-
question_answer1)
Statement I: The plane containing the incident ray and the normal is called plane of incidence. Statement II: The plane containing the incident ray and the normal is called plane of reflection.
A)
Both Statements are true, Statement-II is the correct explanation of Statement-I. done
clear
B)
Both Statements are true. Statement-II is not correct explanation of Statement-I. done
clear
C)
Statement-I is true, Statement-II is false. done
clear
D)
Statement-I is false. Statement-II is true. done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer2)
When the rays of light, diverging from a point, after reflection or refraction, appear to diverge from another point, then the image so formed is called
A)
Virtual image done
clear
B)
Real image done
clear
C)
Both (a) and (b) done
clear
D)
Neither (a) nor (b) done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer3)
When the rays of light, diverging from a point, after reflection or refraction actually converge at some other point then that point is ___ image of the object
A)
Virtual done
clear
B)
Real done
clear
C)
Both (a) and (b) done
clear
D)
Neither (a) nor (b) done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer4)
You are standing in front of a plane mirror, which is approaching you with a speed of 10cm/sec. Then the speed of the image approaching you will be
A)
20 cm/s done
clear
B)
10 cm/s done
clear
C)
15 cm/s done
clear
D)
25 cm/s done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer5)
A lady dressed in a new sari stands in front of a plane mirror fixed on a vertical wall, height of the lady is 160 cm and that of her eyes from the ground is 150 cm, then The length of the mirror required to see her fall view in the mirror is
A)
160 cm done
clear
B)
100 cm done
clear
C)
80 cm done
clear
D)
320 cm done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer6)
In the above problem, find the position of lower edge of the mirror relative to the ground is
A)
160 cm done
clear
B)
75 cm done
clear
C)
100 cm done
clear
D)
200 cm done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer7)
A lady dressed in a new sari stands in front of a plane mirror fixed on a vertical wall, height of the lady is 160 cm and that of her eyes from the ground is 150 cm, then find the position of upper edge of the mirror relative to the ground is
A)
155 cm done
clear
B)
160 cm done
clear
C)
100 cm done
clear
D)
200 cm done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer8)
Statement I: A concave mirror has a real focus. Statement II: A convex mirror has a virtual focus.
A)
Both Statements are true. Statement-II is the correct explanation of Statement-I. done
clear
B)
Both Statements are true. Statement-II is not correct explanation of Statement-I. done
clear
C)
Statement-I is true. Statement-II is false. done
clear
D)
Statement-I is false. Statement-II is true. done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer9)
The image formed by a convex mirror of real object is larger than the object.
A)
When u < 2f done
clear
B)
When u > 2f done
clear
C)
for all values ofu done
clear
D)
for no value of u done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer10)
Statement I: The radius of curvature and focal length of convex mirror are 80 cm and 40 cm Statement II: The relation between radius of curvature and focal length is R = 2f.
A)
Both Statements are true, Statement-II is the correct explanation of Statement-I. done
clear
B)
Both Statements are true, Statement-II is not correct explanation of Statement-I. done
clear
C)
Statement-I is true. Statement-II is false. done
clear
D)
Statement-I is false. Statement-II is true. done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer11)
The property that which a light a ray passes obliquely from one medium into another it bends at interface is
A)
Reflection done
clear
B)
Refraction done
clear
C)
Interference done
clear
D)
Polarization done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer12)
Light starting from a medium of refractive index \[\mu \] undergoes refraction into a medium \[{{\mu }^{\text{l}}}\] If i and r stand for angles of incidence and refraction respectively, then
A)
\[\frac{\sin i}{\sin r}=\frac{\mu }{{{\mu }^{\text{l}}}}\] done
clear
B)
\[\frac{\sin i}{\sin r}=\frac{{{\mu }^{\text{l}}}}{\mu }\] done
clear
C)
\[\frac{\cos i}{\cos r}=\frac{{{\mu }^{\text{l}}}}{\mu }\] done
clear
D)
\[\frac{sini}{sinr}=\frac{1}{\mu {{\mu }^{\text{l}}}}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer13)
When a light ray passes from one medium \[({{\mu }_{1}})\] to other medium \[({{\mu }_{2}})\]. Refraction does not take place in the following situation.
