| Direction: Q.16 to Q.20 |
| The resistance of a conductor at temperature \[t{}^\circ C\]is given by \[{{R}_{t}}={{R}_{0}}(1+\alpha t)\] |
| where R, is the resistance at t° C, Ry is the resistance at \[0{}^\circ C\] and \[\alpha \] is the characteristics constants of the material of the conductor. |
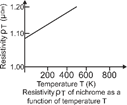
| Over a limited range of temperatures, that is not too large. The resistivity of a metallic conductor is approximately given by \[{{\rho }_{t}}={{\rho }_{0}}(1+\alpha t)\]. |
| where, \[\alpha \] is the temperature coefficient of resistivity. Its unit is \[{{K}^{-1}}\] or \[{}^\circ {{C}^{-1}}\]. |
| For metals, a is positive i.e., resistance increases with rise in temperature. |
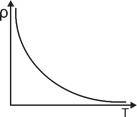
| For insulators and semiconductors, \[\alpha \] is negative i.e., resistance decreases with rise in temperature. |
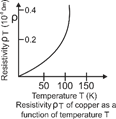  |
 |
| Read the above passage carefully and give the answer of the following questions. |
A) resistivity
B) temperature coefficient of resistivity
C) conductivity
D) drift velocity
Correct Answer: B
Solution :
(b) temperature coefficient of resistivity Temperature coefficient of resistivity is defined as the fractional increase in resistivity per unit increase in temperature.You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
