Answer:
Let H be the height and R be the radius of cylinder inscribed in the cone of height h and radius r. 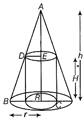 Curved surface area of cylinder \[S=2\pi RH\] ?(i) Since, \[\Delta ABC\sim \Delta ADE,\] \[\frac{AC}{AE}=\frac{BC}{DE}\] \[\Rightarrow \] \[\frac{h}{h-H}=\frac{r}{R}\] \[\Rightarrow \] \[\frac{h-H}{h}=\frac{R}{r}\] \[\Rightarrow \]\[1-\frac{H}{h}=\frac{R}{r}\] \[\Rightarrow \] \[1-\frac{R}{r}=\frac{H}{h}\] \[\Rightarrow \] \[H=h\left( 1-\frac{R}{r} \right)\] ...(ii) On putting the value of H in Eq. (i) we get \[S=2\pi Rh\left( 1-\frac{R}{r} \right)\]\[\Rightarrow \] \[S=2\pi h\left( R-\frac{{{R}^{2}}}{r} \right)\] ?(iii) On differentiating both sides w.r.t.R, we get \[\frac{dS}{dR}=2\pi h\left( 1-\frac{2R}{r} \right)\] For maximum or minimum curved surface area, we have \[\frac{dS}{dR}=0\] \[\Rightarrow \] \[2\pi h\left( 1-\frac{2R}{r} \right)=0\] \[\Rightarrow \] \[1-\frac{2R}{r}=0\] \[[\because h\ne 0]\] \[\Rightarrow \] \[1=\frac{2R}{r}\] \[\Rightarrow \]\[\frac{r}{2}=R\] Now, \[\frac{{{d}^{2}}S}{d{{R}^{2}}}=\frac{d}{dR}\left\{ 2\pi h\left( 1-\frac{2R}{r} \right) \right\}\] \[=2\pi h\left( 0-\frac{2}{r} \right)=-\frac{4\pi h}{r}\] \[\Rightarrow \] \[{{\left[ \frac{{{d}^{2}}S}{d{{R}^{2}}} \right]}_{R\,\,=\,\frac{r}{2}}}=-\frac{4\pi h}{r}<0\] \[\therefore \] Curved surface is maximum, when Hence proved.
Curved surface area of cylinder \[S=2\pi RH\] ?(i) Since, \[\Delta ABC\sim \Delta ADE,\] \[\frac{AC}{AE}=\frac{BC}{DE}\] \[\Rightarrow \] \[\frac{h}{h-H}=\frac{r}{R}\] \[\Rightarrow \] \[\frac{h-H}{h}=\frac{R}{r}\] \[\Rightarrow \]\[1-\frac{H}{h}=\frac{R}{r}\] \[\Rightarrow \] \[1-\frac{R}{r}=\frac{H}{h}\] \[\Rightarrow \] \[H=h\left( 1-\frac{R}{r} \right)\] ...(ii) On putting the value of H in Eq. (i) we get \[S=2\pi Rh\left( 1-\frac{R}{r} \right)\]\[\Rightarrow \] \[S=2\pi h\left( R-\frac{{{R}^{2}}}{r} \right)\] ?(iii) On differentiating both sides w.r.t.R, we get \[\frac{dS}{dR}=2\pi h\left( 1-\frac{2R}{r} \right)\] For maximum or minimum curved surface area, we have \[\frac{dS}{dR}=0\] \[\Rightarrow \] \[2\pi h\left( 1-\frac{2R}{r} \right)=0\] \[\Rightarrow \] \[1-\frac{2R}{r}=0\] \[[\because h\ne 0]\] \[\Rightarrow \] \[1=\frac{2R}{r}\] \[\Rightarrow \]\[\frac{r}{2}=R\] Now, \[\frac{{{d}^{2}}S}{d{{R}^{2}}}=\frac{d}{dR}\left\{ 2\pi h\left( 1-\frac{2R}{r} \right) \right\}\] \[=2\pi h\left( 0-\frac{2}{r} \right)=-\frac{4\pi h}{r}\] \[\Rightarrow \] \[{{\left[ \frac{{{d}^{2}}S}{d{{R}^{2}}} \right]}_{R\,\,=\,\frac{r}{2}}}=-\frac{4\pi h}{r}<0\] \[\therefore \] Curved surface is maximum, when Hence proved.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
