A) \[5\times {{10}^{-5}}\Omega \]
B) \[5\times {{10}^{-3}}\Omega \]
C) \[5\times {{10}^{-2}}\Omega \]
D) \[5\times {{10}^{-4}}\Omega \]
Correct Answer: D
Solution :
The resistance of the galvanometer \[G=50\Omega \] The current required for a full scale deflection \[{{I}_{FS}}=100\mu A\] \[\therefore \] The voltage applied across the galvanometer \[E=50\times 100\times {{10}^{-6}}\] \[=5\times {{10}^{-3}}V=5mV\]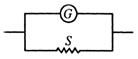 Now to convert this galvanometer into an ammeter we need to put a shunt S in parallel with the galvanometer. The total resistance will be determined by the maximum current read by the ammeter which is 10 A \[\therefore \] \[R=\frac{E}{I}=\frac{5\times {{10}^{-3}}}{10}=5\times {{10}^{-4}}\Omega \] We can find S from the relation \[\frac{1}{R}=\frac{1}{S}+\frac{1}{G}\] \[\Rightarrow \] \[\frac{1}{R}=\frac{1}{S}-\frac{1}{G}=\frac{1}{5\times {{10}^{-4}}}-\frac{1}{50}\] \[=\frac{{{10}^{5}}}{50}-\frac{1}{50}\overset{\sim }{\mathop{=}}\,\frac{{{10}^{5}}}{50}\] \[\therefore \] \[S=\frac{50}{{{10}^{5}}}=5\times {{10}^{-4}}\Omega \]
Now to convert this galvanometer into an ammeter we need to put a shunt S in parallel with the galvanometer. The total resistance will be determined by the maximum current read by the ammeter which is 10 A \[\therefore \] \[R=\frac{E}{I}=\frac{5\times {{10}^{-3}}}{10}=5\times {{10}^{-4}}\Omega \] We can find S from the relation \[\frac{1}{R}=\frac{1}{S}+\frac{1}{G}\] \[\Rightarrow \] \[\frac{1}{R}=\frac{1}{S}-\frac{1}{G}=\frac{1}{5\times {{10}^{-4}}}-\frac{1}{50}\] \[=\frac{{{10}^{5}}}{50}-\frac{1}{50}\overset{\sim }{\mathop{=}}\,\frac{{{10}^{5}}}{50}\] \[\therefore \] \[S=\frac{50}{{{10}^{5}}}=5\times {{10}^{-4}}\Omega \]
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
