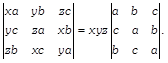
Answer:
Given, \[x+y+z=0\] Now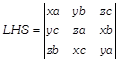 On expanding along \[{{R}_{1}}\]we get \[LHS=xa\,(yz{{a}^{2}}-{{x}^{2}}bc)-yb\,({{y}^{2}}ac-xz{{b}^{2}})\] \[+zc\,(xy{{c}^{2}}-{{z}^{2}}ab)\] \[=xyz{{a}^{3}}-{{x}^{3}}abc-{{y}^{3}}abc+xyz{{b}^{3}}+xyz{{c}^{3}}-{{z}^{3}}abc\] \[=xyz\,({{a}^{3}}+{{b}^{3}}+{{c}^{3}})-abc\,({{x}^{3}}+{{y}^{3}}+{{z}^{3}})\] ?(i) According to the question,\[x+y+z=0\] \[\therefore \] \[{{x}^{3}}+{{y}^{3}}+{{z}^{3}}=3xyz\] On putting the value of \[{{x}^{3}}+{{y}^{3}}+{{z}^{3}}\]in Eq. (i), we get \[LHS=xyz\,({{a}^{3}}+{{b}^{3}}+{{c}^{3}})-abc\,(3xyz)\] \[=xyz\,({{a}^{3}}+{{b}^{3}}+{{z}^{3}}-3abc)\] Now,
On expanding along \[{{R}_{1}}\]we get \[LHS=xa\,(yz{{a}^{2}}-{{x}^{2}}bc)-yb\,({{y}^{2}}ac-xz{{b}^{2}})\] \[+zc\,(xy{{c}^{2}}-{{z}^{2}}ab)\] \[=xyz{{a}^{3}}-{{x}^{3}}abc-{{y}^{3}}abc+xyz{{b}^{3}}+xyz{{c}^{3}}-{{z}^{3}}abc\] \[=xyz\,({{a}^{3}}+{{b}^{3}}+{{c}^{3}})-abc\,({{x}^{3}}+{{y}^{3}}+{{z}^{3}})\] ?(i) According to the question,\[x+y+z=0\] \[\therefore \] \[{{x}^{3}}+{{y}^{3}}+{{z}^{3}}=3xyz\] On putting the value of \[{{x}^{3}}+{{y}^{3}}+{{z}^{3}}\]in Eq. (i), we get \[LHS=xyz\,({{a}^{3}}+{{b}^{3}}+{{c}^{3}})-abc\,(3xyz)\] \[=xyz\,({{a}^{3}}+{{b}^{3}}+{{z}^{3}}-3abc)\] Now, 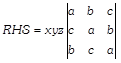 On expanding along \[{{R}_{1}}\]we get \[LHS=xyz\,[a\,({{a}^{2}}-bc)-b\,(ac-{{b}^{2}})+c\,({{c}^{2}}-ab)]\] \[=xyz\,[{{a}^{3}}-abc-abc+{{b}^{3}}+{{c}^{3}}-abc]\] \[=xyz\,({{a}^{3}}+{{b}^{3}}+{{c}^{3}}-3abc)=LHS\] \[\therefore \] \[LHS=RHS\] Hence proved.
On expanding along \[{{R}_{1}}\]we get \[LHS=xyz\,[a\,({{a}^{2}}-bc)-b\,(ac-{{b}^{2}})+c\,({{c}^{2}}-ab)]\] \[=xyz\,[{{a}^{3}}-abc-abc+{{b}^{3}}+{{c}^{3}}-abc]\] \[=xyz\,({{a}^{3}}+{{b}^{3}}+{{c}^{3}}-3abc)=LHS\] \[\therefore \] \[LHS=RHS\] Hence proved.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
