A) \[\left( -\frac{1}{2},\frac{1}{2} \right)\]
B) \[\left[ -\frac{1}{2},\frac{1}{2} \right]\]
C) \[\left( -\frac{1}{2},\frac{1}{2} \right)-\{0\}\]
D) \[\left\{ -\frac{1}{2},0,\frac{1}{2} \right\}\]
Correct Answer: C
Solution :
[c] \[\int\limits_{2}^{x}{g(t)dt=\frac{{{x}^{2}}}{2}+\int\limits_{x}^{2}{{{t}^{2}}g(t)dt}}\] Differentiating w.r.t. x, we get \[g(x)=x+(-{{x}^{2}}(g(x))\Rightarrow g(x)=\frac{x}{1+{{x}^{2}}}\]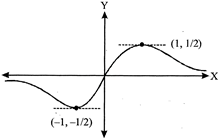 Clearly from graph, \[\alpha \in \left( -\frac{1}{2},\frac{1}{2} \right)-\{0\}\]
Clearly from graph, \[\alpha \in \left( -\frac{1}{2},\frac{1}{2} \right)-\{0\}\]
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
