|
|
6.
|
Spices processing
|
Indore, Ujjain, Neemuch, Ratlam
|
|
7.
|
Cane and bamboo
|
Mandsaur, Neemuch; Rang mahal, Ratlam; Block Bhabra, Jhabua; Kalyanpura, Jhabua; Balod, Dhar; Ujjain; Indore; Bhopal
|
|
8.
|
Ready to eat
|
Indore, Jabalpur, Ratlam, Ujjain
|
Causes of Backwardness of Food Processing Industry in Madhya Pradesh
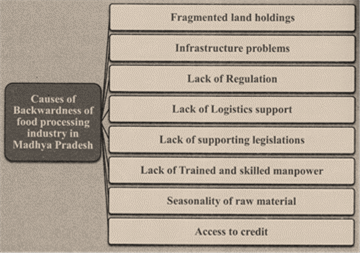
- Fragmented land holdings- In Madhya Pradesh supply-side problems are inherent because there are fragmented land holdings which mean that the industry has to coordinate with a large number of small farmers who are inept in handling technical issues. There is also the issue of low farm productivity which means there cannot be a dearth of quality food items needed by the industry.
- Infrastructure problems- Due to lack of warehouses, cold chain infrastructure and lack of specialized logistics like refrigerator trucks etc.
- Lack of regulation- As 42% of the industry is under unorganized sector due to the inability of small players to go for technology up-gradation and diversification.
- Lack of logistics support- As compared to other states the level of food processing remains low in M.P. which is a grim reminder of the fact that there are huge logistics and related challenges faced by the state's food processing industry.
- Lack of supporting legislations- Despite the presence of multiple incentive schemes like mega food park scheme, the results have not been seen on the ground level as there is an absence of supporting legislation on contract farming, land leasing etc. There is also the irritant of inadequate implementation of the APMC act. (Agriculture Produce and Livestock Market Committee.)
- Lack of trained and skilled manpower- It also hampers the efficiency of this sector.
- Seasonality of raw material- The industry is based on agricultural and horticulture produce. The seasonality of the raw material makes it imperative for the units to hold a larger proportion of inventory. This increases the investment in inventory holding facilities at the premises and also blocks the capital. This is a big problem as the small and medium enterprises (SMEs) have limited financialcapacity.
- Access to Credit- Like in any other industry, the biggest challenge for any SME is access to credit. Even though the food processing industry has been included for priority sector lending, the credit facilities extended to the SMEs is still lower due to the inherent risk involved with small enterprises.
MP government efforts to enhance food processing industry
- Madhya Pradesh with the second largest geographical area in the country is one of the leading states in Agriculture. Of late it has acquired significant importance in the field of Horticulture and is now among the leading States in terms production of Fruits (Mango, Orange, Guava), Vegetables and Spices. The State is looking to march ahead with renewed vigour to face complex challenges and to harness domestic and global opportunities for the welfare of the farmers, consumers and other stakeholders in the supply chain. The efforts would be to become a leading state in the country which is responsive, vibrant and sensitive to the needs of its stakeholders. Food processing, one of the most important value addition activity connects all the stakeholders and can play a vital role in accomplishing these objectives. Therefore, State government has decided to give impetus to the sector and prepare a vision for way forward.
- To become favourable and leading food processing destination in the country and to increase agri-business activity in the state by increasing the level of processing of cereals and pulses from 20% to 25%, horticultural produce (fruits, vegetables and spices) from 0.7% to 2% and livestock produce from 12% to 24% by 2024.
- Tap production strength and locational advantage with an entrepreneurial touch for better and sustainable agricultural production and processing.
- To accomplish the vision and the mission of the food processing sector in the State, highest priority is given to farmers and processors, and entire strategy is based on 'farmers and processors'. State government is determined to continuously strive hard to transform the existing food processing environment into a vibrant food processing environment. It would concentrate on the following key areas-
- Promote processing cluster formation to improve farmer income and processing capacity in the state.
- Promote private sector participation through development of processing facilities in PPP mode.
- Promote and assist formation of cooperatives and societies to facilitate farmers of the state.
- Promote development/upgradation of marketing infrastructure to assist in better price realization to farmers and ensuring better raw material availability to" processors.
- Address skill gaps through establishing education institutes imparting education and research and enhance human resource befitting global competition.
Suggestions
- Storage capacities and infrastructure should be increased.
- Develop the agricultural facility with good agricultural practice which leads to the transition from staple food crops to diversification of crops.
- Backward linkages to farmers need to be made more robust. Contract farming can be promoted. According to the Model Contract Farming Act, 2018, the contract will specify the quantity, quality and price of produce being supplied. This would shield farmers from price volatility, subject to quality commitments.
