Answer:
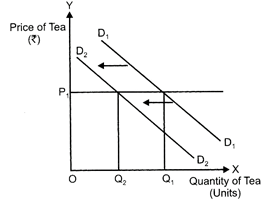
Goods are said to be related when price of one good (say \['X'\]) causes change in demand for other good (say \['Y'\]). Related goods are of two types: (a) Substitute goods (direct relationship): Substitute goods are a pair of goods which can be used (substituted) in place of each other. They are competitive good. Like Pepsi and coca ? cola or tea and coffee. Demand for a given commodity is affected if the price of its substitute rises or falls. For the case of tea and coffee?the demand for tea will fall when the price of its substitute?coffee falls. A fall in the price of substitute good (tea) reduces the consumers demand for given good (coffee). If related good is a substitute of a given good, then a rise in price of substitute good will lead to rise in demand for given good because it becomes relatively cheaper. 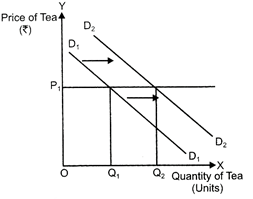
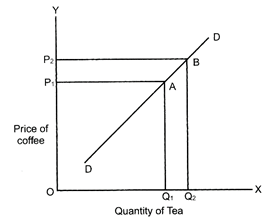
As can be seen is the above graph that when the price of coffee is\[O{{P}_{1}}\], the demand for tea is\[O{{Q}_{1}}\]. When the price of coffee rises to\[O{{P}_{2}}\], the demand for tea increased to\[O{{Q}_{2}}\]. Hence there is direct relationship between price of coffee and demand for tea. (b) Complementary goods (inverse relationship): Complementary goods are pair of goods which are used together to satisfy a given want. They are complementary to each other in the sense that they complete the deficiencies of each other. For eg fountain pen and ink. A fall in the price of one commodity leads to rise in the demand for the other commodity also. If the price of ink falls, demand for its complementary good ? fountain pen will rise. Thus, a fall in price of one complementary good increases the demand for the other complementary good. If related good is complementary to the given good, then a rise in price of complementary good will result in fall in demand of given good. 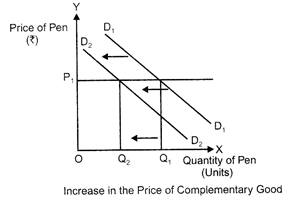
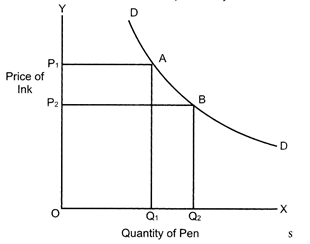
As can be seen is the above graph that when price of the ink was\[O{{P}_{1}}\], the demand for pen was\[O{{Q}_{1}}\]. When the price of ink falls to\[O{{P}_{2}}\], the demand for pen rises to\[O{{Q}_{2}}\]. Hence there is an inverse relationship between price of ink and demand for pen.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
