A) 2
B) 4
C) 8
D) 16
Correct Answer: C
Solution :
| [c] From the figure |
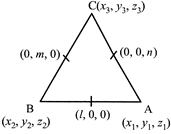 |
| \[{{x}_{1}}+{{x}_{2}}=21,{{y}_{1}}+{{y}_{2}}=0,{{z}_{1}}+{{z}_{2}}=0\] |
| \[{{x}_{2}}+{{x}_{3}}=0,{{y}_{2}}+{{y}_{3}}=2m,{{z}_{1}}+{{z}_{3}}=0\] |
| and \[{{x}_{1}}+{{x}_{3}}=0,{{y}_{1}}+{{y}_{3}}=0,{{z}_{1}}+{{z}_{3}}=2n\] |
| On solving, we get \[{{x}_{1}}=l,{{x}_{2}}=l,{{x}_{3}}=-1\] |
| \[{{y}_{1}}=-m,{{y}_{2}}=m,{{y}_{3}}=m\] and \[{{z}_{1}}=n,{{z}_{2}}=-n,{{z}_{3}}=n\] |
| \[\therefore \] Coordinates are \[A(l,-m,n),\,B(l,m,-n)\] and \[C(-l,m,n)\] |
| \[\therefore \frac{A{{B}^{2}}+B{{C}^{2}}+C{{A}^{2}}}{{{l}^{2}}+{{m}^{2}}+{{n}^{2}}}\] |
| \[=\frac{(4{{m}^{2}}+4{{n}^{2}})+(4{{l}^{2}}+4{{n}^{2}})+(4{{l}^{2}}+4{{m}^{2}})}{{{l}^{2}}+{{m}^{2}}+{{n}^{2}}}=8\] |
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