- Skilling is required at two levels. First at the farm gate in promoting agricultural best practices and in processing activities.
- Public investment and connectivity should be increased.
- Slaughter animal rules should be framed in a comprehensive policy framework.
- Farm pattern diversification which leads to a production of variety of crops other than constant set of crops which creates lot of job opportunities.
- Second Green Revolution should be updated with the diversified technologies.
- We have to encourage the domestic startups and industry than the international companies.
- There should be a Centre of Excellence between centre and state.
- New technology should be updated in the training institutes and skill development should be given the top most priority.
Mineral Based Industries
These industries mostly located in the Western Madhya Pradesh. Major centres of such industries are in Pithampur, Dhar, Dewas, Indore, Ratlam, Mandideep, Rajgarh, Jhabua, etc. The major mineral based industries are:-

Cement Industry
Cement is indispensible for building and construction work and cement industry is considered to be an important infrastructure core industry. It is one of the most advanced industries of Madhya Pradesh. In a developing country like India, the cement industry can play a significant role in the overall economic growth. Limestone is found in abundance in Madhya Pradesh.
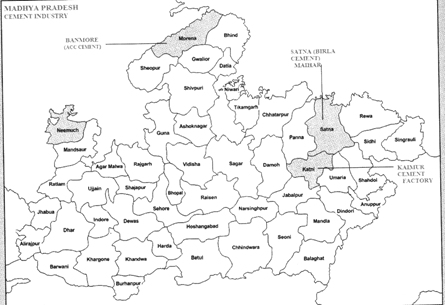
- Banmore Factory:-The first Cement Factory was established in the year 1922 in Morena district under the ownership of associated cement limited. It manufactures ordinary Portland cement.
- Kaimur Factor-Associated company limited had setup Portland & Porcelain Cement manufacturing Plant in Kami
- in 1923. It is also manufacturing Asbestos & Cement sheets.
- Satna Cement Works:-This is Portland cement manufacturing plant. It was setup by Birla Jute Manufacturing Company in 1959.
- Neemuch Factory:-It had been established in 1980-81 in Mandsaur District.
- Maihar Factory:- It had been established in 1980-81 in Satna District.
Locational factors
Manufacturing of cement requires heavy, low value and weight loosing materials and is primarily a raw material oriented industry. Availability of raw materials, bulk transport facilities at reasonably low cost and market are the three main localization factors, in that order, this favours the growth of cement industry in Madhya Pradesh.
- Raw Material: Limestone is the main raw material and comprises 60-65 per cent of the total product. On an average 1.5 tonnes of limestone are required to produce one tonne of cement. Hence, the location of a cement plant is based on the limestone deposits. Cement factories get limestone from Jabalpur, katni, satna, rewa and sidhi.
- Transport facilities: The transportation cost is also reduced if the manufacturing plant is located near the market. In fact ready market is the pre-requisite for the proper growth of an industry, producing heavy commodity with low specific cost like cement. For instance Kaimur cement plant located near the main Railway line by which it can easily get ready market.
- Availability of Capital- Government policies providing loan and low cost electricity affect cement Industry significantly.
- Availability of water- According to the figure put out by Cement Manufacture Association an average dry-process cement plant uses 100-200 liter water Per tonne of clinker produces.
- Low cost of energy: Power is used in raw material grinding, clinkerization of limestone in the kiln operation and clinker grinding along with gypsum to form cement. The older plants required 120 to 130 units per tonne of cement produced. Modem energy efficient plants consume only 80 to 90 units per tonne.
- Cheap Labour: Relatively lower cost and easy availability of the labour in Madhya Pradesh and nearby states has enabled the growth of the cement industries in the state.
- Availability of Market- Due to the large population in Madhya Pradesh, the market is available in large quantities.
China Clay Industry
- Availability of the China clay in the state has enabled the development of the China clay industries in Madhya Pradesh.
- In Gwalior, Jabalpur and Ratlam, some major China clay factories have been developed due to the easy available of China clay in the state.
Fire Clay Industry
- In Jabalpur and Katni, fire clay brick are manufactured. Fire clay is used in utensils like cups, plates, frays, pots, etc.
Fertilizer Industry
- This industry is located in Dharampuri (Indore) and Guna. Rock Phosphate found in Jhabua is used in fertilizer industry.
Diamond Industry
- There was one industrial scale diamond mine in India, the manjhgawan mine, near the town of panna, Madhya Pradesh. The mine is owned by the National Mineral Development Corporation and has a productive capacity of 84000 carats per year. The Diamond Cutting and polishing plant is set up at Pithampur by Vijay Kumar International.
