A)
 -730 J
-730 J
B) -365 J
C) -530 J
D) -1460 J
Correct Answer: A
Solution :
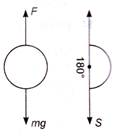
From work-energy theorem we have, work done = gain in kinetic energy ... (i) Also, work done W = force (F) \[\times \] displacement ...(ii) The net downward force is Mg - F From Eq. (ii), putting d = 20 m work done \[(W)=(mg-F)\times 20\] Gain in \[KE=\frac{1}{2}m{{v}^{2}}\] \[\therefore \] \[(mg-F)\times 20=\frac{1}{2}m{{v}^{2}}\] \[\Rightarrow \] \[mg-F=\frac{1}{40}m{{v}^{2}}\] \[\Rightarrow \] \[F=5\times 9.8-\frac{1}{40}\times 5\times {{10}^{2}}\] \[\Rightarrow \] F = 36.5 N Work done by push of air \[=Fs\,\cos \theta \] \[=36.5\times 20\times \cos {{180}^{o}}\] \[=-730\,J\]You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
