A) \[\frac{\pi }{3},\frac{\pi }{6}\]
B) \[\frac{\pi }{4},\frac{\pi }{4}\]
C) \[\frac{\pi }{8},\frac{3\pi }{8}\]
D) \[\frac{\pi }{12},\frac{5\pi }{12}\]
Correct Answer: C
Solution :
We have, AD = p and \[BC=2\sqrt{2}p\] Clearly, \[p=a\sin \theta =b\cos \theta \]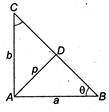 Since, \[{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}={{(2\sqrt{2}p)}^{2}}\] \[\Rightarrow \] \[{{p}^{2}}\left[ \frac{1}{{{\sin }^{2}}\theta }+\frac{1}{{{\cos }^{2}}\theta } \right]=8{{p}^{2}}\] \[\Rightarrow \] \[1=2{{\sin }^{2}}2\theta \Rightarrow \sin 2\theta \pm \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\] \[\Rightarrow \] \[\sin 2\theta =\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\Rightarrow 2\theta =\frac{\pi }{4}\Rightarrow \theta =\frac{\pi }{8}\] So, the other angle is \[\frac{\pi }{2}-\theta =\frac{\pi }{2}-\frac{\pi }{8}=\frac{3\pi }{8}\]
Since, \[{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}={{(2\sqrt{2}p)}^{2}}\] \[\Rightarrow \] \[{{p}^{2}}\left[ \frac{1}{{{\sin }^{2}}\theta }+\frac{1}{{{\cos }^{2}}\theta } \right]=8{{p}^{2}}\] \[\Rightarrow \] \[1=2{{\sin }^{2}}2\theta \Rightarrow \sin 2\theta \pm \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\] \[\Rightarrow \] \[\sin 2\theta =\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\Rightarrow 2\theta =\frac{\pi }{4}\Rightarrow \theta =\frac{\pi }{8}\] So, the other angle is \[\frac{\pi }{2}-\theta =\frac{\pi }{2}-\frac{\pi }{8}=\frac{3\pi }{8}\]
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