Heavy Electric Appliances Industry
- In 1956, with the help of an Industry form Britain, Heavy Electronic Appliances Industry had been established in Bhopal. It has started production in 1960.
- In 1964 another company BHEL established successfully. It is known by the name of Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited (BHEL). In such factories, transformers, capacitors, switchgears, electric fraction, industial motors, etc are produced.
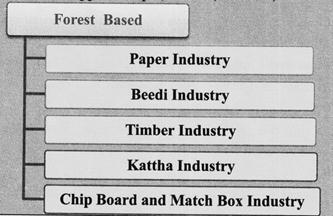
Forests Based Industries
Almost 30.7% of the geographical area of Madhya Pradesh is under forests. Though forest preservation is preferred over the forest based industries, still some major industries based on the byproduct of forest are-
Paper Industry
- The first paper mill in the state was National News Print and Paper Mill established at Nepanagar Burhanpur in 1948 near Khandwa and started its production from 1956. At present there are 9 registered paper mills in the state.
- Orient Paper Mill established at Arnlai near Shahdol district is the most important district is the most important of all. The Note Printing Press Mill setup in 1967-68 is located If Hoshangabad. Here, Currency Paper are manufactured mainly. Bank note press war established by government of India in 1974 at dewas, high denomination notes are printed here. On 30 May, 2015 a new paper line unit was started in Hoshangabad. Other paper mills are located in Anuppur, Bhopal, Ratlam, Gwalior, etc.
Locational factors of the pulp and paper industry are as follows:
- Raw Material: Wood is the primary raw material for this industry. Pulp mills must be located near the forests because this minimizes the difficulty of transporting the bulk logs as well as reduces cost also. The forest in the area must be extensive and capable of supplying large quantities of suitable timber. For Eg- Nepanagar mill get raw material from the forest of Stapura and Khandawa.
- Water: Paper industry requires a large quantity of water. To make 1 ton of newsprint, about 100 tons of water is needed, and since, it is essential to maintain a copious production, vast quantities of clear chemical free, fresh water must be available. These conditions are usually available in thinly populated forested areas rather than in major industrial complexes. For Eg- Nepanagar Industry got water from Tapti River and Oriental paper mill get water from Son River.
- Power: A ton of newsprint may require about 2,000 kilowatt hours of electricity and thus, vast power sources are essential. Paper plants show an affinity towards cheap hydel- power sources. For Eg- Oriental paper mill located near Thermal Power plant and Nepanagar paper Industry located near Chandni power plant.
- Transport: For steady supply of raw material, a good network of transport and communication is a prime requisite.
- Capital: Paper industry is a capital-intensive industry; therefore, large capital is required for sophisticated machinery and other works.
- Labour: Labour is available at the local level which helps in the smooth operation of industries.
Beedi Industry
- Madhya Pradesh is the first in the procurement of tendu leaves in the country. Approximately 50% of Tendu leaves are obtained from the forests of Madhya Pradesh which are used in the beedi industry.
- Beedi Rolling is a home based activity in M.P. and the system of production is through contractors or middlemen called sattedars or thekedars.
- In Madhya Pradesh beedi industry has been established in Satna, Jabalpur, Damoh, katni, Sagar, Chhatarpur etc. Around 280 factories related to beedi industry have been set up all over Madhya Pradesh.
Timber Industry
- In Chhindwara and Mandala, Timber industry is majorly established. Major furniture of Teak and Sal tree are made in the state and main centre is Jabalpur. Kattha Industry
- The Kattha industry is very well flourished in the state due to the abundance of Kattha frees in the state. It is majorly run by the tribes of Khairwar tribe. This industry is in Shivpuri and Banmore (Morena).
Chip Board and Match Box Industry
- The factory of chip board and match box is situated in Itarsi and Gwalior. Local raw materials are used in the factory.
Mineral Based Industries in Madhya Pradesh
|
Location
|
Industry
|
|
Katni
|
Asbestos cement sheet, Marble cutting and polishing, Thermal power, Cement, Hydrated lime, Refractory's
|
|
Rewa
|
Cement, Thermal power
|
|
Jabalpur
|
Ceramics, Refractory's
|
|
Satna
|
Cement, Thermal power, Hydrated lime
|
|
Betui
|
Thermal power
|
|
Ratlam
|
Ceramics. Refractory's
|
|
Ujjain
|
Thermal power, Potteries
|
|
Anuppur
|
Coal washeries
|
|
Hoshangabad
|
Roofing tiles
|
|
Mandsaur
|
Slate Pencil
|
|
Gwalior
|
Flagstone cutting and polishing
|
|
Chhindwara
|
Coal washeries
|
|
Balaghat
|
Roofing tiles
|
|
Tikamgarh
|
Granite cutting and polishing
|
|
Damoh
|
Cement, Thermal power
|
|
Umaria
|
Laakh
|
Other Important Industries
Some other important industries of Madhya Pradesh include cottage and small sale industries, Pharma industries, petro chemical industries, electronic industries, vehicle industries, etc. These are discussed below:
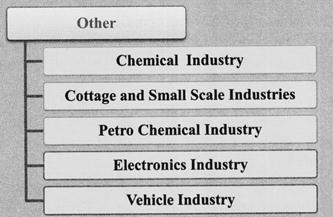
Chemical Industries
- In Ujjain, Pithampur, Mandideep, (Raisen) Baidhan, Maksi (Ujjain), Sehore, Ratlam, Panna, Nimach and other places, chemicals, fertilizers and pesticides manufacturing units have been developed.
