| The term 'biodiversity' is used to describe the diversity at all levels of biological organisation ranging from macromolecules inside the cells to biomes. What are the three inter - related hierarchial levels of diversity? |
| Or |
| (i) Draw an ideal pyramid of energy upto four trophic levels where 1,000,000 J energy is available (from sunlight) to the primary producers. Indicate the amount of energy available at each trophic level. |
| (ii) State the relation between gross and net primary productivity. |
| (iii) State what standing state of a trophic level represents. |
Answer:
Biodiversity refers to the variety and variability of living organisms on the planet earth. The three interrelated hierarchial levels of the diversity are as follows 1. Genetic Diversity A single species shows high diversity at the gene level. There are more than 20000 species of ants, 30000 species of beetles, 28000 species of fishes and nearby 20000 species of orchids. Greater the genetic diversity among organisms of a species, more sustance it has against the environmental disturbances. Genetic diversity within the species creates different sub-species, variety, breed, forms, etc. India has more than 50000 genetically different strains of rice and 1000 varieties of mango. 2. Species Diversity It is the measure of the variety of species and their relative abundance present within a region, e.g. Western ghats has more amphibian species than Eastern ghats. Two important measures of species diversity are (i) Species richness It refers to the number of species per unit area. Species diversity increases, if the species richness is higher. (ii) Species evenness It refers to the relative abundance of species in an area. The number of individuals and varieties determines the level of diversity of an ecosystem. 3. Ecological Diversity It refers to the diversity of different types of species present in the environment. It is also related to the genetic diversity at ecological level. Due to the presence of more variety of ecosystems and habitats, i.e. rainforest, desert, wetlands, mangroves, coral reefs, alpine meadows, etc. India has a greater ecological diversity than Scandinavian countries. Or (i) 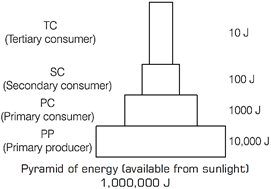
(ii) The relationship between gross and net primary productivity can be explained by the given equation GPP - R= NPP While, GPP is total amount of organic matter produced during photosynthesis and NPP is same amount of organic matter (biomass) for the consumption of heterotrophs, except for some respiratory losses, i.e. energy utilised by plants during respiration. (iii) Standing crop of a trophic level represents the amount of living matter or biomass at a given time.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
