Answer:
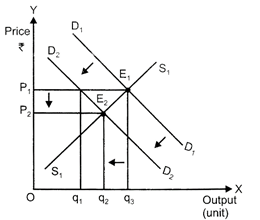
A decrease in the demand for the commodity leads to a fall in the equilibrium price and quantity. Let us understand how it happens: \[{{D}_{1}}{{D}_{1}}\] and \[S{{ & }_{1}}{{S}_{1}}\] represent the market demand and market supply respectively. The initial equilibrium occurs at \[{{E}_{1}},\] where the demand and the supply intersect each other. Due to the decrease in the demand for the commodity, the demand curve will shift leftward parallel from \[{{D}_{1}}{{D}_{1}}\] to \[{{D}_{2}}{{D}_{2}},\] while the supply curve will remain unchanged. Hence, there will be a situation of excess supply, equivalent to \[(q{{ & }_{3}}-{{q}_{1}})\]. Consequently, the price will fall due to excess supply. The price will continue to fall until it reaches\[{{E}_{2}}\] (new equilibrium), where \[{{D}_{2}}{{D}_{2}}\] intersects the supply curve \[S{{ & }_{1}}{{S}_{1}}\]. The equilibrium price falls from\[{{P}_{1}}\] to\[{{P}_{2}}\] and the equilibrium output falls from\[{{q}_{3}}\,\,to\,\,{{q}_{2}}\].
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