- National fertilizer limited has established with the help of USA and Italy.
- In 2015 Fertilizer industry established in Jabalpur and Jhabua.
Cottage and Small Scale Industries
- Handicraft industries are cottage industries important in Madhya Pradesh. These are located in Chanderi (Ashoknagar), Maheshwar (Khargone) Burhanpur, Jabalpur.
- Various small and cottage industries are working which manufactures different items like jewellery from glass, pearls, diamond polish industries, embroidery on clothes, etc. Handloom garments like Chanderi saree is world famous. Bagh print and Bhairavgarh prints are equally important.
- Jewellery of Glass, Gems & Lakh, Diamond cutting & Polishing, Articles of khajoor leaves. Printing on Clothes, Wooden Toys, Furniture, Paper Manufacturing, leather works etc are other important Cottage industries of Madhya Pradesh.
Mrignayani Emporium
Madhya Pradesh Industries Authority conducts 10 emporiums in this name at Bhopal, Inore, Gwalior, Jabalpur, Raipur, Bhilai, Rewa, Ujjain, New Delhi and Kolkata, Here, the handicrafts made by cottage industries are sold.
Pharmaceutical Industries
- There are 26 pharma units across the state. Major centres are Bhopal, Indore, Chhindwara, Dewas, Dhar, Jabalpur, Kami, Malanpur and Pilukhedi.
Petro Chemical Industries
- In Bhopal, Mandia, Pithampur, Sehore and Jabalpur, the cooking gas filling stations are located.
Electronics Industries
- Television industry is located at Bhopal and Pithampur, television parts industry is located at Malanpur and photo copiers industry is located at Indore.
- Electronics complex is situated in Indore.
Vehicle Industries
- Pithampur near Indore is being developed as centre of the vehicle industry of the state. Here, scooters, cars, engines and light transport vehicles are manufactured. Hence it is called Detroit of India.
- At Jabalpur, the military vehicles production unit is located and in Betui and Pithampur tyres and tubes production are being carried out.
- Diesel fuel plant is situated in business capital of the state Indore, State's first diesel locomotive plant is situated in Sehore and Railway Wagon Workshop is situated in Bhopal.
Some other important industries
|
Industry
|
Place
|
|
Bicycle Industry
|
Guna
|
|
Metal Works (nails and wires)
|
Vidisha
|
|
Engineering Works
|
Indore
|
|
Agricultural Instruments
|
Khandwa
|
|
Brush and Sports Industry
|
Indore
|
|
Umbrella Industry
|
Mhow
|
|
Alcohol Plant and Carbon Dioxide Industries
|
Ratlam
|
Schemes for Industrial Development
Schemes for Industrial development in the state are as follows:
SEZ Indore Madhya Pradesh allotted 1113.72 hectares of land for SEZ. The land was allotted by Government of India, under SEZ, 2006 in Kalibillod in Indore and Kherabardari, Jamadi and Akoliya village in Dhar.
Pithampur Auto Cluster, Indore
- The auto cluster scheme is accepted by Government of India for Pithampur industriral areas. Total outlay of the project is Rs. 73.29 crores, which include the share of both State Government as well as Indian Government.
Food Park
- In Madhya Pradesh, there are 6 food parks developed by different industrial centres development corporations. These are Jaggakhedi (Mandsaur), Nimrani (Khargaun), Malanpur-Ghirongi (Bhind), Babai-Pipariya (Hoshangabad), Boregaon (Chhindwara) and Maneri (Manala).
- Madhya Pradesh got its first Mega Food Park at village Pahwa Tehsil Kasarwad, Khargone on February 2016.
Apparel Park
- Indian Government gave an approval for Apparel Park in Indore under SEZ.
- Industrial Infrastructure Zone (IIZ) Under IIZ, National Automative Testing and Infrastructure Project is development at Pithampur (Dhar).
