| Explain the concept of Inflationary Gap. Explain the role of Repo Rate in reducing this gap. |
| Or |
| Explain the concept of Deflationary Gap and the role of 'Open Market Operations' in reducing this gap. |
Answer:
Due to the excess of aggregate demand, there exists a difference (or gap) between the actual level of aggregate demand and full employment level of demand. This difference is termed as inflationary gap. This gap measures the amount of surplus in the level of aggregate demand. Graphically, it is represented by the vertical distance between the actual level of aggregate demand (\[A{{D}_{e}}\]) and the full employment level of output (\[A{{D}_{f}}\]). In the figure, EY denotes the aggregate demand at the full employment level of output and FY denotes the actual aggregate demand. The vertical distance between these two represents inflationary gap. That is,
\[FYEY=FE\] (Inflationary Gap)
Let us understand the situation of excess demand and concept of inflationary gap with the help of the following figure.
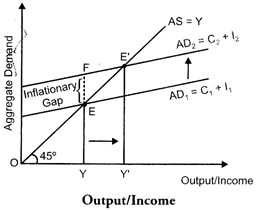
In the figure,\[A{{D}_{1}}\] and AS represents the aggregate demand curve and aggregate supply curve respectively. The economy is at full employment equilibrium at point ?E?, where\[A{{D}_{1}}\] intersects AS curve. At this equilibrium point, OY represents full employment level and EY is aggregate demand at the full employment level of output.
Let us suppose that the actual aggregate demand for output is FY, which is higher than EY. This implies that actual aggregate output demanded by the economy FY is more than the potential (full employment) aggregate output EY. Thus, the economy is facing surplus demand. This situation is termed as excess demand. As a result of the excess demand, inflationary gap arises. The inflationary gap is measured by the vertical distance between the actual aggregate demand for output and the potential (or full employment level) aggregate demand. In other words, the distance between FY and EY, i.e. FE represents the inflationary gap.
Repo rate refers to the rate at which the central bank lends to the commercial bank. In such inflationary gap, the central bank would increase repo rate. An increase in the repo rate increases the cost of borrowings for the commercial banks.
This discourages the demand for loans and borrowings. Thereby, the consumption expenditure falls, and hence aggregate demand falls.
Or
Due to the deficiency in the aggregate demand, there exists a difference (or gap) between the actual level of aggregate demand and full employment level of demand. This difference gap. This gap measures the amount of deficiency in the level of aggregate demand. Graphically, it is represented by the vertical distance between the aggregate demand at the full employment level of output (\[A{{D}_{e}}\]) and the-actual level of aggregate demand (\[A{{D}_{f}}\]). In the figure below, EY denotes the aggregate demand at fall employment level of output and CY denotes the actual aggregate demand. The vertical distance between these two represents deflationary gap. That is,
\[EYCY=EC\](Deflationary Gap)
Let us understand the situation of deficit demand and concept of deflationary gap with the help of the following figure.
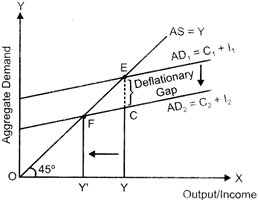
In the figure,\[A{{D}_{1}}\] and AS represents the aggregate demand curve and aggregate supply curve. The economy is at full employment equilibrium at point ?E?, where\[A{{D}_{1}}\] intersects AS curve. At this equilibrium point, OY represents the full employment level of output and EY is the aggregate demand at the full employment level of output.
Let us suppose that the actual aggregate demand for output is only CY, which is lower than EY. This implies that actual aggregate output demanded by the economy CY falls short of the potential (full employment) aggregate output EY. Thus, the economy is facing a deficiency in demand. This situation is termed as deficit demand. As a result of the deficit demand, deflationary gap arises. The deflationary gap is measured by the vertical distance between the potential (or full employment level) aggregate demand and the actual aggregate demand for output. In other words, the distance between EY and CY, i.e. EC represents the deflationary gap.
To correct deflationary gap, the central bank purchases the securities in the market, thereby, increasing the flow of money and subsequently enhancing the purchasing power of the people. The higher purchasing power increases the aggregate demand.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
