| Find the angle of intersection of the curves \[{{y}^{2}}=x\] and \[{{x}^{2}}=y.\] |
| OR |
| A metal box with a square base and vertical sides is to contain \[1024\,\,c{{m}^{3}}.\] If the material for the top and bottom costs Rs. 5 per \[c{{m}^{2}}.\] and the material for the sides Rs. 2.50 per \[c{{m}^{2}}\]. Then, find the least cost of the box. |
Answer:
equations of curves are \[{{y}^{2}}=x\] ? (i) and \[{{x}^{2}}=y\] ? (ii) On solving Eqs. (i) and (ii), we have \[{{x}^{4}}=x\] [Substituting the value of y from Eq. (ii) to Eq. (i)] \[\Rightarrow \] \[{{x}^{4}}-x=0\] \[\Rightarrow \] \[x({{x}^{3}}-1)=0\] \[\Rightarrow \] x = 0 or \[{{x}^{3}}=1\] \[\Rightarrow \] x = 0, 1 When x = 0, then y = 0 and when x = 1, then y = 1 Thus, points of intersection are (0, 0) and (1, 1). Now, consider \[{{y}^{2}}=x\] \[\Rightarrow \] \[2y\frac{dy}{dx}=1\] \[\Rightarrow \] \[\frac{dy}{dx}=\frac{1}{2y}\] and \[{{x}^{2}}=y\] \[\Rightarrow \] \[\frac{dy}{dx}=2x\] Now, at (1, 1), slope of tangent to the curve \[{{y}^{2}}=x\] is equal to \[\frac{1}{2}\] and that of \[{{x}^{2}}=y\] is 2. \[\therefore \] \[\tan \theta =\left| \frac{2-\frac{1}{2}}{1+2\cdot \frac{1}{2}} \right|=\frac{3}{4}\] \[\Rightarrow \] \[\theta ={{\tan }^{-1}}\frac{3}{4}\] \[\therefore \] Angle of intersection is \[{{\tan }^{-1}}\frac{3}{4}.\] Also, at (0, 0), slope of tangent to the curve \[{{y}^{2}}=x\] is parallel to Y-axis. and that of \[{{x}^{2}}=y\] is parallel to X-axis. \[\therefore \] Angle of intersection \[=\frac{\pi }{2}\] OR Given, volume of the box \[=1024\,\,c{{m}^{3}}.\] Let length of the side of square base be x cm and height of the box be y cm. 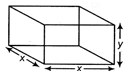
\[\therefore \] Volume of the box (V) \[={{x}^{2}}\cdot y=1024\] [given] \[\Rightarrow \] \[y=\frac{1024}{{{x}^{2}}}\] ? (i) Let C denotes the cost of the box. \[\therefore \] \[C=2{{x}^{2}}\times 5+4xy\times 2.50\] [total area of top and bottom \[=2{{x}^{2}}\] and area of one side = xy] \[=10{{x}^{2}}+10xy\] \[=10{{x}^{2}}+10x\left( \frac{1024}{{{x}^{2}}} \right)\] [from Eq. (i)] \[\Rightarrow \] \[C=10{{x}^{2}}+\frac{10240}{{{x}^{2}}}\] ? (ii) On differentiating both sides w.r.t. x, we get \[\frac{dC}{dx}=20x+10240{{(-x)}^{-\,2}}\] \[=20x-\frac{10240}{{{x}^{2}}}\] ? (iii) Now, for maxima or minima, put \[\frac{dC}{dx}=0\] \[\Rightarrow \] \[20x=\frac{10240}{{{x}^{2}}}\] \[\Rightarrow \] \[20{{x}^{3}}=10240\] \[\Rightarrow \] \[{{x}^{3}}=512={{8}^{3}}\] \[\Rightarrow \] x = 8 Again, differentiating Eq. (Hi) w.r.t. x, we get \[\frac{{{d}^{2}}C}{d{{x}^{2}}}=20-10240\,(-\,2)\cdot \frac{1}{{{x}^{3}}}\] \[=20+\frac{20480}{{{x}^{3}}}\] Now, \[{{\left( \frac{{{d}^{2}}C}{d{{x}^{2}}} \right)}_{x\,\,=\,\,8}}=20+\frac{20480}{512}=60>0\] Thus at x = 8, cost is minimum and the corresponding least cost of the box is \[C(8)=10.{{(8)}^{2}}+\frac{10240}{8}\] [from Eq. (ii)] \[=640+1280\] = Rs. 1920 .
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