- Methane Gas Pipeline Project
- A pipeline has been set up by Reliance Gas Limited under this project. It has been set up to transfer coal gas from Sohagpur (Shahdol) to Phulpur (Uttar Pradesh).
- Special Economic Zone is an area in which trade and business laws are different from the rest of the country. Economic zones are that areas where producers have world class infrastructure for production operations, such as-Roads, Rail communication. Uninterrupted power supply, Education, Health facilities etc.
- Designated duty-free industrial park to be treated as foreign territory for trade operations, duties and tariffs.
- No license required for import, i.e. Single window clearances.
- Exemption from custom duty on import of capital goods, raw materials, consumable spares etc.
- Exemption from central excise duty on procurement of capital goods, raw materials, consumables, spares etc. in the domestic market.
- Facilities like Bank, Insurance should be available at low cost.
- 100% Foreign Direct Investment in the manufacturing sector allowed, except few sectors.
- Profits allowed to be repatriated freely without any dividend balancing requirement.
- No routine examination by Customers of export and import cargo.
- No separate documentation required for customs and EXIM Policy.
- Developed Plots and ready to use build up space.
Special Economic Zone (SEZ) of Madhya Pradesh
- MP's first SEZ has been setup in Pithampur in Dhar district.
- So far 10 Special economic zones have been notified in Madhya Pradesh. Out of these, two areas have been established, while others are under construction or proposed.
Special Economic Zone (SEZ) in Madhya Pradesh
|
SEZ
|
Development Agency
|
Location
|
Present Status
|
|
Multi-product SEZ
|
Industrial Centre Development Authority, Indore
|
Dhar
|
Operational, First working Greenfield SEZ of the state
|
|
Crystal IT Park
|
Industrial Centre Development Authority, Indore
|
Indore
|
Operational
|
|
Multi-product SEZ, Gwalior
|
Industrial Centre Development Authority, Gwalior
|
Gwalior
|
Board of Approval, Commerce Ministry, Government of India recognized for ITSEZ
|
|
IT/ITE SEZ, Indore
|
Medicaps Limited, Indore
|
Indore
|
Board of Approval, Commerce Ministry Government of India recognise for ITSEZ
|
|
IT SEZ, Indore
|
Parshvanath Development Ltd, New Delhi
|
Indore
|
Board of Approval, Commerce Ministry, Government of India recognied for ITSEZ
|
|
Aluminium products based SEZ
|
Hindaico Industries
|
Singrauli
|
Board of Approval, Commerce Ministry, Government of India recognised for ITSEZ
|
|
Mining product-based SEZ and an produce based
|
Madhya Pradesh Audyogik Vikas Kendra
|
Hargarh Jabalpur
|
-
|
Dry port
- Madhya Pradesh is a land locked state. Instead of allowing this situation to become a obstacle, the state government has established dry ports at many places. These dry being established with various relaxations, are proving to be helpful in eliminating the problems of freight. As a result, many export oriented industries have come and coming in the state.
- Container depots have been established at Malanpur (Bhind), Mandideep (Raisen), Pawarkheda, Pithampur, Dhannad and Tihi.
Industrial Zones in Madhya Pradesh
Industries are located in various industrial zones in the state. Special facilities are provided by the government to develop industries in designated industrial areas around cities. Madhya Pradesh government has worked diligently over the past decade to develop the state as an industrial hub and promote it as a potential investment destination.
Opportunities
- Madhya Pradesh stands 4th among Indian states in Ease of doing business ranking conducted by World Bank and DIPP.
- Six Inland Container Depots (ICDs) have been established in the state.
- State falls under influence area of Delhi Mumbai Industrial Corridor (DMIC) and has developed industrial and investment regions like Pithampur-Dhar- Mhow, Ratlam-Nagda, Shajapur-Dewas and Neemach-Nayagaon along the corridor.
- State is developing four investment corridors (Bhopal-Indore, Bhopal-Bina, Jabalpur-Katni- Satni-Smgrauli, Morena-Gwalior- Shivpuri-Guna) to promote industrial development and employment opportunities.
Major Industrial zones are
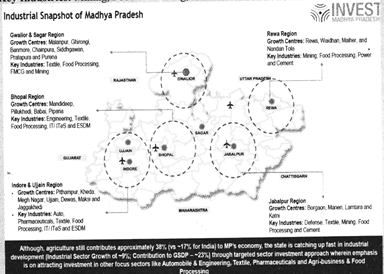
Gwalior & Sagar Region:
- Growth Centres: Malanpur, Ghirongi, Banmore, Chainpura, Siddhgawan, Pratapura and Morena.
- Key Industries: Textile, Food Processing, FMCG and Mining.
Bhopal Region:
- Growth Centres: Mandideep, Pilukhedi, Babai, Piparia.
