 Fig. 6.48
Fig. 6.48
Answer:
(a) Heat energy required for the burning of the casing of a
rocket in flight is obtained from the rocket itself. It is obtained at the
expense of the mass of the rocket and its kinetic and potential energies.
(b) The gravitational force acting on
the comet is a conservative force. The work done by a conservative over any
path is equal to the negative of the change in P.E. Over a complete orbit of
any shape, there is no change in P.E. of the comet. Hence no work is done by
the gravitational force on the comet.
(c) As the satellite comes
closer to the earth, its potential energy decreases. As the sum of kinetic and potential
energy remains constant, the kinetic energy and velocity of the satellite
increase. But the total energy of the satellite goes on decreasing due to the
loss of energy against friction.
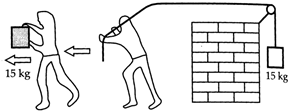
(d) In case (i), no work is done
against gravity because he displacement of 2 m (horizontal) and the weight of 15
kg (acting vertically downwards) are perpendicular to each other. Work is done
only against friction.
In case (ii), work has to be done
against gravity ![]() in
addition to the work to be lone against friction while moving a distance of 2
m. Thus lie work done in case (ii) is greater than that in case (i).
in
addition to the work to be lone against friction while moving a distance of 2
m. Thus lie work done in case (ii) is greater than that in case (i).
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
