A) \[C{{H}_{3}}-C{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{2}}\overset{\begin{smallmatrix} O \\ || \end{smallmatrix}}{\mathop{C}}\,-C{{H}_{3}}\]
B) \[{{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{2}}C=O\]
C) \[C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}CHO\]
D) \[C{{H}_{3}}CHO\]
Correct Answer: D
Solution :
| [d] | 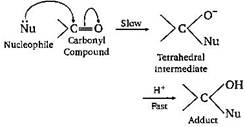 |
| The carbonyl compounds undergo nucleophilic addition reaction, because oxygen is more electronegative than carbon. As such, it withdraws shared it electron pair towards itself and gets partial negative charge, therefore carbon get partial positive charge and becomes susceptible to nucleophilic attack. | |
| Aldehydes are more reactive than ketones towards nucleophiles. This can be explained on the basis of inductive effect as well as steric effect. The addition of nucleophiles is based upon the positive charge present on carbon atom of | |
| Order of \[+I\] effect in alkly group | |
| | |
| order of nucleophilic addition in given carbonyl compound is | |
| \[C{{H}_{3}}CHO>C{{H}_{3}}-C{{H}_{2}}-CHO>{{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{2}}CO>\] | |
| \[\begin{align} & \,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,O \\ & C{{H}_{3}}-C{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{2}}-\overset{||}{\mathop{C}}\,-C{{H}_{3}} \\ \end{align}\] |
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
