A) \[f=\frac{d}{{{m}_{1}}-{{m}_{2}}}\]
B) \[f=\frac{d}{{{m}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}}\]
C) \[f=\frac{{{m}_{1}}-{{m}_{2}}}{d}\]
D) either (a) and (b)
Correct Answer: A
Solution :
For the first position \[{{m}_{1}}=\frac{\upsilon }{u}\]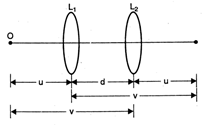 For the second position \[{{m}_{2}}=\frac{u}{\upsilon }\] From the lens formula \[f=\frac{u\upsilon }{u+\upsilon }\] or \[f=\frac{u\upsilon }{u+\upsilon }\times \frac{\upsilon -u}{\upsilon -u}\] \[=\frac{(\upsilon -u)}{({{\upsilon }^{2}}-{{u}^{2}})/u\upsilon }\] i.e., \[f=\frac{u-\upsilon }{\left( \frac{\upsilon }{u}-\frac{u}{\upsilon } \right)}\] But \[\upsilon -u=d\] \[\therefore \] \[f=\frac{d}{{{m}_{1}}-{{m}_{2}}}\]
For the second position \[{{m}_{2}}=\frac{u}{\upsilon }\] From the lens formula \[f=\frac{u\upsilon }{u+\upsilon }\] or \[f=\frac{u\upsilon }{u+\upsilon }\times \frac{\upsilon -u}{\upsilon -u}\] \[=\frac{(\upsilon -u)}{({{\upsilon }^{2}}-{{u}^{2}})/u\upsilon }\] i.e., \[f=\frac{u-\upsilon }{\left( \frac{\upsilon }{u}-\frac{u}{\upsilon } \right)}\] But \[\upsilon -u=d\] \[\therefore \] \[f=\frac{d}{{{m}_{1}}-{{m}_{2}}}\]
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
