A) {1, 3}
B) {0, 2}
C) {-1, 3}
D) {-3,-2}
Correct Answer: C
Solution :
\[\because \]A(h, k), B(1,1) and C(2,1) are the vertices of a right angled\[\Delta ABC\].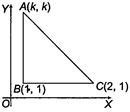 Now, \[AB=\sqrt{{{(1-h)}^{2}}+{{(1-k)}^{2}}}\] or \[BC=\sqrt{{{(2-1)}^{2}}+{{(1-1)}^{2}}}\] or \[CA=\sqrt{{{(h-2)}^{2}}+{{(k-1)}^{2}}}\] Now, by Pythagoras theorem, \[A{{C}^{2}}=A{{B}^{2}}+B{{C}^{2}}\] \[4+{{h}^{2}}-4h+{{k}^{2}}+1-2k\] \[={{h}^{2}}+1-2h+{{k}^{2}}+1-2k+1\] \[\Rightarrow \] \[5-4h=3-2h\Rightarrow h=1\] ...(i) Now, given that area of the triangle is 1. Then, area \[(\Delta ABC)=\frac{1}{2}\times AB\times BC\] \[1=\frac{1}{2}\times \sqrt{{{(1-h)}^{2}}+{{(1-k)}^{2}}}\times 1\] \[2=\sqrt{{{(1-h)}^{2}}+{{(1-k)}^{2}}}\] ...(ii) Putting\[h=1\]from Eq. (i), we get \[2=\sqrt{{{(k-1)}^{2}}}\] Squaring both sides, we get \[4={{k}^{2}}+1-2k\]or \[{{k}^{2}}-2k-3=0\] or \[(k-3)(k+1)=0\] So, \[k=-1,3\] Thus, the set of values of k is {-1, 3}.
Now, \[AB=\sqrt{{{(1-h)}^{2}}+{{(1-k)}^{2}}}\] or \[BC=\sqrt{{{(2-1)}^{2}}+{{(1-1)}^{2}}}\] or \[CA=\sqrt{{{(h-2)}^{2}}+{{(k-1)}^{2}}}\] Now, by Pythagoras theorem, \[A{{C}^{2}}=A{{B}^{2}}+B{{C}^{2}}\] \[4+{{h}^{2}}-4h+{{k}^{2}}+1-2k\] \[={{h}^{2}}+1-2h+{{k}^{2}}+1-2k+1\] \[\Rightarrow \] \[5-4h=3-2h\Rightarrow h=1\] ...(i) Now, given that area of the triangle is 1. Then, area \[(\Delta ABC)=\frac{1}{2}\times AB\times BC\] \[1=\frac{1}{2}\times \sqrt{{{(1-h)}^{2}}+{{(1-k)}^{2}}}\times 1\] \[2=\sqrt{{{(1-h)}^{2}}+{{(1-k)}^{2}}}\] ...(ii) Putting\[h=1\]from Eq. (i), we get \[2=\sqrt{{{(k-1)}^{2}}}\] Squaring both sides, we get \[4={{k}^{2}}+1-2k\]or \[{{k}^{2}}-2k-3=0\] or \[(k-3)(k+1)=0\] So, \[k=-1,3\] Thus, the set of values of k is {-1, 3}.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