- Key Industries: Engineering, Textile, Food Processing, IT/ ITs.
Indore & Ujjain Region:
- Growth Centres: Pithampur, Kheda, Megh Nagar, Ujjain, Dewas, Maksi and Jaggakhedi.
- Key Industries: Auto, Pharmaceuticals, Textile, Food Processing, IT/ ITs and Electronic System Design and Manufacturing.
Jabalpur Region
- Growth Centres: Boregaon, Maneri, Lamtara and Katni.
- Key Industries: Defense, Textile, Mining, Food Processing and Cement.
Rewa Region:
- Growth Centres: Rewa, Waidhan, Maihar, and NandanTola.
- Key Industries: Mining, Food Processing, Power and Cement.
Main Industrial Complexes of Madhya Pradesh
|
Complex
|
Location
|
|
Electronics Complex
|
Indore
|
|
Stainless Steel Complex
|
Sagar
|
|
Leather Complex
|
Dewas
|
|
Readymade Complex
|
Indore (Pardeshipura)
|
|
Textile Complex
|
Chhindwada
|
|
Pharma Park
|
Dhar (Betma)
|
|
Plastic Park
|
Raisen (Tamot)
|
Important Public Enterprises of State Government
|
Industry Name
|
Manufacture
|
Establishment Year
|
Location
|
|
Timber Treatment Plant
|
Timber wood
|
1952
|
Indore
|
|
Gwalior Leather Factory
|
Shoes, tent, canopy
|
1958
|
Gwalior
|
|
Calendaring Plant
|
Painting, bleaching finishing
|
1962
|
Ujjain
|
|
Sanawad Cutting Mill
|
Cotton thread
|
1963-64
|
Sanawad
|
|
Ratlam Alcohol Plant and Carbon dioxide (Co2) Industries
|
Sprit, alcohol and CO2
|
1963-64
|
Ratlam
|
Important Central-Public Sector Industries in Madhya Pradesh
|
Enterprises
|
Related Ministry
|
Establishment Year
|
Location
|
|
The new Bhopal Textile Limited
|
Nation Cloth and Industry Corporation
|
1938-39
|
Bhopal
|
|
Government Ordnance Factory
|
Ministry of Defence
|
1943-44
|
Khamaria
|
|
Government Post and Telegraph Workshop
|
Communications Ministry
|
1943-44
|
Jabalpur
|
|
Bharat Heavy Electrical Limited (BHEL)
|
Central Public Establishment Corporation
|
1961-62
|
Piplani (Bhopal)
|
|
Cotton Seed Solvent Extraction Plant
|
Ministry of Food Corporation
|
1963-64
|
Ujjain
|
|
Security Paper Mills
|
Ministry of Finance
|
1967-68
|
Hoshangabad
|
|
Beladeela Iron Project
|
Ministry of Mining
|
1967-68
|
Bacheli
|
|
Railway Coach Factory
|
Ministry of Railway
|
1975-76
|
Bhopal
|
|
Gun Carriage Factory
|
-
|
1943-44
|
Jabalpur
|
Central Government Ministerial Undertaking
|
Name
|
Location
|
|
Security Paper Mill
|
Hoshangabad
|
|
Bank Note Press
|
Dewas
|
|
Ordnance Factory
|
Katni
|
|
Defence Vehicle Factory
|
Jabalpur
|
|
Railway Zone
|
Jabalpur
|
|
Telecom Facory
|
Jabalpur
|
Central Public Sector Undertaking in Madhya Pradesh
|
Name
|
Location
|
|
Heawy Vehicle Factory
|
Jabalpur
|
|
Ordinance Factory
|
Itarsi
|
|
Ordinance Factory, Jabalpur
|
Khamariya
|
|
Rail Coach Repair workshop
|
Bhopal
|
|
Gray-Iron Foundary
|
Jabalpur
|
|
Name
|
Location
|
|
GAIL India Limited
|
Guna
|
|
Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited (BHEL)
|
Bhopal
|
|
Hindustan Copper Limited Malajkhnd
|
Balaghat
|
|
Northern Coal Fields Limited Singrauli
|
Sidhi
|
|
National Fertilizer Limited
|
Guna
|
|
Manganese Ore India Limited (MOIL)
|
Balaghat
|
|
National Thermal Power Corporation (NTPC)
|
Singrauli
|
Industries and their of Madhya Pradesh
|
City
|
Industry
|
|
Bhopal
|
Dry battery, Insecticides, Heavy Electricals Industries, Engine valve. Graphite electrode
|
|
Indore
|
Plate Round, Plastic, Art and Skill Fabrics, compressed, Oxygen and dissolve ethylene. Fine paper industry, Tungsten Filament Midweight electrodes, Rayon silk industry. Mini steel plant, Steel casting foundry and rerolling mills
|
|
Jabalpur
|
Gem refining centre, Gelatin factory, Government Post and Telegraph Workshop, Mini steel plant, Gun carriage factory, Transmission hovers, Ordnance factory
|
|
Gwalior
|
Textile Machinery, Biscuit factory, Moped unit. Rayon silk industry. Steel casting foundry and rerolling mill
|
|
Ratlam
|
Drugs and Pharmaceuticals, Mined steel and GI wire, Mini steel plant, Alcohol
