| Directions : (11-15) |
| Helical Motion |
| The path of a charged particle in magnetic field depends upon angle between velocity and magnetic field. |
| If velocity \[\overrightarrow{v}\] is at angle \[\theta \] to \[\overrightarrow{B}\] component of velocity parallel to magnetic field \[\left( v\,\sin \theta \right)\]reamains constant and component of velocity perpendicular to magnetic field (v sin\[\theta \]) is responsible for circular motion, thus the charge particle moves in a helical path. |
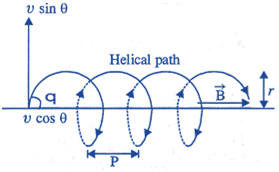 |
| The plane of the circle is perpendicular to the magnetic field and the axis of the helix is parallel to the magnetic field. |
| The charged particle moves along helical path touching the line parallel to the magnetic field passing through the starting point after each rotation. |
| Radius of circular path is \[r=\frac{mv\,\sin \theta }{qB}\] |
| Hence the resultant path of the charged particle will be a helix, with its axis along the direction of \[\overrightarrow{B}\] as shown in figure. |
A) (i) only
B) (i) or (ii)
C) (i) or (iii)
D) any one of (i), (ii) and (iii).
Correct Answer: D
Solution :
any one of (i), (ii) and (iii).You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
