A) catalyst
B) reducing agent
C) acid
D) base
Correct Answer: D
Solution :
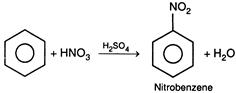 Nitrating mixture\[=HN{{O}_{3}}+{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}\]. \[HON{{O}_{2}}+\underset{Nitrating\text{ }mixture}{\mathop{{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}}}\,\xrightarrow[{}]{{}}HSO_{4}^{-}+\underset{\begin{smallmatrix} | \\ H \end{smallmatrix}}{\overset{\oplus }{\mathop{HO}}}\,-N{{O}_{2}}\] \[\underset{\begin{smallmatrix} | \\ H \end{smallmatrix}}{\overset{\oplus }{\mathop{HO}}}\,-N{{O}_{2}}\xrightarrow[{}]{{}}{{H}_{2}}O+\overset{\oplus }{\mathop{N{{O}_{2}}}}\,\] Here,\[{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}\]protonates\[HN{{O}_{3}}\]and causes the split of\[HN{{O}_{3}}\]in\[{{H}_{2}}O\]and\[\overset{\oplus }{\mathop{N{{O}_{2}}}}\,\] \[\therefore \]\[HN{{O}_{3}}\]behaves as a base and\[{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}\]behaves as acid.
Nitrating mixture\[=HN{{O}_{3}}+{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}\]. \[HON{{O}_{2}}+\underset{Nitrating\text{ }mixture}{\mathop{{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}}}\,\xrightarrow[{}]{{}}HSO_{4}^{-}+\underset{\begin{smallmatrix} | \\ H \end{smallmatrix}}{\overset{\oplus }{\mathop{HO}}}\,-N{{O}_{2}}\] \[\underset{\begin{smallmatrix} | \\ H \end{smallmatrix}}{\overset{\oplus }{\mathop{HO}}}\,-N{{O}_{2}}\xrightarrow[{}]{{}}{{H}_{2}}O+\overset{\oplus }{\mathop{N{{O}_{2}}}}\,\] Here,\[{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}\]protonates\[HN{{O}_{3}}\]and causes the split of\[HN{{O}_{3}}\]in\[{{H}_{2}}O\]and\[\overset{\oplus }{\mathop{N{{O}_{2}}}}\,\] \[\therefore \]\[HN{{O}_{3}}\]behaves as a base and\[{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}\]behaves as acid.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