|
|
Ujjain
|
Steel casting, foundry and rerolling mills, Synthetic fibre factory
|
|
Dewas
|
Steel casting foundry and rerolling mills, leather industry electrical pump, currency and Bank note press, and mini steel plant
|
|
Amlai
|
Paper mill. Caustic soda,
|
|
Shahdol
|
Orient paper mill, Coal mine industries
|
|
Nagada
|
Rayon silk industry, Synthetic fibre factory, Sulphuric acid. Caustic soda
|
|
Chhindwara
|
Coal mine industries,
|
|
Kumhari
|
Sulphuric acid, Steel casting foundry and rerolling mills
|
|
Pithampur
|
Automobile industry complex
|
|
Bhilai and Bangrod
|
Steel casting factory and rerolling mills
|
|
Mandideep in Raisen district
|
Optical fiber factory in collaboration with Japan Government
|
|
Betul
|
Coal mine industry. Watch factory
|
|
Vidisha
|
Nail and wire factory
|
|
Burhanpur
|
Power loom industry
|
|
Kaimur
|
Asbestos factory, Cement factory
|
|
Guna
|
Fertilizer factory
|
|
Sehore (Budhani)
|
Railway sleeper factory, Sugar mill, Diesel locomotive plant
|
|
Kailaras, Javara, Daloda, Dabra and Mahidpur
|
Sugar mill
|
|
Umaria
|
Lakh making factory
|
|
Sagar
|
Oil refinery
|
|
Rajgarh
|
Jute mills
|
|
Neemuch
|
Alkaloid factory
|
|
Satna, Maihar, Banmaur, Jamur and Silta
|
Cement factory
|
Special Initiative
Diesel Locomotive Plant
- For this project Land is acquitted in Sherpur (Sehore). A private firm Daulatram Engineer is developing this project with the help of National Railway Equipment Company (America)
Methane Gas Pipeline Project
- Coal gas is to be transferred from Sohagpur (Shahdol) to Phoolpur (Uttar Pradesh) and for this purpose; Reliance Gas Limited has set up a pipeline. Reliance Industries Sohagupur has planned to generate 3.5 million metric cubic metre of Gas through eastern & western Coal bed methane (CBM).
Bharat - Oman Refinery Ltd.
- An oil refinery of 6 million ton Capacity has been setup at Asagod in Bina.
Diesel Traction Alteration Factory
- This Factore was announced in Budget 2012-13 set up in Vidisha.
Summary
Agriculture Based Industries
- Sugar industry.
- Rice, Pulses and Straw Board Mill.
- Hydrogenated Oil Industry.
- Handloom Industry.
- Cotton Textile industry.
Sugar Industry
- The first sugar mill in the state was established at Jawra (Ratlam) in 1934, Since, sugarcane is cultivated majorly in the Western districts of the state, major sugar mills are situated in the Western districts of the state.
Rice, Pulses and Straw Board Mill
- Rice mills are located in Indore, Bhopal, Jabalpur and Rewa district.
- Pulses mills are located in Indore, Ujjain and Sagar district.
Hydrogenated Oil Industry
- Oilseeds and soybean are cultivated in the state on a mass scale. Hence, the production of hydrogenated oil is popular here.
- Most of the factories are situated in the oil producing belts of the state like Malwa Plateau, Betul-Chhindwara Plateau, Central Narmada Valley and Chambal Valley area.
Cotton Textile industry
- MP ranks third in the production of cotton.
- First cotton mill of the state was established in 1906 at Burhanpur.
- There are about 513 mills in the state and Indore is the largest centre of production of cotton in the state.
Factors for localization of-Textile Industry
- Raw material.
- Means of transport.
- Availability of cheap labour.
- Availability of capital and land,
- Market proximity.
- Availability of energy and water.
Food Processing Industries
- Food Processing includes process under which any raw product of agriculture, dairy, animal husbandry, meat, poultry or fishing is transformed through a process (involving employees, power, machines or money) in such a way that its original physical properties undergo a change and the transformed product has commercial value and is suitable for human and animal consumption.
Causes of backwardness of food processing Industry in Madhya Pradesh
- Fragmented land holdings.
