Answer:
(a) Arithmetic growth In arithmetic growth, following mitotic cell division, only one daughter cell continues to divide while the other differentiates and matures. Example is a root elongating at a constant rate.
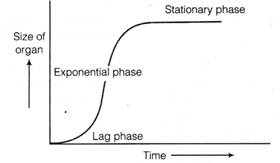
(b) Geometric growth In geometrical growth, in most systems, the initial growth is slow (lag phase), and it increases rapidly thereafter at an exponential rate (log or exponential phase). Here, both the progeny cells following mitotic cell division retain the ability to divide and continue to do so.
(c) Sigmoid growth curve If we plot the parameter of growth against time, we get a typical sigmoid or S-curve. A Sigmoid curve is a characteristic of living organism growing in a natural environment. It is typical for all cells, tissues and organs of a plant.
 (d) Absolute and relative growth rates The measurement and the comparison of total growth per unit time is called the absolute growth rate. And the growth of the given system per unit time expressed on a common basis, e.g., per unit initial parameter is called the relative growth rate.
(d) Absolute and relative growth rates The measurement and the comparison of total growth per unit time is called the absolute growth rate. And the growth of the given system per unit time expressed on a common basis, e.g., per unit initial parameter is called the relative growth rate.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
