| Explain consumer's equilibrium with the help of Indifference Curve Analysis. |
| Or |
| Explain the relationship between |
| (i) Prices of other goods and demand for the given good. |
| (ii) Income of the buyers and demand for a good. |
Answer:
Consumers equilibrium refers to the optimum combination of the two goods which a consumer can afford (given his income and price of two commodities) and this combination gives him maximum satisfaction that he possibly can get.
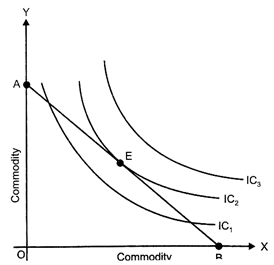
According to indifference curve analysis, consumed equilibrium is established at a point where budget line is tangent to the highest attainable indifference curve. At this, point the slope of indifference curve i.e. MRS \[\frac{\Delta y}{\Delta x}\] is equal to the slope of Budget line, i.e., \[\frac{\Pr ice\,\,of\,x}{\Pr ice\,\,of\,y}\]
\[\therefore \] At point of consumer equilibrium (E),
\[MRS=\frac{Px}{Py}\,\,or\,\,\frac{\Delta x}{\Delta y}=\frac{Px}{Py}\]
Conditions for consumer's equilibrium are:
(i) Budget line should be tangent to the indifference curve,
i.e., \[MR{{S}_{xy}}\]= \[\frac{Px}{Py}\] i.e., Slope of Indifference curve,
\[{{I}_{c}}\] = Slope of Budget line.
(ii) MRS is diminishing or Indifference curve is convex to the point of origin.
Or
(i) Price of other goods and demand for the given good. Demand for a commodity may be affected by the prices of other goods. The other goods may be substitute goods and complementary goods.
Prices of substitute goods. Those goods which can be used at the place of another are known as substitute goods like tea and coffee. If the price of tea increases then the demand of coffee will increases because now it is cheaper in comparison to tea on the other side, if the price of tea falls, the demand of tea will increases, because now it is cheaper than coffee.
Price of complementary goods. Those goods which we cannot use without one another are known as complementary goods. Such as car and petrol if the price of car rises then the demand for petrol falls down. The reverse will happen when the price of car falls.
(ii) Income of the buyers and demand for a good. Income of the buyers affect the demand of goods. Generally, we can see when the income of buyer increases the demand increases and vice versa. The effect of increase in income is not uniform on the demand of all goods. When income increases, the demand of normal goods increases and that for inferior goods decreases. The reverse of it happens when income falls.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