- Infrastructure problems.
- Lack of regulation.
- Lack of logistics support.
- Lack of supporting legislations.
- Lack of trained and skilled manpower.
- Seasonality of raw material.
- Access to Credit.
Mineral Based Industries
- These industries mostly located in the Western Madhya Pradesh. Major centres of such industries are in Pithampur, Dhar, Dewas, Indore, Ratlam, Mandideep, Rajgarh, Jhabua, etc. The major mineral based industries are:
Cement Industry
- Cement is indispensible for building and construction work and cement industry is considered to be an important infrastructure core industry. It is one of the most advanced industries of Madhya Pradesh,
Locational factors
- Raw Material
- Transport facilities
- Low cost of energy
- Low Laboue cost
China Clay Industry
- Availability of the China clay in the state has enabled the development of the China clay industries in Madhya Pradesh.
Fire Clay Industry
- In Jabalpur and Kami, fire clay brick are manufactured. Fire clay is used in utensils like cups, plates, trays, pots, etc.
Fertilizer Industry
- This industry is located in Dharampuri and Guna. Rock Phosphate found in Jhabua is used in fertilizer industry.
Diamond Industry
- Diamond is excavated in Panna. Majhagawa Diamond mine is the first mechanical mine in Asia. The Diamond Cutting and polishing plant is set up at Pithampur by Vijay Kumar International
Beedi Industry
- Madhya Pradesh is the first in the procurement of tendu leaves in the country. Approximately 50% of Tendu leaves are obtained from the forests of Madhya Pradesh which are used in the beedi industry.
Locational factors of the pulp and paper industry
- Raw Material.
- Water.
- Power.
- Transport.
- Capital.
- Labour.
Timber Industry
- In Chhindwara and Mandala, Timber industry is majorly established. Major furniture of Teak and Sal tree are made in the state and main centre is Jabalpur
Chip Board and Match Box Industry
- The factory of chip board and match box is situated in Itarsi and Gwalior. Local raw materials are used in the factory.
- Cottage and Small Scale Industries
- Handicraft industries are cottage industries important in Madhya Pradesh. These are located in Chancery, Maheshwar, Burhanpur, Jabalpur.
- Various small and cottage industries are working in manufacturing different items like jewellery from glass, pearls, diamond polish industries, embroidery on clothes, etc Handloom garments like Chanderisaree is world famous. Bagh print and Bhairavgarh prints are equally important.
Pharmaceutical Industry
- There are 26 pharma units across the state. Major centres are Bhopal, Indore, Chhindwara, Dewas, Dhar, Jabalpur, Katni, Malanpur and Pilukheda.
Special Economic Zone
- A special economic zone is an area in which the business and trade laws are different from me rest of the country. SEZs are located within a country's national borders, and their aims include increased trade balance, employment, increased investment, job creation and effective administration.
Probable Questions
1. Very Short Questions
- Name three agro based industries in Madhya Pradesh.
- Name the mineral based industries in Madhya Pradesh.
- Give names of the important centers of the cement industries in Madhya Pradesh.
- Name industrial zones of Madhya Pradesh.
- Give names of the important centers of me Textile industry in Madhya Pradesh.
- Give names of the important centers of the Pharmaceutical industry in Madhya Pradesh.
- Plastic Park is located in which district of Madhya Pradesh?
- Give names of the important centers of the paper industry of Madhya Pradesh. (MPPSC 2018)
2. Short Questions
- What are the location factors behind the location of Paper industry in, Madhya Pradesh?
- Elaborate cottage industries in Madhya Pradesh.
- Discuss the locational factor behind the Sugar industry in Madhya Pradesh.
- Discuss the industrial development in Madhya Pradesh with special reference to Agro based Industries MPPSC 2014)
- Discuss cement industry of Madhya Pradesh. (MPPSC 2015)
- Give names of important centers of industry of Madhya Pradesh. (MPPSC 2018)
- Give detailed account of localization of cement industry in Madhya Pradesh. (MPPSC 2018)
- Describe in detail the industrial zones and their major industries in Madhya Pradesh. (MPPSC 2018)
3. Long Questions
- Throw light on the various efforts made by the Central and state governments to promote industries in Madhya Pradesh.
- What are the reasons for industrial backwardness?
- Write down the efforts made by M.P. government for Industrial promotion.
- What are the possibilities for industrial growth in state?
- Give a detailed account of industrial areas which have came up/developed around main cities of Madhya Pradesh. (MPPSC 2014)
- Describe in detail the industrial zones and their major industries in Madhya Pradesh. (MPPSC 2016)
- Describe agro-based industries of Madhya Pradesh. (MPPSC 2018)