A)
for normal incidence done
clear
B)
\[{{\mu }_{1}}>{{\mu }_{2}}\] done
clear
C)
\[{{\mu }_{1}}={{\mu }_{2}}\] done
clear
D)
\[{{\mu }_{1}}<{{\mu }_{2}}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer14)
Light of the wave length \[7200{{A}^{o}}\] in air has a wave length in glass is equal to (\[\mu =1.5\])
A)
\[7200\overset{\text{o}}{\mathop{\text{A}}}\,\] done
clear
B)
\[4800\overset{\text{o}}{\mathop{\text{A}}}\,\] done
clear
C)
\[1080\overset{\text{o}}{\mathop{\text{A}}}\,\] done
clear
D)
\[3600\overset{\text{o}}{\mathop{\text{A}}}\,\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer15)
A ray of light incident on a refracting surface. If the angle of incidence \[{{60}^{o}}\] and the angle of refraction is \[{{45}^{o}}\], then angle of deviation is
A)
\[{{30}^{o}}\] done
clear
B)
\[{{90}^{o}}\] done
clear
C)
\[{{15}^{o}}\] done
clear
D)
\[{{0}^{o}}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer16)
The velocity of light in air is \[3\times {{10}^{8}}m{{s}^{-1}}\] and in glass is \[2\times 108m{{s}^{-1}}\].. The refractive index of glass w.r.t air is
A)
2/3 done
clear
B)
3/2 done
clear
C)
4/3 done
clear
D)
9/4 done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer17)
A fish is raising vertically to the surface of water in a lake uniformly at the rate of \[2m{{s}^{-1}}\] observes a bird diving vertically towards the water at a rate \[4m{{s}^{-1}}\] vertically above it. The refractive index of water is 4/3. The actual velocity of the bird is
A)
3/2 done
clear
B)
2/3 done
clear
C)
4/3 done
clear
D)
3/4 done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
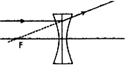
question_answer18)
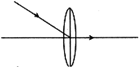
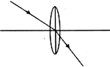
Which of the following diagrams correctly represents the ray of light passing through the optical centre?
A)
B)
C)
D)
View Solution play_arrow
-
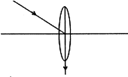
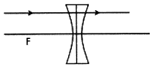
question_answer19)
A ray of light is incident on a concave lens parallel to its principal axis. The path of the refracted ray is correctly depicted by
A)
B)
C)
D)
View Solution play_arrow
-
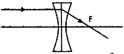
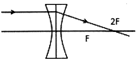
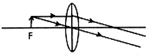
question_answer20)
An object AB is placed in front of a convex lens at its principal focus as shown in the Figure.
Which of the ray diagram given below correctly depicts the refraction through the lens L?
A)
B)
C)
D)
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer21)
Which of the following parts of the eye has enormous number of photo-sensitive cells?
A)
Iris done
clear
B)
Pupil done
clear
C)
Retina done
clear
D)
Cornea done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer22)
The focal length of the eye lens is adjusted by the
A)
vitreous humour done
clear
B)
aqueous humour done
clear
C)
ciliary muscles done
clear
D)
optic nerves done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer23)
In the human eye, the function of the optic nerves is to
A)
adjust the focus of the eye lens done
clear
B)
transmit electrical signals to the brain done
clear
C)
control the number of rod and cone cells done
clear
D)
convert light signals into electrical signals done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer24)
The primary function of the crystalline lens in the human eye is to
A)
reduce the intensity of light done
clear
B)
focus the incident light rays done
clear
C)
adjust the size of the pupil done
clear
D)
filter out the dust particles done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer25)
The given diagram is that of the human eye. In the given diagram, the parts labelled as I and II are respectively the
A)
eye lens and the cornea done
clear
B)
pupil and the eye lens done
clear
C)
cornea and the pupil done
clear
D)
pupil and the iris done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer26)
Four statements about the blind spot of the human eye: I It is devoid of photosensitive cells. II No image is formed at the blind spot. III It connects the optic nerves to the retina. IV Its malfunctioning makes a person blind. Which of the given statements is incorrect?
A)
I done
clear
B)
II done
clear
C)
III done
clear
D)
IV done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer27)
When we look at a distant object, the ciliary muscles__i__, making the eye lens __ii__. This iii the focal length of the eye lens so that the image of that object gets focused on the retina. The information in which alternative completes the given statements?
A)
i-get released, ii-thicker, iii-decreases done
clear
B)
i-contract, ii-thicker, iii-increases done
clear
C)
i-get released, ii-thinner, iii-increses done
clear
D)
i-contract, ii-thinner, iii-decreases done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer28)
Which of the following pairs of eye parts is responsible for controlling the amount of light entering into the eye?
A)
Iris and pupil done
clear
B)
Cornea and eye lens done
clear
C)
Cilliary muscles and iris done
clear
D)
Cilliary muscles and pupil done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer29)
Tina has a defect in her eyes. She is not able to contract her iris properly. As a result of the defect in her eyes, Tina will not be able to see
A)
in dim light done
clear
B)
near objects done
clear
C)
in bright light done
clear
D)
distant objects done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer30)
The range of vision of a normal human eye lies between
A)
25 m and infinity done
clear
B)
2.5 m and 5 km done
clear
C)
2.5 cm and 5 km done
clear
D)
25 cm and infinity done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer31)
Myopia is a defect of vision caused by
A)
a decrease in the retinal distance from the lens done
clear
B)
a decrease in the diameter of the eyeball done
clear
C)
an increase in the thickness of the lens done
clear
D)
an increase in the curvature of the lens done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer32)
Shyam views a certain object and finds that it is not properly visible to him. The image of the said object is formed by his eye lens 3 cm away from the pupil of his eye.Shyam can correct the defect in his vision by using
A)
convex lens done
clear
B)
bifocal lens done
clear
C)
concave lens done
clear
D)
cylindrical lens done
clear
View Solution play_arrow