Answer:
Experiments show that electrons are
ejected from the surface of certain metals (like Cs, K and Rb having low ionisation
energies) when they are illuminated by light or any other radiation of suitable
frequency or wavelength. This phenomenon is known as photoelectric effect.
The electrons so emitted are called photoelectrons.
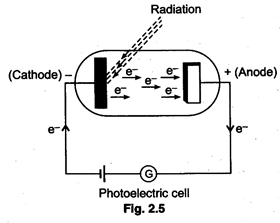
The experiment is carried out in
a photoelectric cell which consist or an evacuated glass tube fitted with two electrodes
connected through an outer circuit as shown in figure given below. The cathode
is coated with a metal such as caesium. When light of sufficiently high energy,
i.e., high frequency strikes the metal, the electrons are ejected as shown in
the figure and move towards anode and a current flows through the circuit.
 Absorbed quantum = Threshold +
Kinetic Energy
\[E\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,=\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,{{E}_{0}}+KE\]
\[hv\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,=\,\,\,h{{v}_{0}}+\frac{1}{2}m{{\upsilon
}^{2}}\]
\[h\frac{c}{\lambda
}=h\frac{c}{{{\lambda }_{0}}}+\frac{1}{2}m{{\upsilon }^{2}}\]
Maxwell theory of light
explained its rectilinear propogation, reflection, refraction, interference,
diffraction, polarisation etc. quite successfully but it failed to explain
black body radiation and photoelectric effect.
Absorbed quantum = Threshold +
Kinetic Energy
\[E\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,=\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,{{E}_{0}}+KE\]
\[hv\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,=\,\,\,h{{v}_{0}}+\frac{1}{2}m{{\upsilon
}^{2}}\]
\[h\frac{c}{\lambda
}=h\frac{c}{{{\lambda }_{0}}}+\frac{1}{2}m{{\upsilon }^{2}}\]
Maxwell theory of light
explained its rectilinear propogation, reflection, refraction, interference,
diffraction, polarisation etc. quite successfully but it failed to explain
black body radiation and photoelectric effect.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
