Answer:
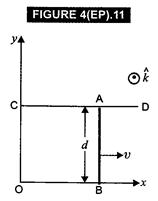
In Fig. 4(EP). 11, we
have shown a wire AB of length ![]() = d,
resistance R moving with a velocity
= d,
resistance R moving with a velocity ![]() along positive
direction of X-axis over two parallel wires OX and CD at y = 0 and y = d
respectively.
The
magnetic field covering the region is
along positive
direction of X-axis over two parallel wires OX and CD at y = 0 and y = d
respectively.
The
magnetic field covering the region is![]() At
t = 0, AB is at
At
t = 0, AB is at ![]() = 0 and velocity
=
= 0 and velocity
= ![]() At
t = t, AB is at
At
t = t, AB is at ![]() =
= ![]() t
Motional
emf in AB =
t
Motional
emf in AB = ![]() Its
direction, as per Fleming's right hand rule is along negative y-axis.
e.m.f.
due to change in magnetic field =
Its
direction, as per Fleming's right hand rule is along negative y-axis.
e.m.f.
due to change in magnetic field =![]() It
is also along negative y-axis.
It
is also along negative y-axis.
![]() total e.m.f. induced =
total e.m.f. induced =
![]()
![]() Current
induced,
Current
induced,![]() The
direction of current is clockwise, i.e., along ABOC (absorbing negative sign).
The
direction of current is clockwise, i.e., along ABOC (absorbing negative sign).
![]() Force needed along
Force needed along ![]() ; F =
; F = ![]() F =
F = ![]() F =
F = ![]()
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
