A) 16/25
B) 2/5
C) 3/5
D) 9/25
Correct Answer: B
Solution :
If ball falls from height \[{{h}_{1}}\] and bounces back up to height \[{{h}_{2}}\] then \[e=\sqrt{\frac{{{h}_{2}}}{{{h}_{1}}}}\]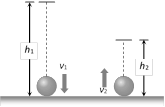 Similarly if the velocity of ball before and after collision are \[{{v}_{1}}\] and \[{{v}_{2}}\] respectively then \[e=\frac{{{v}_{2}}}{{{v}_{1}}}\] So \[\frac{{{v}_{2}}}{{{v}_{1}}}=\sqrt{\frac{{{h}_{2}}}{{{h}_{1}}}}=\sqrt{\frac{1.8}{5}}=\sqrt{\frac{9}{25}}=\frac{3}{5}\] i.e. fractional loss in velocity \[=1-\frac{{{v}_{2}}}{{{v}_{1}}}=1-\frac{3}{5}=\frac{2}{5}\]
Similarly if the velocity of ball before and after collision are \[{{v}_{1}}\] and \[{{v}_{2}}\] respectively then \[e=\frac{{{v}_{2}}}{{{v}_{1}}}\] So \[\frac{{{v}_{2}}}{{{v}_{1}}}=\sqrt{\frac{{{h}_{2}}}{{{h}_{1}}}}=\sqrt{\frac{1.8}{5}}=\sqrt{\frac{9}{25}}=\frac{3}{5}\] i.e. fractional loss in velocity \[=1-\frac{{{v}_{2}}}{{{v}_{1}}}=1-\frac{3}{5}=\frac{2}{5}\]
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
